Ostrovský Radovan
Plant Pathology and Mycology RG
Researcher

Ing. Radovan Ostrovský, PhD.
Slovak Academy of Sciences
Institute of Forest Ecology
Plant Pathology & Mycology Research Group
Akademická 2
949 01 Nitra
Phone: +421 37 6943 336
Email: radovan.ostrovsky@ife.sk
Research Interests: plant protection, acoustic tomography, fungal diseases of woody plants, biological control, geographic information system, scanning electron microscopy.
Education:
- PhD. in Special Crop Production, Faculty of Agrobiology and Food Resources, Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra (2011)
- Ing. (MSc.) in Landscape Engineering, Horticulture and Landscape Engineering Faculty, Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra (2003)
Academic employment:
- Researcher: Slovak Academy of Sciences, Institute of Forest Ecology, Branch for Woody Plants Biology (since 2013)
- Researcher: Slovak University of Agriculture, Institute of Biodiversity Conservation and Biosafety; plants genepool evaluation and preservation, scanning electron microscopy, geographical information systems (2005 – 2016)
Projects:
- VEGA 2/0122/22 – Diversity and pathogenicity of ophiostomatoid fungi in Scots pine stands infested by bark beetles (2022-2025, member of research team)
- VEGA 2/0132/22 – Impact of climate change on the distribution of selected pathogens of Pinus sp. trees (2022-2025, member of research team)
- MVTS Ochrana mestských stromov (2021-2025, member of research team)
- VEGA 2/0077/18 – Identification, genetic variability a pathogenicity of economically important needle cast species on pines (2018-2021, member of research team)
- VEGA 2/0062/18 – Ash dieback: the causal agents and disease control strategy (2018-2021, member of research team)
- SK-FR-2017-0025 – Spatial analyses in population genetic studies of tree pathogens (2018-2019, member of research team)
- VEGA 2/0143/15 – Štúdium vplyvu faktorov prostredia na výskyt a rozšírenie rakoviny kôry gaštana jedlého (Castanea sativa) na Slovensku a možností ochrany proti tejto chorobe
- COST FP1406 – PINESTRENGTH „Pine pitch canker“- stratégie pre manažment Gibberella circinata v skleníkoch a lesoch
- VEGA 2/0071/14 – Druhová diverzita a biologické vlastnosti parazitických húb podieľajúcich sa na poškodení a usychaní drevín
- VEGA 2/0069/14 – Biológia, rozšírenie a diagnostika škodlivého činiteľa Dothistroma septosporum (Mycosphaerella pini), D. pini a iných škodlivých činiteľov asimilačných orgánov borovíc.
- VEGA 2/0214/10 – Štúdium fenotypickej a genetickej variability a rôznej citlivosti k hubovým chorobám pri gaštane jedlom (Castanea sativa Mill.)
Internships:
- 2009, Short term research stay at Research and Breeding Institute of Pomology Holovousy Ltd., Czech Republic
List of my publications:
2025 |
|
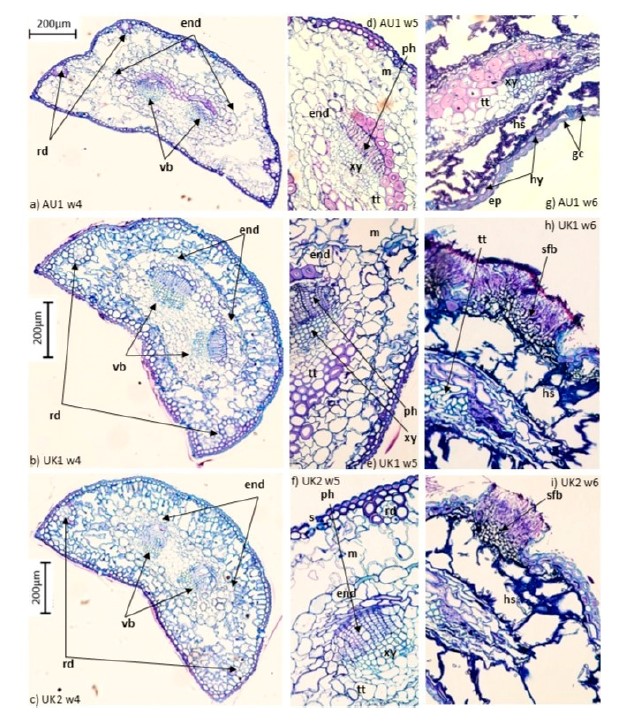 | Jánošíková, Z; Adamčíková, K; Ondrušková, E; Ostrovský, R; Woodward, S; Fraser, S Histological Analysis of Dothistroma septosporum Infection on Different Provenances of Pinus sylvestris Journal Article Forests, 16 , pp. 973, 2025, ISSN: 1999-4907. @article{Jánošíková2025, title = {Histological Analysis of Dothistroma septosporum Infection on Different Provenances of Pinus sylvestris}, author = {Z. Jánošíková and K. Adamčíková and E. Ondrušková and R. Ostrovský and S. Woodward and S. Fraser}, url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/fig-5.jpg}, doi = {10.3390/f16060973}, issn = {1999-4907}, year = {2025}, date = {2025-06-09}, journal = {Forests}, volume = {16}, pages = {973}, abstract = {Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) is