2022
|
 | Janík, Rastislav; Kubov, Martin; Schieber, Branislav The ground-level ozone concentration in forest and urban environments in central Slovakia Journal Article Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195 (1), 2022, ISSN: 1573-2959. Links | BibTeX @article{Jan_k_2022,
title = {The ground-level ozone concentration in forest and urban environments in central Slovakia},
author = {Rastislav Janík and Martin Kubov and Branislav Schieber},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10605-8},
doi = {10.1007/s10661-022-10605-8},
issn = {1573-2959},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-01},
journal = {Environmental Monitoring and Assessment},
volume = {195},
number = {1},
publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media LLC},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
 | Kubov, Martin; Schieber, Branislav; Janík, Rastislav Effect of Selected Meteorological Variables on Full Flowering of Some Forest Herbs in the Western Carpathians Journal Article Atmosphere, 13 (2), pp. 195, 2022, ISSN: 2073-4433. Links | BibTeX @article{Kubov_2022,
title = {Effect of Selected Meteorological Variables on Full Flowering of Some Forest Herbs in the Western Carpathians},
author = {Martin Kubov and Branislav Schieber and Rastislav Janík},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020195},
doi = {10.3390/atmos13020195},
issn = {2073-4433},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Atmosphere},
volume = {13},
number = {2},
pages = {195},
publisher = {MDPI AG},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2020
|
 | Janík, Rastislav; Kubov, Martin; Schieber, Branislav The ground-level ozone concentration in beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forests in the West Carpathian Mountains Journal Article Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192 (4), pp. 47-56, 2020, ISSN: 0167-6369. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Janík2020,
title = {The ground-level ozone concentration in beech (\textit{Fagus sylvatica} L.) forests in the West Carpathian Mountains},
author = {Rastislav Janík and Martin Kubov and Branislav Schieber },
doi = {10.1007/s10661-020-8176-7},
issn = {0167-6369},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-03-12},
journal = {Environmental Monitoring and Assessment},
volume = {192},
number = {4},
pages = {47-56},
abstract = {The amount of ground-level ozone in beech forests depends not only on the pollution intensity but also on the other environmental factors. This paper presents the analysis of the concentrations of ground-level ozone during the growing season (April–September) of beech trees, which represent the main objects modifying the microclimate conditions inside the forest. The research was localized in the Kremnické vrchy Mountains in Slovakia and realized during the period of 2004–2013. The study was carried out on four research plots with different stand structure which was caused by various intensities of cuts. Our results showed that the maximum concentration of ozone during this period was observed on the plot where the original beech stand (without management intervention) grown—maximal concentration reached the values from 44.0 to 50.0 ppb (in the sub-periods 2004–2008 and 2009–2013, respectively). On the other hand, the minimum concentration, 14.0 ppb, was found immediately after the cutting in 2004 on the plot, where all adult trees were removed. A similar course was found within average values of the ozone concentration on the research plots. Despite the fact that the results did not confirm significant differences among the plots, temporal trend showed an increasing concentration of ozone on all plots during the study period.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The amount of ground-level ozone in beech forests depends not only on the pollution intensity but also on the other environmental factors. This paper presents the analysis of the concentrations of ground-level ozone during the growing season (April–September) of beech trees, which represent the main objects modifying the microclimate conditions inside the forest. The research was localized in the Kremnické vrchy Mountains in Slovakia and realized during the period of 2004–2013. The study was carried out on four research plots with different stand structure which was caused by various intensities of cuts. Our results showed that the maximum concentration of ozone during this period was observed on the plot where the original beech stand (without management intervention) grown—maximal concentration reached the values from 44.0 to 50.0 ppb (in the sub-periods 2004–2008 and 2009–2013, respectively). On the other hand, the minimum concentration, 14.0 ppb, was found immediately after the cutting in 2004 on the plot, where all adult trees were removed. A similar course was found within average values of the ozone concentration on the research plots. Despite the fact that the results did not confirm significant differences among the plots, temporal trend showed an increasing concentration of ozone on all plots during the study period. |
2019
|
 | Dudáš, Matej; Malovcová-Staníková, Miroslava; Pliszko, Artur; Schieber, Branislav; Zieliński, Jerzy New floristic records from Central Europe 4 (reports 41–53) Journal Article Thaiszia, 29 (2), pp. 231-237, 2019, ISSN: 1210-0420. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Dudáš2019,
title = {New floristic records from Central Europe 4 (reports 41–53)},
author = {Matej Dudáš and Miroslava Malovcová-Staníková and Artur Pliszko and Branislav Schieber and Jerzy Zieliński },
doi = {10.33542/TJB2019-2-08},
issn = {1210-0420},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-11-29},
journal = {Thaiszia},
volume = {29},
number = {2},
pages = {231-237},
abstract = {The fourth part of the series includes 13 new chorological records of vascular plants from Poland and Slovakia. From Poland, the first record of Rubus austroslovacus from the Vistula River valley is given as well as the first record of Erigeron ×huelsenii from Silesia. Beside this, spontaneous occurrence of Portulaca grandiflora in Kraków and P. oleracea subsp. oleracea in Suwałki has been recorded outside the cultivation. In Slovakia, new sites of endangered species Dichostylis micheliana and Stipa pulcherrima were found as well as new distribution data about Sonchus palustris and Reynoutria japonica. From railway stations, Tribulus terrestris is reported for the first time from eastern Slovakia likewise two new sites of alien species Euphorbia davidii, previously reported from only single locality in southeastern Slovakia. Alien species Xanthium spinosum was reported from the Štiavnické vrchy Mts. and also Sisyrinchium montanum in the Slanské vrchy Mts. Third report of Sagittaria latifolia in Slovakia is given with short characteristic of its coenological conditions.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The fourth part of the series includes 13 new chorological records of vascular plants from Poland and Slovakia. From Poland, the first record of Rubus austroslovacus from the Vistula River valley is given as well as the first record of Erigeron ×huelsenii from Silesia. Beside this, spontaneous occurrence of Portulaca grandiflora in Kraków and P. oleracea subsp. oleracea in Suwałki has been recorded outside the cultivation. In Slovakia, new sites of endangered species Dichostylis micheliana and Stipa pulcherrima were found as well as new distribution data about Sonchus palustris and Reynoutria japonica. From railway stations, Tribulus terrestris is reported for the first time from eastern Slovakia likewise two new sites of alien species Euphorbia davidii, previously reported from only single locality in southeastern Slovakia. Alien species Xanthium spinosum was reported from the Štiavnické vrchy Mts. and also Sisyrinchium montanum in the Slanské vrchy Mts. Third report of Sagittaria latifolia in Slovakia is given with short characteristic of its coenological conditions. |
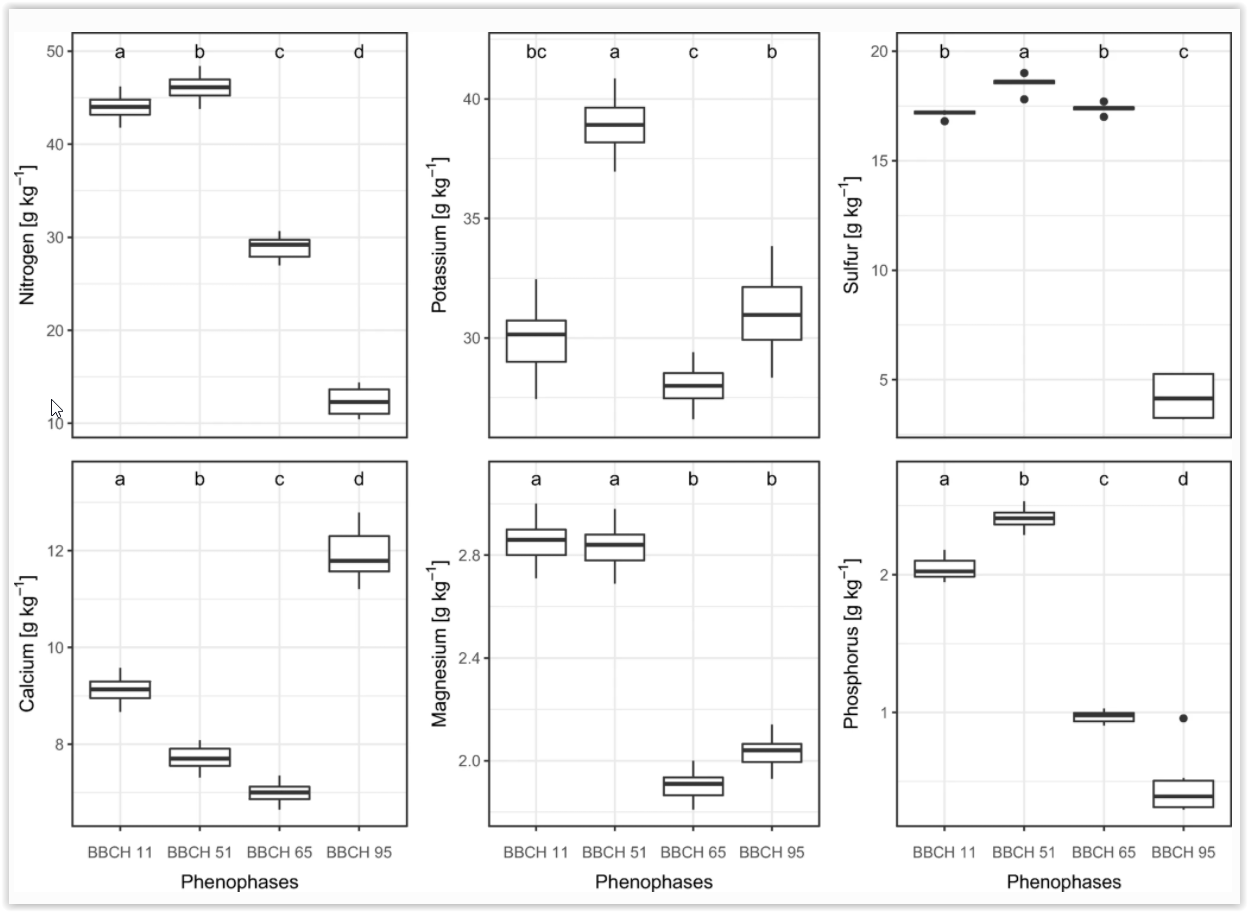 | Kubov, Martin; Schieber, Branislav; Janík, Rastislav Seasonal dynamics of macronutrients in aboveground biomass of two herb-layer species in a beech forest Journal Article Biologia, 74 (11), pp. 1415-1424, 2019, ISSN: 0006-3088. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Kubov2019,
title = {Seasonal dynamics of macronutrients in aboveground biomass of two herb-layer species in a beech forest},
author = {Martin Kubov and Branislav Schieber and Rastislav Janík},
doi = {10.2478/s11756-019-00317-9},
issn = {0006-3088},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-08-08},
journal = {Biologia},
volume = {74},
number = {11},
pages = {1415-1424},