one of the most significant diseases of conifers, causing premature defoliation, growth reduction, and, in extreme cases, mortality. Histological analysis was undertaken on inoculated seedlings of three different seed sources of Pinus sylvestris L. to investigate the process of infection and degradation of needle tissue on this host species. Seedlings were inoculated using a single spore isolate of Dothistroma septosporum (Doroguine) M. Morelet (D636) from northern Scotland. Mesophyll degradation in the needles occurred by four weeks after inoculation; collapse of mesophyll, bundle sheath tissues, and tracheids by five weeks; and eruption of fruiting bodies in near proximity to stomatal openings by six weeks. Significantly greater collapse of mesophyll during the early stages of infection occurred in the Austrian provenance compared with the United Kingdom provenance, although in the later stages of infection, this difference disappeared. Furthermore, disease severity, assessed as the proportion of needles with D. septosporum conidiomata on each tree, was not significantly different between seed sources.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) is one of the most significant diseases of conifers, causing premature defoliation, growth reduction, and, in extreme cases, mortality. Histological analysis was undertaken on inoculated seedlings of three different seed sources of Pinus sylvestris L. to investigate the process of infection and degradation of needle tissue on this host species. Seedlings were inoculated using a single spore isolate of Dothistroma septosporum (Doroguine) M. Morelet (D636) from northern Scotland. Mesophyll degradation in the needles occurred by four weeks after inoculation; collapse of mesophyll, bundle sheath tissues, and tracheids by five weeks; and eruption of fruiting bodies in near proximity to stomatal openings by six weeks. Significantly greater collapse of mesophyll during the early stages of infection occurred in the Austrian provenance compared with the United Kingdom provenance, although in the later stages of infection, this difference disappeared. Furthermore, disease severity, assessed as the proportion of needles with D. septosporum conidiomata on each tree, was not significantly different between seed sources. |
2024 |
|
Jánošíková, Z; Kobza, M; Ondrušková, E; Ostrovský, R; Pažitný, J; Adamčíková, K Virulence of Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini on Pinus nigra and P. mugo under conditions of natural infection Journal Article European Journal of Plant Pathology, 168 (2), pp. 775-785, 2024. @article{Jánošíková2024, title = {Virulence of Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini on Pinus nigra and P. mugo under conditions of natural infection}, author = {Z. Jánošíková and M. Kobza and E. Ondrušková and R. Ostrovský and J. Pažitný and K. Adamčíková}, url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Fig_edited.jpghttp://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/final-1-2.jpg}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-023-02799-5}, year = {2024}, date = {2024-04-04}, journal = {European Journal of Plant Pathology}, volume = {168}, number = {2}, pages = {775-785}, abstract = {Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) is a severe needle disease of pines worldwide, caused by two closely related species, Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini. The two fungal species are similar not only in their morphological characteristics, but also cause very similar symptoms in their hosts, and have a similar