abstract = {The content of six macronutrients (N, P, K, S, Ca, Mg) in the aboveground biomass of two forest plants representing different life forms (Carex pilosa, a hemicryptophyte, and Dentaria bulbifera, a geophyte) was analysed in relation to selected phenological phases. The ability of the plants to accumulate nutrients from the soil into the biomass was studied using transfer coefficients (TCs). Additionally, we examined the temporal changes in nutrient ratios for both species. The study was performed in a beech ecosystem in central Slovakia (Kremnické vrchy Mountains). The content of available nutrients in the soil (Eutric Cambisol) decreased as follows: N > Ca > S > Mg > K > P. A higher ability to accumulate all elements into the biomass was found for Dentaria bulbifera in comparison to Carex pilosa. We found different patterns of nutrient accumulation between Dentaria bulbifera (N > K > S > Ca > Mg > P) and Carex pilosa (K > N > Ca > S > Mg > P). Temporal changes in the content of nutrients were more noticeable in Dentaria bulbifera, especially for N, S and P – the content of these nutrients diminished. On the other hand, the content of K and Ca in Carex pilosa rose over time. For both species, the highest TC was detected in the case of P and K. Clear temporal variability was also revealed in some nutrient ratios, e.g., [N:K] and [Ca:P]. We confirmed that the nutrient content, nutrient ratio and transfer of macronutrients from the soil to plant biomass vary throughout the growing season in relation to the phenological phases of the plants. Similarly, the dynamics of both nutrient content and the accumulation of macronutrients in the biomass are related to the life form of the plant.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The content of six macronutrients (N, P, K, S, Ca, Mg) in the aboveground biomass of two forest plants representing different life forms (Carex pilosa, a hemicryptophyte, and Dentaria bulbifera, a geophyte) was analysed in relation to selected phenological phases. The ability of the plants to accumulate nutrients from the soil into the biomass was studied using transfer coefficients (TCs). Additionally, we examined the temporal changes in nutrient ratios for both species. The study was performed in a beech ecosystem in central Slovakia (Kremnické vrchy Mountains). The content of available nutrients in the soil (Eutric Cambisol) decreased as follows: N > Ca > S > Mg > K > P. A higher ability to accumulate all elements into the biomass was found for Dentaria bulbifera in comparison to Carex pilosa. We found different patterns of nutrient accumulation between Dentaria bulbifera (N > K > S > Ca > Mg > P) and Carex pilosa (K > N > Ca > S > Mg > P). Temporal changes in the content of nutrients were more noticeable in Dentaria bulbifera, especially for N, S and P – the content of these nutrients diminished. On the other hand, the content of K and Ca in Carex pilosa rose over time. For both species, the highest TC was detected in the case of P and K. Clear temporal variability was also revealed in some nutrient ratios, e.g., [N:K] and [Ca:P]. We confirmed that the nutrient content, nutrient ratio and transfer of macronutrients from the soil to plant biomass vary throughout the growing season in relation to the phenological phases of the plants. Similarly, the dynamics of both nutrient content and the accumulation of macronutrients in the biomass are related to the life form of the plant. |
2018
|
| KUBOV M., SCHIEBER JANÍK B R Fenológia vybraných lesných bylín vo vzťahu k meniacej sa klíme Inproceedings Hnilička, F (Ed.): Vliv abiotických a biotických stresorů na vlastnosti rostlin 2018., pp. 158–164, ČZU Praha, ÚEL SAV Zvolen, 2018, ISBN: 978-80-89408-31-3. BibTeX @inproceedings{KUBOV2018,
title = {Fenológia vybraných lesných bylín vo vzťahu k meniacej sa klíme},
author = {KUBOV, M., SCHIEBER, B., JANÍK, R},
editor = {Hnilička, F.},
isbn = {978-80-89408-31-3},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-09-05},
booktitle = {Vliv abiotických a biotických stresorů na vlastnosti rostlin 2018.},
pages = {158–164},
publisher = {ČZU Praha, ÚEL SAV Zvolen},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
|
| JANÍK Rastislav - BUBLINEC, Eduard KUBOV Martin KUKLA SCHIEBER Branislav - - Ján - Sulphate contamination, pH and conductivity of forest soils in two neighbouring mountains with different pollution in Slovakia from 1989 to 2013. Journal Article Soil and Water Research, 13 (3), pp. 139–149, 2018, ISSN: 1801-5395. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{JANÍK2018,
title = {Sulphate contamination, pH and conductivity of forest soils in two neighbouring mountains with different pollution in Slovakia from 1989 to 2013.},
author = {JANÍK, Rastislav - BUBLINEC, Eduard - KUBOV, Martin - KUKLA, Ján - SCHIEBER, Branislav},
url = {https://www.agriculturejournals.cz/web/swr.htm?volume=13&firstPage=129&type=publishedArticle},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.17221/218/2015-SWR},
issn = {1801-5395},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Soil and Water Research},
volume = {13},
number = {3},
pages = {139–149},
abstract = {The Štiavnické vrchy Mts. were strongly affected by pollution mostly from an aluminium plant in 1953–1989.
This paper compares contamination of soils between Štiavnické vrchy Mts. and the neighbouring little polluted
Kremnické vrchy Mts. from results of a 25-year study. After a decrease of emissions in Slovakia at the beginning
of the 1990s the sulphate sulphur content, acidity and conductivity of soil water have decreased only on the
surface and at a depth of 0.10 m at the study site in the Štiavnické vrchy Mts. At the depth 0.25 m the increase
of sulphurization (23.68 kg/ha S-SO4 2– per year) and acidity (pH 4.92) was observed. During the research, the
total sulphate sulphur influx to this soil depth was 568.3 kg/ha. The average sulphur input in the study areas of
the Kremnické vrchy Mts. decreased with depth: from 18.48 kg/ha/year in the surface humus to 6.85 kg/ha/year
at a depth of 0.25 m. The maximum sulphur influx at the open plot was 24.06 kg/ha/year and in total 553.34 kg
S-SO4 2–. A small increase of acidity at soil depths of 0.25 m at some sites was observed also in the Kremnické
vrchy Mts. Regression analysis revealed a statistically significant influence of sulphate sulphur content in the
atmospheric precipitation on the sulphur amount in the soil water. A significant correlation was also observed
between the precipitation amount and the sulphur content in soil water. Data from monitoring revealed significant
differences between the sulphur amounts at depths of 0.10 m and 0.25 m in these study areas.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The Štiavnické vrchy Mts. were strongly affected by pollution mostly from an aluminium plant in 1953–1989.
This paper compares contamination of soils between Štiavnické vrchy Mts. and the neighbouring little polluted
Kremnické vrchy Mts. from results of a 25-year study. After a decrease of emissions in Slovakia at the beginning
of the 1990s the sulphate sulphur content, acidity and conductivity of soil water have decreased only on the
surface and at a depth of 0.10 m at the study site in the Štiavnické vrchy Mts. At the depth 0.25 m the increase
of sulphurization (23.68 kg/ha S-SO4 2– per year) and acidity (pH 4.92) was observed. During the research, the
total sulphate sulphur influx to this soil depth was 568.3 kg/ha. The average sulphur input in the study areas of
the Kremnické vrchy Mts. decreased with depth: from 18.48 kg/ha/year in the surface humus to 6.85 kg/ha/year
at a depth of 0.25 m. The maximum sulphur influx at the open plot was 24.06 kg/ha/year and in total 553.34 kg
S-SO4 2–. A small increase of acidity at soil depths of 0.25 m at some sites was observed also in the Kremnické
vrchy Mts. Regression analysis revealed a statistically significant influence of sulphate sulphur content in the
atmospheric precipitation on the sulphur amount in the soil water. A significant correlation was also observed
between the precipitation amount and the sulphur content in soil water. Data from monitoring revealed significant
differences between the sulphur amounts at depths of 0.10 m and 0.25 m in these study areas. |
2017
|
| Schieber, B; Kubov, M; Janík, R Effects of climate warming on vegetative phenology of the common beech Fagus sylvatica in a submontane forest of the Western Carpathians: two-decade analysis Journal Article Polish Journal of Ecology, 65 (3), pp. 339-351, 2017, ISSN: 2450-1395. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{B.2017,
title = {Effects of climate warming on vegetative phenology of the common beech Fagus sylvatica in a submontane forest of the Western Carpathians: two-decade analysis},
author = {B. Schieber and M. Kubov and R. Janík},
url = {http://www.bioone.org/doi/10.3161/15052249PJE2017.65.3.003},
doi = {10.3161/15052249PJE2017.65.3.003},
issn = {2450-1395},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-11-01},
journal = {Polish Journal of Ecology},
volume = {65},
number = {3},
pages = {339-351},
abstract = {The paper examines the results of phenological research on common beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) during a period of 21 years (1995–2015) in the submontane beech forest of central Slovakia (Inner Western Carpathians). We focused on bud-burst, leaf unfolding and leaf colouring. Temporal analysis indicated that the mean monthly air temperature increased, especially from April to August. An extraordinary increase of air temperature in March and April, mostly in the last decade, was detected. The precipitation from May to August varied considerably, but in the range of the long-term mean value. During the study period, the mean/earliest/latest onset of the bud-burst of common beech was observed on the 110th /101st/120th day of the year (DOY), respectively. As for leaf unfolding 10% and 50% (LU 10 and LU 50), we found the mean/earliest/latest onset on the 114th/103rd/122nd DOY and on the 118th/108th/124th DOY, respectively. The mean/earliest/latest onset of leaf colouring 10% (LC 10) and 50% (LC 50) started on the 272nd/262nd/288th DOY and on 286th/276 th/298th, respectively. A medium degree of negative correlation (r = -0.68, P < 0.05) was found between air temperature and spring plant development (LU 50). In contrast, for both the cumulative temperature and precipitation, we found very low correlation with autumnal leaf phenology (r ≤ 0.3, P > 0.05). The vegetation period of the examined tree species lasted for 168 days on average (min/max were 155/183 days). Trend analysis revealed an earlier onset of spring phenophases by 7 days/2 decades. Conversely, a delay of autumnal phenophases by 9 days was recorded, so the vegetation period of beech extended by more than two weeks during the study period.