ecology. The aim of this study was to compare the virulence of the two Dothistroma species in natural infection experiments on 2-year-old seedlings of two DNB susceptible pine species, Pinus nigra and P. mugo, in two seedling stands for each pathogen species. The virulence of the pathogens and presence of symptoms (symptomatic needles, red bands and acervuli) were assessed after 2 years of exposure to inoculum. The incidence of seedlings with DNB symptoms was 65% and 76% for P. nigra and P. mugo, respectively. No difference was found between D. septosporum and D. pini in any of the three DNB symptoms evaluated on seedlings of P. mugo. However, symptoms of disease differed between the two Dothistroma species on P. nigra. Variables, which reflect the intensity of disease development, the number of red bands and acervuli per needle, showed a difference in virulence between D. septosporum and D. pini, but only in the case of the host species P. nigra. The results suggest that the virulence of the two Dothistroma species could be affected by host pine species and that there are differences in susceptibility of individual pine species to D. septosporum and D. pini. Further factors could affect the virulence of these pathogens, including isolate origin, climatic or environmental factors.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) is a severe needle disease of pines worldwide, caused by two closely related species, Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini. The two fungal species are similar not only in their morphological characteristics, but also cause very similar symptoms in their hosts, and have a similar ecology. The aim of this study was to compare the virulence of the two Dothistroma species in natural infection experiments on 2-year-old seedlings of two DNB susceptible pine species, Pinus nigra and P. mugo, in two seedling stands for each pathogen species. The virulence of the pathogens and presence of symptoms (symptomatic needles, red bands and acervuli) were assessed after 2 years of exposure to inoculum. The incidence of seedlings with DNB symptoms was 65% and 76% for P. nigra and P. mugo, respectively. No difference was found between D. septosporum and D. pini in any of the three DNB symptoms evaluated on seedlings of P. mugo. However, symptoms of disease differed between the two Dothistroma species on P. nigra. Variables, which reflect the intensity of disease development, the number of red bands and acervuli per needle, showed a difference in virulence between D. septosporum and D. pini, but only in the case of the host species P. nigra. The results suggest that the virulence of the two Dothistroma species could be affected by host pine species and that there are differences in susceptibility of individual pine species to D. septosporum and D. pini. Further factors could affect the virulence of these pathogens, including isolate origin, climatic or environmental factors. | |
2023 |
|
 | Brindza, Ján; Ďurišová, Ľuba; Ostrovský, Radovan Morfologická charakteristika peľových zŕn niektorých medonosných druhov rastlín Book AgroBioNet, Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita v Nitre, 2023, ISBN: 978–80–552‐2708‐5. @book{Brindza31.1, title = {Morfologická charakteristika peľových zŕn niektorých medonosných druhov rastlín}, author = {Ján Brindza and Ľuba Ďurišová and Radovan Ostrovský}, url = {http://www.slpk.sk/eldo/2023/dl/9788055227085/9788055227085.html}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.15414/2023.9788055227085}, isbn = {978–80–552‐2708‐5}, year = {2023}, date = {2023-12-31}, booktitle = {Morfologická charakteristika peľových zŕn niektorých medonosných druhov rastlín}, pages = {119}, publisher = {Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita v Nitre}, edition = {AgroBioNet}, abstract = {The aim of the monography is presentation of pollen grain characteristics from selected group of plant species. The evaluated group consists of plants that are traditionally cultivated such as Helianthus annuus L., Prunus avium (L.) L.; rarely used such as Castanea sativa Mill., Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliott; less known species Diospyros kaki L.; invasive species Solidago gigantea Aiton; ornamental species Mahonia aquifolium (Pursh) Nutt., naturally occurring plant species Taraxacum sect. Ruderalia, Lamium purpureum L., Cichorium intybus L, Crataegus monogyna Jacq.; as well as species used for bees’ pasture in Slovakia such as Phacelia tanacetifolia Benth., from which bees are gathering nectar and pollen for their feeding. Flowers were gathered from selected plants at the start of full bloom. In laboratory conditions, the pollen was released from stamen and subsequently dried and placed on stubs to be prepared for observation and photographed on scanning electron microscope. Pollen grains were classified based on internationally recognized methodology (Ertdtman, 1952). We evaluated fundamental morphological characteristics of pollen grains – size of grains based on length of polar (P) and equatorial (E) axis, shape of pollen grains (P/E), outline, pollen unit, polarity of pollen grains, symmetry, number and shape of apertures, exine sculpture. Results confirmed that identifying characteristics, also applicable for detection of species spectrum of pollen in honey, is unique and steady exine sculpture as well as number and shape of apertures, which is documented by SEM observations especially on details of surface sculpture. We determined length of polar axis (P) in range from 20.51 μm (Castanea sativa Mill.) to 58.03 μm (Diospyros kaki L.), length of equatorial axis (E) in range from 9.37 μm (Castanea sativa Mill.) to 39.05 μm (Cichorium intybus L.) and shape index (P/E) in range from 1.00 (Cichorium intybus L.) to 2.34 (Phacelia tanacetifolia Benth.). Acquired results will be used for creation of database of pollen grains from plant species growing in Slovakia and also for evaluation of botanical and geographical origin of honey samples and other bees’ products, which will serve the apiculture public and other target groups in Slovakia. Group of evaluated plants in this monography represents the preview of oncoming extended set of plant species in frame of international palynological database of Slovakia.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {book} } The aim of the monography is presentation of pollen grain characteristics from selected group of plant species. The evaluated group consists of plants that are traditionally cultivated such as Helianthus annuus L., Prunus avium (L.) L.; rarely used such as Castanea sativa Mill., Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliott; less known species Diospyros kaki L.; invasive species Solidago gigantea Aiton; ornamental species Mahonia aquifolium (Pursh) Nutt., naturally occurring plant species Taraxacum sect. Ruderalia, Lamium purpureum L., Cichorium intybus L, Crataegus monogyna Jacq.; as well as species used for bees’ pasture in Slovakia such as Phacelia tanacetifolia Benth., from which bees are gathering nectar and pollen for their feeding. Flowers were gathered from selected plants at the start of full bloom. In