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The paper examines the results of phenological research on common beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) during a period of 21 years (1995–2015) in the submontane beech forest of central Slovakia (Inner Western Carpathians). We focused on bud-burst, leaf unfolding and leaf colouring. Temporal analysis indicated that the mean monthly air temperature increased, especially from April to August. An extraordinary increase of air temperature in March and April, mostly in the last decade, was detected. The precipitation from May to August varied considerably, but in the range of the long-term mean value. During the study period, the mean/earliest/latest onset of the bud-burst of common beech was observed on the 110th /101st/120th day of the year (DOY), respectively. As for leaf unfolding 10% and 50% (LU 10 and LU 50), we found the mean/earliest/latest onset on the 114th/103rd/122nd DOY and on the 118th/108th/124th DOY, respectively. The mean/earliest/latest onset of leaf colouring 10% (LC 10) and 50% (LC 50) started on the 272nd/262nd/288th DOY and on 286th/276 th/298th, respectively. A medium degree of negative correlation (r = -0.68, P < 0.05) was found between air temperature and spring plant development (LU 50). In contrast, for both the cumulative temperature and precipitation, we found very low correlation with autumnal leaf phenology (r ≤ 0.3, P > 0.05). The vegetation period of the examined tree species lasted for 168 days on average (min/max were 155/183 days). Trend analysis revealed an earlier onset of spring phenophases by 7 days/2 decades. Conversely, a delay of autumnal phenophases by 9 days was recorded, so the vegetation period of beech extended by more than two weeks during the study period. |
| Kukla, J; Bublinec, E; Schieber, B; Kellerová, D; Bičárová, S; Janík, R Immission-load-related dynamics of S-SO42– in precipitation and in lysimetric solutions penetrating through beech ecosystems Journal Article Folia Oecologica, 44 (2), pp. 96-106, 2017, ISBN: 1336-5266. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Kukla2017,
title = {Immission-load-related dynamics of S-SO_{4}^{2–} in precipitation and in lysimetric solutions penetrating through beech ecosystems},
author = {J. Kukla and E. Bublinec and B. Schieber and D. Kellerová and S. Bičárová and R. Janík},
url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/foecol-2017-0005-1.pdf},
doi = {10.1515/foecol-2017-0012},
isbn = {1336-5266},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {Folia Oecologica},
volume = {44},
number = {2},
pages = {96-106},
abstract = {The paper presents the results of a 23-year study of sulphate sulphur dynamics in beech ecosystems exposed to different immission loads. The amounts of S-SO42– in precipitation water entering the ecosystems were: the Kremnické vrchy Mts, a clear-cut area 519 kg ha–1 (24.7 kg ha–1 per year), a beech forest 476 kg ha–1 (22.7 kg ha–1 per year); the Štiavnické vrchy Mts an open place 401 kg ha–1 (24.6 kg ha–1 per year), a beech forest 324 kg ha–1 (19.1 kg ha–1 per year). The average SO42– concentrations in lysimetric solutions penetrating through surface humus to a depth of Cambisol 10 and 25 cm were increased as follows: in the Kremnické vrchy Mts from 12.71 to 16.17 mg l–1 and in the Štiavnické vrchy Mts from 18.73 to 28.80 mg l–1. The S-SO4-2 amounts penetrating the individual soil layers in the Kremnické vrchy Mts were as follows: in case of surface humus on clear-cut area 459 kg ha–1 (20.9 kg ha–1 per year), in beech forest 433 kg ha–1 (19.7 kg ha–1 per year); below 10 cm organo-mineral layer of the mentioned plots penetrated 169–171 kg ha–1 (7.7–7.8 kg ha–1 per year), and below 25 cm mineral layer 155–255 kg ha–1 (7.1–11.6 kg ha–1 per year) – a higher amount was found on clear-cut area with an episodic lateral flow of soil solutions. In beech forest of the Štiavnické vrchy Mts penetrated below surface humus 424 kg ha–1 S-SO42– (18.9 kg ha–1 per year), below 10 cm mineral layer 458 kg ha–1 S-SO42– (19.9 kg ha–1 per year), and below 25 cm mineral layer as much as 599 kg ha–1 S-SO42– (26.0 kg ha–1 per year). This fact was caused by frequent lateral flow of soil solutions. The results indicate that the assumption about lower immission load of the beech ecosystem in the Kremnické vrchy Mts is wrong, at least in the case of S-SO42–. The testing has revealed that the studied beech ecosystems differ very significantly in sulphur amounts penetrating under 0.10 m and 0.25 m. The inter-annual differences were insignificant.