laboratory conditions, the pollen was released from stamen and subsequently dried and placed on stubs to be prepared for observation and photographed on scanning electron microscope. Pollen grains were classified based on internationally recognized methodology (Ertdtman, 1952). We evaluated fundamental morphological characteristics of pollen grains – size of grains based on length of polar (P) and equatorial (E) axis, shape of pollen grains (P/E), outline, pollen unit, polarity of pollen grains, symmetry, number and shape of apertures, exine sculpture. Results confirmed that identifying characteristics, also applicable for detection of species spectrum of pollen in honey, is unique and steady exine sculpture as well as number and shape of apertures, which is documented by SEM observations especially on details of surface sculpture. We determined length of polar axis (P) in range from 20.51 μm (Castanea sativa Mill.) to 58.03 μm (Diospyros kaki L.), length of equatorial axis (E) in range from 9.37 μm (Castanea sativa Mill.) to 39.05 μm (Cichorium intybus L.) and shape index (P/E) in range from 1.00 (Cichorium intybus L.) to 2.34 (Phacelia tanacetifolia Benth.). Acquired results will be used for creation of database of pollen grains from plant species growing in Slovakia and also for evaluation of botanical and geographical origin of honey samples and other bees’ products, which will serve the apiculture public and other target groups in Slovakia. Group of evaluated plants in this monography represents the preview of oncoming extended set of plant species in frame of international palynological database of Slovakia. |
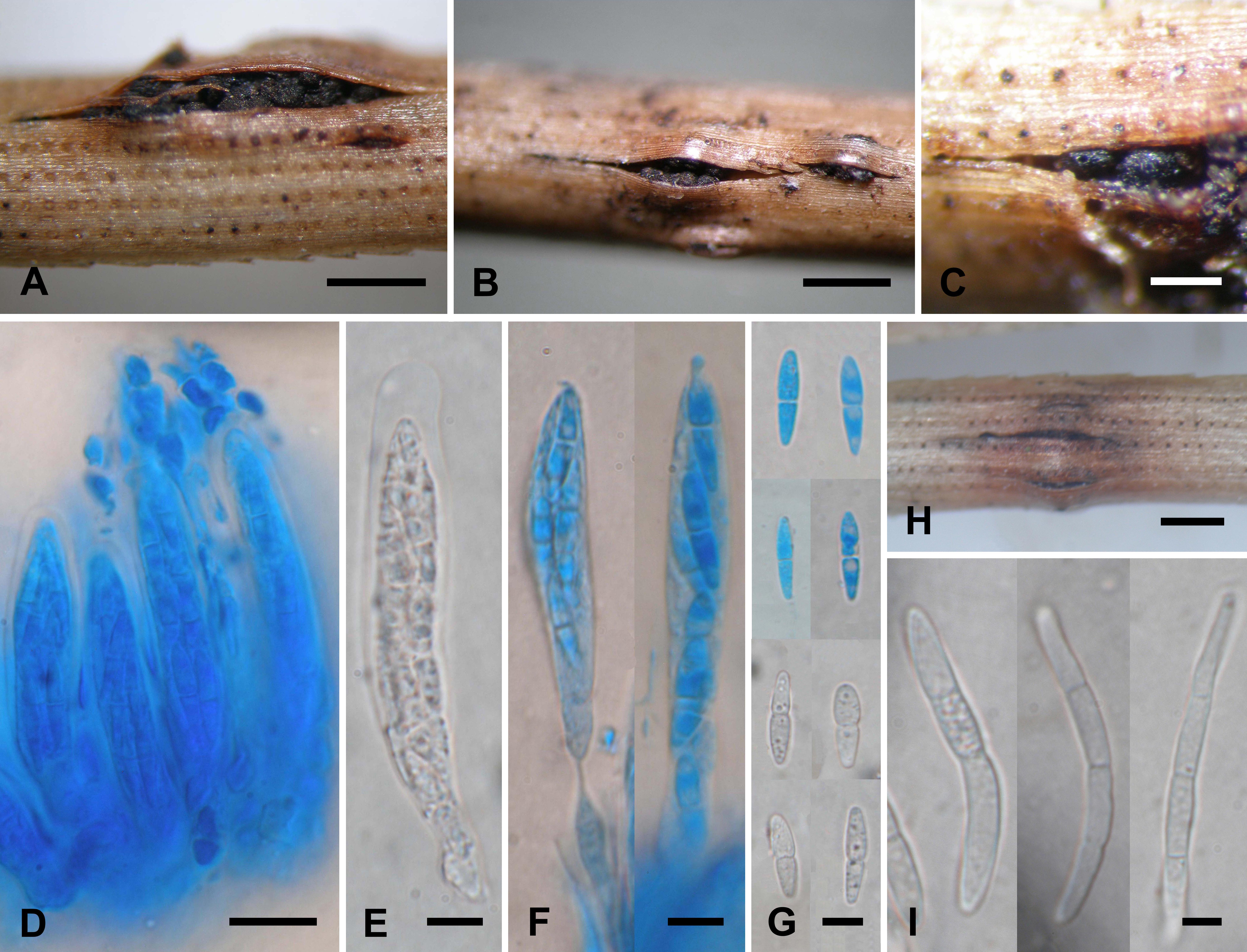 | Adamčíková, K; Pastirčáková, K; Jánošíková, Z; Ostrovský, R; Pastirčák, M; Pažitný, J; Kobza, M; Adamčík, S; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Ondrušková, E New regional records of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens from Slovakia: distribution, hosts and pathogens characterization Journal Article Annals of Forest Research, 66 (1), pp. 99-111, 2023, ISSN: 1844-8135. @article{Adamčíková2023, title = {New regional records of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens from Slovakia: distribution, hosts and pathogens characterization}, author = {K. Adamčíková and K. Pastirčáková and Z. Jánošíková and R. Ostrovský and M. Pastirčák and J. Pažitný and M. Kobza and S. Adamčík and M. Kádasi-Horáková and E. Ondrušková}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.15287/afr.2023.2427}, issn = {1844-8135}, year = {2023}, date = {2023-07-25}, journal = {Annals of Forest Research}, volume = {66}, number = {1}, pages = {99-111}, abstract = {Dothistroma needle blight is one of the most severe needle diseases of pines caused by two closely related species, Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini. The further spread and distribution of this disease was investigated in Slovakia as well as new hosts and stand types were identified at regional level. Dothistroma septosporum was recorded in a natural stand at higher altitude on Pinus cembra in the High Tatras and the P. uncinata records are new host reports for Slovakia for this pathogen. Moreover, for D. pini, P. cembra as a new host at the country level was recorded and P. armandii was identified as new host species worldwide. Mating types for all collected samples and ITS haplotypes for D. pini isolates were determined. For D. pini, five localities with the presence of both mating types and three ITS haplotypes (Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2 and Dp_HAP.4) were reported. Samples where both mating types of the pathogens were identified, were selected for the microscopic examination of fruiting bodies aimed to detect sexual reproductive organs. In all inspected needle samples of D. pini, only conidiomata with typical hyaline cylindrical conidia were identified. The sexual state of D. septosporum was recorded in one sample of P. nigra needles.