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The paper presents the results of a 23-year study of sulphate sulphur dynamics in beech ecosystems exposed to different immission loads. The amounts of S-SO42– in precipitation water entering the ecosystems were: the Kremnické vrchy Mts, a clear-cut area 519 kg ha–1 (24.7 kg ha–1 per year), a beech forest 476 kg ha–1 (22.7 kg ha–1 per year); the Štiavnické vrchy Mts an open place 401 kg ha–1 (24.6 kg ha–1 per year), a beech forest 324 kg ha–1 (19.1 kg ha–1 per year). The average SO42– concentrations in lysimetric solutions penetrating through surface humus to a depth of Cambisol 10 and 25 cm were increased as follows: in the Kremnické vrchy Mts from 12.71 to 16.17 mg l–1 and in the Štiavnické vrchy Mts from 18.73 to 28.80 mg l–1. The S-SO4-2 amounts penetrating the individual soil layers in the Kremnické vrchy Mts were as follows: in case of surface humus on clear-cut area 459 kg ha–1 (20.9 kg ha–1 per year), in beech forest 433 kg ha–1 (19.7 kg ha–1 per year); below 10 cm organo-mineral layer of the mentioned plots penetrated 169–171 kg ha–1 (7.7–7.8 kg ha–1 per year), and below 25 cm mineral layer 155–255 kg ha–1 (7.1–11.6 kg ha–1 per year) – a higher amount was found on clear-cut area with an episodic lateral flow of soil solutions. In beech forest of the Štiavnické vrchy Mts penetrated below surface humus 424 kg ha–1 S-SO42– (18.9 kg ha–1 per year), below 10 cm mineral layer 458 kg ha–1 S-SO42– (19.9 kg ha–1 per year), and below 25 cm mineral layer as much as 599 kg ha–1 S-SO42– (26.0 kg ha–1 per year). This fact was caused by frequent lateral flow of soil solutions. The results indicate that the assumption about lower immission load of the beech ecosystem in the Kremnické vrchy Mts is wrong, at least in the case of S-SO42–. The testing has revealed that the studied beech ecosystems differ very significantly in sulphur amounts penetrating under 0.10 m and 0.25 m. The inter-annual differences were insignificant. |
2016
|
| Schieber, B; Kubov, M Fenológia vybraných listnatých lesných drevín v submontánnej bučine: dvadsaťročná analýza. Phenology of selected broad-leaved forest trees in a submountain beech forest: two-decade analysis. Journal Article Zprávy lesnického výzkumu, 61 (2), pp. 90-99, 2016, ISSN: 0322-9688. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Schieber2016c,
title = {Fenológia vybraných listnatých lesných drevín v submontánnej bučine: dvadsaťročná analýza. Phenology of selected broad-leaved forest trees in a submountain beech forest: two-decade analysis.},
author = {B. Schieber and M. Kubov},
url = {https://www.google.sk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=3&ved=0ahUKEwjht5uIlJ3WAhXNh7QKHTrkCqUQFggvMAI&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.agriculturejournals.cz%2FpublicFiles%2F03481.pdf&usg=AFQjCNGpVrc3EsM3mAlec2l6w24q2uRCDw},
issn = {0322-9688},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-06-30},
journal = {Zprávy lesnického výzkumu},
volume = {61},
number = {2},
pages = {90-99},
abstract = {Phenology of three selected deciduous forest tree species (Carpinus betulus L., Tilia cordata Mill. Quercus dalechampii Ten.) was studied in a submountain beech forest stand in central Slovakia. Two spring phenological phases – bud-burst and leaf unfolding 50% as well as two autumnal phases – leaf discolouration 10% and 50%, respectively were monitored over the period of twenty years (1995–2014). Analysis of the air temperature showed its increasing values mainly in the period from April to August. On the other hand, the values of cumulative rainfall totals for the period from May to August had not clear trend. They were strongly volatile among the years with oscillation around the longterm average. Results of phenological research referred to the interannual variability in dating of phenological phases within the species, also the differences among the species were found. The significant correlations (P < 0.05) were detected between dating of leaf unfolding and air
temperature; the coefficients of correlation (r) moved from 0.83 (hornbeam) to 0.90 (oak). Correlations between cumulative rainfall totals and timing of autumnal leaf discolouration were significantly lower. Trend analysis revealed temporal changes in onset of the phenophases. Average onset of spring phenological phases was shifted to earlier dates, but trend in onset of the autumnal phenophases was the opposite. Onset of leaf discolouration was shifted to later dates, so vegetation period was extended. Among the trees, the dynamics of leaf unfolding did not show significant temporal changes, only hornbeam was the exception.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Phenology of three selected deciduous forest tree species (Carpinus betulus L., Tilia cordata Mill. Quercus dalechampii Ten.) was studied in a submountain beech forest stand in central Slovakia. Two spring phenological phases – bud-burst and leaf unfolding 50% as well as two autumnal phases – leaf discolouration 10% and 50%, respectively were monitored over the period of twenty years (1995–2014). Analysis of the air temperature showed its increasing values mainly in the period from April to August. On the other hand, the values of cumulative rainfall totals for the period from May to August had not clear trend. They were strongly volatile among the years with oscillation around the longterm average. Results of phenological research referred to the interannual variability in dating of phenological phases within the species, also the differences among the species were found. The significant correlations (P < 0.05) were detected between dating of leaf unfolding and air
temperature; the coefficients of correlation (r) moved from 0.83 (hornbeam) to 0.90 (oak). Correlations between cumulative rainfall totals and timing of autumnal leaf discolouration were significantly lower. Trend analysis revealed temporal changes in onset of the phenophases. Average onset of spring phenological phases was shifted to earlier dates, but trend in onset of the autumnal phenophases was the opposite. Onset of leaf discolouration was shifted to later dates, so vegetation period was extended. Among the trees, the dynamics of leaf unfolding did not show significant temporal changes, only hornbeam was the exception.
|
2015
|
| Janík, R; Kellerová, D; Schieber, B Spatial and temporal variations in O3 concentration in Western Carpathian rural mountain enviornments Journal Article Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 24 (5), pp. 2003-2008, 2015. Links | BibTeX @article{R.2015b,
title = {Spatial and temporal variations in O_{3} concentration in Western Carpathian rural mountain enviornments},
author = {R. Janík and D. Kellerová and B. Schieber},
url = {http://www.pjoes.com/pdf/24.5/Pol.J.Environ.Stud.Vol.24.No.5.2003-2008.pdf},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-05-14},
journal = {Polish Journal of Environmental Studies},
volume = {24},
number = {5},
pages = {2003-2008},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2013
|
| Schieber, B; Janík, R; Snopková, Z Phenology of common beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) along the altitudinal gradient in Slovakia (Inner Western Carpathians) Journal Article Journal of Forest Science, 59 (4), pp. 176-184, 2013, ISSN: 1212-4834. Links | BibTeX @article{SCHIEBER2013,
title = {Phenology of common beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) along the altitudinal gradient in Slovakia (Inner Western Carpathians)},
author = {B. Schieber and R. Janík and Z. Snopková},
editor = {B. Schieber and R. Janík and Z. Snopková},
url = {https://www.google.sk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwi03Kv5lJ3WAhWDJ1AKHWgzAOMQFggwMAE&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.agriculturejournals.cz%2FpublicFiles%2F90914.pdf&usg=AFQjCNE43HTJCBOZNWlb_EpEw6vy1dufLQ},
issn = {1212-4834},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-06-30},
journal = {Journal of Forest Science},
volume = {59},
number = {4},
pages = {176-184},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2009
|
| Schieber, B; Janík, R; Snopková, Z Phenology of four broad-leaved forest trees in a submountain beech forest. Journal Article Journal of Forest Science, 55 (1), pp. 15-22, 2009, ISSN: 1212-4834. Links | BibTeX @article{SCHIEBER2009,
title = {Phenology of four broad-leaved forest trees in a submountain beech forest.},
author = {B. Schieber and R. Janík and Z. Snopková},
editor = {B. Schieber and R. Janík and Z. Snopková},
url = {https://www.google.sk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwjro93jl53WAhWSaVAKHYUKCrIQFggoMAA&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.agriculturejournals.cz%2FpublicFiles%2F03481.pdf&usg=AFQjCNGpVrc3EsM3mAlec2l6w24q2uRCDw},
issn = {1212-4834},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-06-30},
journal = {Journal of Forest Science},
volume = {55},
number = {1},
pages = {15-22},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2007
|
| Schieber, B Changes of flowering phenology of six herbal species in a beech forest (Central Slovakia):a decade analysis Journal Article Polish Journal of Ecology, 55 (2), pp. 233-244, 2007, ISSN: 1505-2249. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Schieber2007,
title = {Changes of flowering phenology of six herbal species in a beech forest (Central Slovakia):a decade analysis},
author = {B. Schieber},
editor = {B. Schieber},
url = {http://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-article-BGPK-1772-6489},
issn = {1505-2249},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-12-30},
journal = {Polish Journal of Ecology},
volume = {55},
number = {2},
pages = {233-244},
abstract = {The variability in flowering phenology of six forest herbaceous species: Pulmonaria officinalis L. (early spring species), Dentaria bulbifera L. (mid spring), Galium odoratum Scop, (late spring), Veronica officinalis L. (early summer), Mycelis muralis (L.) Dumort. (mid summer) and Campanula trachelium L. (mid/late summer) was analysed over the period of the past ten years (1995-2004). Observations were done in a beech forest at the Ecological Experimental Stationary in Kremnicke vrchy Mts (Central Slovakia, 48[degree] 38'N, 19[degree] 04'E, 450-520 m a.s.l.)- Two phenological events - the first flowering and full flowering as well as the duration of interphase interval were analysed. The timing of observed phenological events was related to selected climatic factors (temperature and precipitation). The highest variation in the first flowering date was observed in early spring species- standard deviation (SD) was equal to 7.2 days. As for full flowering date, the highest value of standard deviation was detected in late summer species (SD = 8.5 days). In respect to the duration of inter-phase interval (in days), the highest relative vari.ability (c[v] > 53%) was ascertained in early spring species. The significant correlations (P <0.001) were detected between dating of full flowering and cumulative temperatures in all phenological types (excepting early spring); the coefficients of correlation (r) moved from - 0.85 (early summer and mid summer species) to - 0.91 (mid spring species). Significant correlations were revealed between precipitation and timing of flowering only for mid summer (r = +0.70) and late summer species (r = +0.75), respectively. Despite of the fact, that no significant trends were detected in timing of flowering in the species, the effect of the global warming is evident. The values of the possitive deviations of the mean air temperatures averaged for the period of the last decade were increased in comparison to the long-term mean. Onsetof flowering has been shifted earlier a few days in majority of the spe.cies during the past decade. Decade tendency showed a slight increasing of values of cumulative temperatures during the periods crucial for the development of the phenophases.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The variability in flowering phenology of six forest herbaceous species: Pulmonaria officinalis L. (early spring species), Dentaria bulbifera L. (mid spring), Galium odoratum Scop, (late spring), Veronica officinalis L. (early summer), Mycelis muralis (L.) Dumort. (mid summer) and Campanula trachelium L. (mid/late summer) was analysed over the period of the past ten years (1995-2004). Observations were done in a beech forest at the Ecological Experimental Stationary in Kremnicke vrchy Mts (Central Slovakia, 48[degree] 38'N, 19[degree] 04'E, 450-520 m a.s.l.)