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Dothistroma needle blight is one of the most severe needle diseases of pines caused by two closely related species, Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini. The further spread and distribution of this disease was investigated in Slovakia as well as new hosts and stand types were identified at regional level. Dothistroma septosporum was recorded in a natural stand at higher altitude on Pinus cembra in the High Tatras and the P. uncinata records are new host reports for Slovakia for this pathogen. Moreover, for D. pini, P. cembra as a new host at the country level was recorded and P. armandii was identified as new host species worldwide. Mating types for all collected samples and ITS haplotypes for D. pini isolates were determined. For D. pini, five localities with the presence of both mating types and three ITS haplotypes (Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2 and Dp_HAP.4) were reported. Samples where both mating types of the pathogens were identified, were selected for the microscopic examination of fruiting bodies aimed to detect sexual reproductive organs. In all inspected needle samples of D. pini, only conidiomata with typical hyaline cylindrical conidia were identified. The sexual state of D. septosporum was recorded in one sample of P. nigra needles. |
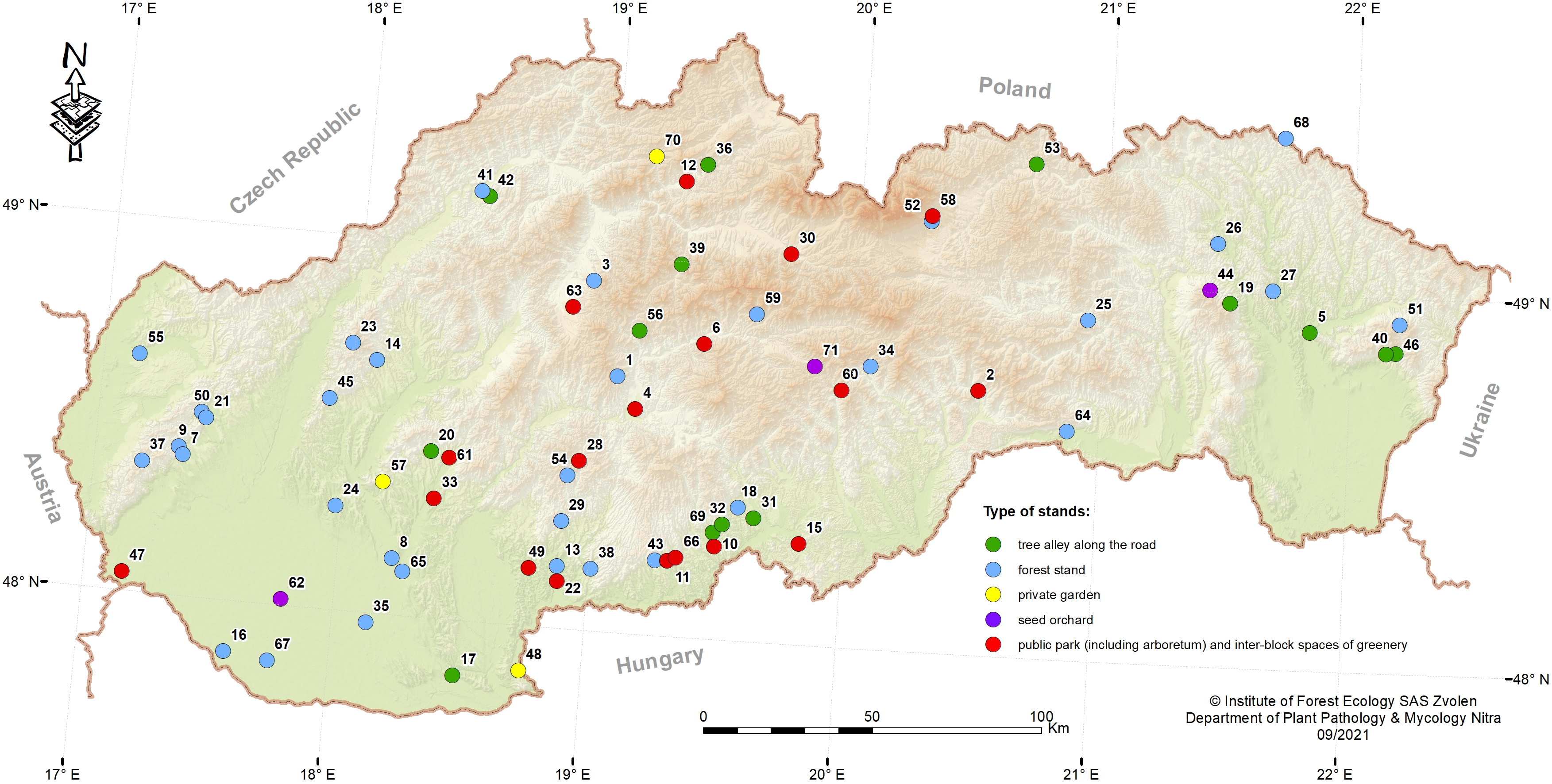 | Kádasi-Horáková, M; Barta, M; Adamčíková, K; Ostrovský, R; Pastirčáková, K Hymenoscyphus fraxineus on Fraxinus excelsior in Slovakia: distribution and mating types Journal Article Biologia, 78 (5), pp. 1219-1230, 2023, ISSN: 0006-3088. @article{Kádasi-Horáková2023, title = {\textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus} on \textit{Fraxinus excelsior} in Slovakia: distribution and mating types}, author = {M. Kádasi-Horáková and M. Barta and K. Adamčíková and R. Ostrovský and K. Pastirčáková}, doi = {10.1007/s11756-022-01023-9}, issn = {0006-3088}, year = {2023}, date = {2023-05-10}, journal = {Biologia}, volume = {78}, number = {5}, pages = {1219-1230}, abstract = {Hymenoscyphus fraxineus causes ash dieback in Europe and threatens the future existence of Fraxinus excelsior in large parts of its natural distribution range. In this study, we report the first documented distribution of the pathogen on the most common ash species F. excelsior in Slovakia, identified molecularly using species-specific primers and based on sequencing of the ITS region of rDNA. Analysis of the mating type genes of H. fraxineus isolates revealed the presence of both mating types in Slovakia. Hymenoscyphus fraxineus-positive trees were recorded in 70 localities with different types of management in different parts of the country, mainly in forest stands. The results indicate the widespread distribution of H. fraxineus across the entire country, wherever the host is present.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Hymenoscyphus fraxineus causes ash dieback in Europe and threatens the future existence of Fraxinus excelsior in large parts of its natural distribution range. In this study, we report the first documented distribution of the pathogen on the most common ash species F. excelsior in Slovakia, identified molecularly using species-specific primers and based on sequencing of the ITS region of rDNA. Analysis of the mating type genes of H. fraxineus isolates revealed the presence of both mating types in Slovakia. Hymenoscyphus fraxineus-positive trees were recorded in 70 localities with different types of management in different parts of the country, mainly in forest stands. The results indicate the widespread distribution of H. fraxineus across the entire country, wherever the host is present. |