- Two phenological events - the first flowering and full flowering as well as the duration of interphase interval were analysed. The timing of observed phenological events was related to selected climatic factors (temperature and precipitation). The highest variation in the first flowering date was observed in early spring species- standard deviation (SD) was equal to 7.2 days. As for full flowering date, the highest value of standard deviation was detected in late summer species (SD = 8.5 days). In respect to the duration of inter-phase interval (in days), the highest relative vari.ability (c[v] > 53%) was ascertained in early spring species. The significant correlations (P <0.001) were detected between dating of full flowering and cumulative temperatures in all phenological types (excepting early spring); the coefficients of correlation (r) moved from - 0.85 (early summer and mid summer species) to - 0.91 (mid spring species). Significant correlations were revealed between precipitation and timing of flowering only for mid summer (r = +0.70) and late summer species (r = +0.75), respectively. Despite of the fact, that no significant trends were detected in timing of flowering in the species, the effect of the global warming is evident. The values of the possitive deviations of the mean air temperatures averaged for the period of the last decade were increased in comparison to the long-term mean. Onsetof flowering has been shifted earlier a few days in majority of the spe.cies during the past decade. Decade tendency showed a slight increasing of values of cumulative temperatures during the periods crucial for the development of the phenophases. |
| Schieber, B Changes in the seasonal rhythm of two forest communities during secondary succession. Journal Article Biologia, 62 (4), pp. 416-423, 2007, ISSN: 0006-3088. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{B.2007,
title = {Changes in the seasonal rhythm of two forest communities during secondary succession.},
author = {B. Schieber},
editor = {B. Schieber},
url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.2478/s11756-007-0081-9},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-007-0081-9},
issn = {0006-3088},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-08-31},
journal = {Biologia},
volume = {62},
number = {4},
pages = {416-423},
abstract = {Changes in the seasonal rhythm of two plant phytocoenoses in a submountain beech forest during secondary succession were studied. Investigations were done on four monitoring plots with different stand density over the period of four successive years. The rhythm of the associations Dentario bulbiferae-Fagetum and Carici pilosae-Fagetum reflects the course of succession processes running six years after the human impact (cutting) in the ecosystem. Results of the phenological observations of the understorey species with the focus on the changes in flowering and colour spectrum allowed to make the comparisons between both associations in connection with different phyto-climatic conditions and in dependence on time. The most conspicuous changes in the seasonal rhythm and structure of the examined associations were found in conditions of the former clear-cut, currently in succession phase. A clear decrease (56%) in number of taxons with the dominance > 1% in one association towards the end of the 4-year study period was detected here. Simultaneously, a decrease in the number of flowering species was observed, while the relative rate of species being in the vegetative stage increased considerably (from 6 to 67%) over the growing season. The course of flowering of both of the associations missed discernible trends and peaks as well as colour spectra were partially changed during four monitored successive years on the formerly unstocked area.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Changes in the seasonal rhythm of two plant phytocoenoses in a submountain beech forest during secondary succession were studied. Investigations were done on four monitoring plots with different stand density over the period of four successive years. The rhythm of the associations Dentario bulbiferae-Fagetum and Carici pilosae-Fagetum reflects the course of succession processes running six years after the human impact (cutting) in the ecosystem. Results of the phenological observations of the understorey species with the focus on the changes in flowering and colour spectrum allowed to make the comparisons between both associations in connection with different phyto-climatic conditions and in dependence on time. The most conspicuous changes in the seasonal rhythm and structure of the examined associations were found in conditions of the former clear-cut, currently in succession phase. A clear decrease (56%) in number of taxons with the dominance > 1% in one association towards the end of the 4-year study period was detected here. Simultaneously, a decrease in the number of flowering species was observed, while the relative rate of species being in the vegetative stage increased considerably (from 6 to 67%) over the growing season. The course of flowering of both of the associations missed discernible trends and peaks as well as colour spectra were partially changed during four monitored successive years on the formerly unstocked area. |
2005
|
| Kuklová, M; Kukla, J; Schieber, B Individual and population parameters of Carex pilosa Scop. (Cyperaceae) in four forest sites in Western Carpathians (Slovakia) Journal Article Polish Journal of Ecology, 53 (3), pp. 427-434, 2005, ISSN: 1505-2249. BibTeX @article{M.2005,
title = {Individual and population parameters of Carex pilosa Scop. (Cyperaceae) in four forest sites in Western Carpathians (Slovakia) },
author = {M. Kuklová and J. Kukla and B. Schieber},
editor = {M. Kuklová and J. Kukla and B. Schieber},
issn = {1505-2249},
year = {2005},
date = {2005-12-30},
journal = {Polish Journal of Ecology},
volume = {53},
number = {3},
pages = {427-434},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2004
|
| Kukla, J; Kuklová, M; Schieber, B Responses of some herbs to different ecological conditions in spruce ecosystems of the Bielovodská dolina valley Journal Article Ekológia (Bratislava), 23 (3), pp. 252-269, 2004. BibTeX @article{Kukla2004,
title = {Responses of some herbs to different ecological conditions in spruce ecosystems of the Bielovodská dolina valley},
author = {J. Kukla and M. Kuklová and B. Schieber},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Ekológia (Bratislava)},
volume = {23},
number = {3},
pages = {252-269},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2003
|
| Kukla, J; Kováčová, M; Schieber, B Bioparameters of selected herb species in High Tatra Mts. spruce ecosystems Journal Article Polish Journal of Ecology, 51 (3), pp. 369-376, 2003. BibTeX @article{Kukla2003,
title = {Bioparameters of selected herb species in High Tatra Mts. spruce ecosystems},
author = {J. Kukla and M. Kováčová and B. Schieber},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
journal = {Polish Journal of Ecology},
volume = {51},
number = {3},
pages = {369-376},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|