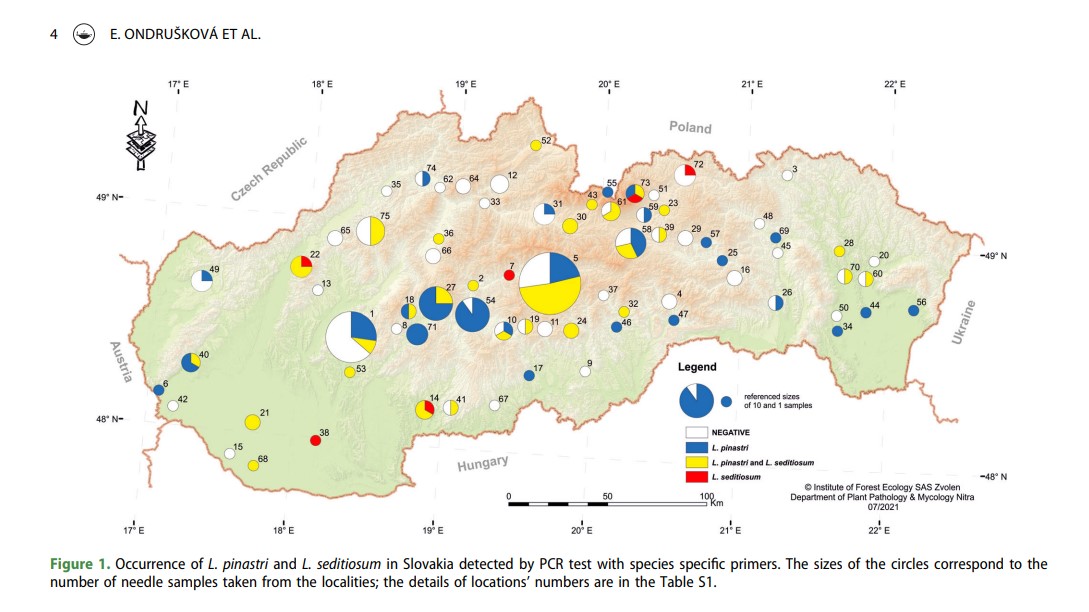 | Ondrušková, E; Adamčík, S; Kobza, M; Jánošíková, Z; Ostrovský, R; Pastirčáková, K; Caboň, M; Adamčíková, K Checking the balance between pathogenic and mutualistic pine needle fungi of the genus Lophodermium in forested and urban areas of Slovakia Journal Article Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 38 (1-2), pp. 39-48, 2023, ISSN: 1651-1891. @article{Ondrušková2023, title = {Checking the balance between pathogenic and mutualistic pine needle fungi of the genus Lophodermium in forested and urban areas of Slovakia}, author = {E. Ondrušková and S. Adamčík and M. Kobza and Z. Jánošíková and R. Ostrovský and K. Pastirčáková and M. Caboň and K. Adamčíková }, doi = { DOI: 10.1080/02827581.2023.2191004}, issn = {1651-1891}, year = {2023}, date = {2023-03-27}, journal = {Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research}, volume = {38}, number = {1-2}, pages = {39-48}, abstract = {Lophodermium species are well known to be among dominant endophytic fungi colonising pine needles. Occurrence of two species with different life strategies on different Pinus trees across Slovakia was detected by PCR using species specific primers. In general, commensalistic species L. pinastri was more frequent than parasitic L. seditiosum. There were no significant differences observed between urban and natural environments, but natural environments have more frequent colonisation by L. pinastri and less frequent were trees negatively tested to Lophodermium colonisation. Among the most frequently sampled trees were non-native P. nigra and native P. sylvestris. Significant difference in Lophodermium incidence was detected between these two species in natural environment, with increased frequency of L. pinastri on native Scots pine. In addition to one clade of L. pinastri, culture based species identification confirmed presence of L. corconticum and an undescribed clade of L. seditiosum that is not sensitive to used PCR primers for the species detection.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Lophodermium species are well known to be among dominant endophytic fungi colonising pine needles. Occurrence of two species with different life strategies on different Pinus trees across Slovakia was detected by PCR using species specific primers. In general, commensalistic species L. pinastri was more frequent than parasitic L. seditiosum. There were no significant differences observed between urban and natural environments, but natural environments have more frequent colonisation by L. pinastri and less frequent were trees negatively tested to Lophodermium colonisation. Among the most frequently sampled trees were non-native P. nigra and native P. sylvestris. Significant difference in Lophodermium incidence was detected between these two species in natural environment, with increased frequency of L. pinastri on native Scots pine. In addition to one clade of L. pinastri, culture based species identification confirmed presence of L. corconticum and an undescribed clade of L. seditiosum that is not sensitive to used PCR primers for the species detection. |
2022 |
|
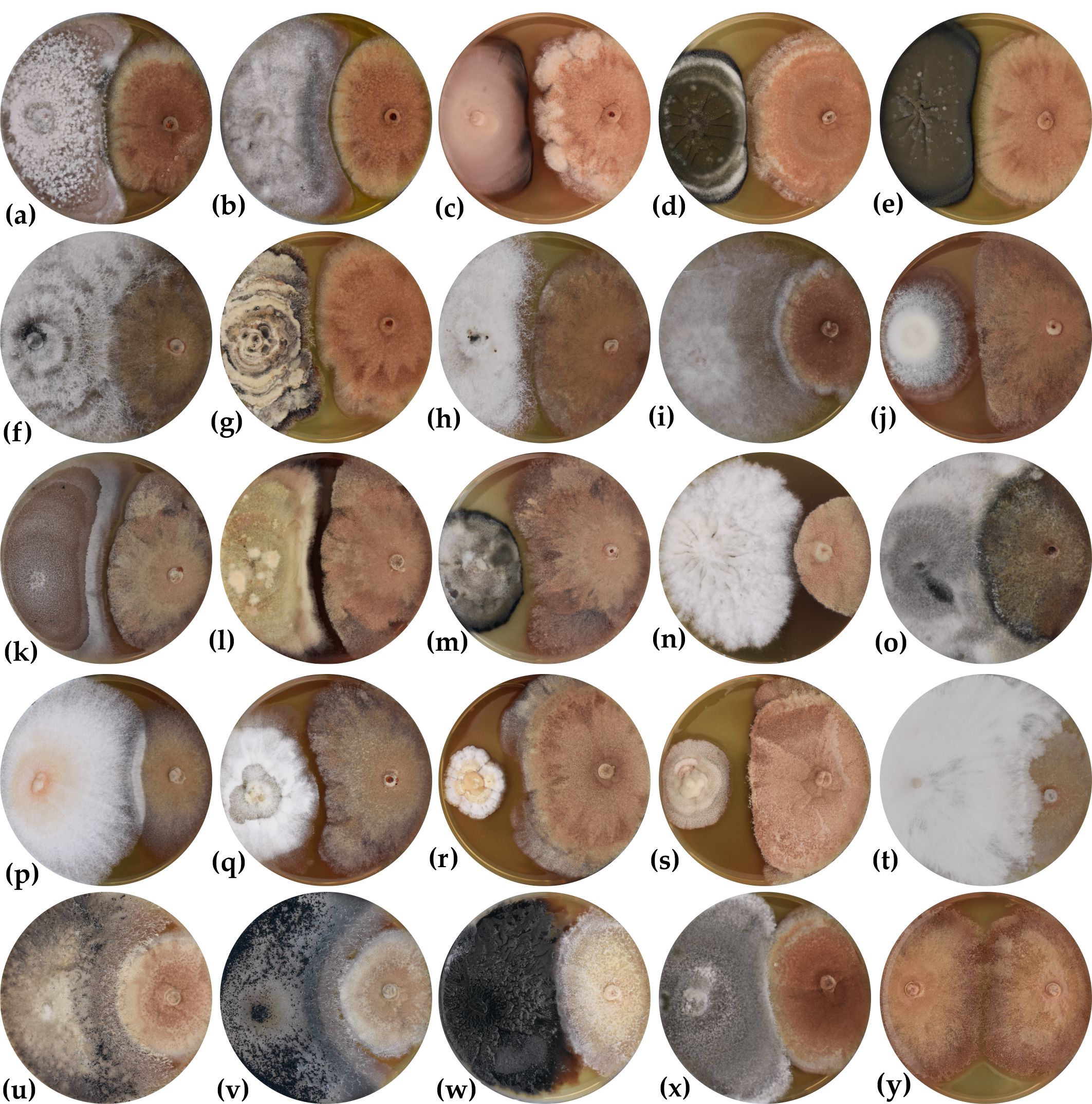 | Barta, M; Pastirčáková, K; Ostrovský, R; Kobza, M; Kádasi-Horáková, M Culturable endophytic fungi in Fraxinus excelsior and their interactions with Hymenoscyphus fraxineus Journal Article Forests, 13 (7), pp. 1-23, Article no. 1098, 2022, ISSN: 1999-4907. @article{Barta2022b, title = {Culturable endophytic fungi in \textit{Fraxinus excelsior} and their interactions with \textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus}}, author = {M. Barta and K. Pastirčáková and R. Ostrovský and M. Kobza and M. Kádasi-Horáková}, doi = {10.3390/f13071098}, issn = {1999-4907}, year = {2022}, date = {2022-07-13}, journal = {Forests}, volume = {13}, number = {7}, pages = {1-23, Article no. 1098}, abstract = {The species diversity of culturable endophytic fungi was studied in the leaves and twigs of symptomatic and asymptomatic Fraxinus excelsior trees. Endophytic mycobiota was dominated by Ascomycota species, with Pleosporales (44.17%) and Diaporthales (23.79%) endophytes being the most frequently observed in the tree samples. The number of endophytic isolates and species richness varied depending on the sampling date (May and October) and tissue location. Of the 54 species identified based on ITS sequences, 14 were classified as dominant. The most frequently isolated species were Diaporthe eres, followed by Alternaria alternata, Dothiorella gregaria, and Fraxinicola fraxini. The inhibitory effect of 41 species (75 isolates) of endophytes on the radial growth of a Hymenoscyphus fraxineus isolate was studied under in vitro conditions (dual cultures). The radial growth of H. fraxineus was the most inhibited by four endophytic fungi from twigs (Fusarium lateritium, Didymella aliena, Didymella macrostoma, and Dothiorella gregaria). The inhibitory effect of the four isolates was also studied under in planta conditions. The isolates artificially inoculated into the trunks of ash trees reduced the length of necroses formed by H. fraxineus co-inoculated in the same trunks. This effect depended on the isolate, and the inhibition was most prominent only on trunks inoculated with F. lateritium and D. aliena. Although the total length of necrotic lesions formed by the H. fraxineus infection was shorter in the ash trunks co-inoculated with the endophytes, the difference was not significant.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The species diversity of culturable endophytic fungi was studied in the leaves and twigs of symptomatic and asymptomatic Fraxinus excelsior trees. Endophytic mycobiota was dominated by Ascomycota species, with Pleosporales (44.17%) and Diaporthales (23.79%) endophytes being the most frequently observed in the tree samples. The number of endophytic isolates and species richness varied depending on the sampling date (May and October) and tissue location. Of the 54 species identified based on ITS sequences, 14 were classified as dominant. The most frequently isolated species were Diaporthe eres, followed by Alternaria alternata, Dothiorella gregaria, and Fraxinicola fraxini. The inhibitory effect of 41 species (75 isolates) of endophytes on the radial growth of a Hymenoscyphus fraxineus isolate was studied under in vitro conditions (dual cultures). The radial growth of H. fraxineus was the most inhibited by four endophytic fungi from twigs (Fusarium lateritium, Didymella aliena, Didymella macrostoma, and Dothiorella gregaria). The inhibitory effect of the four isolates was also studied under in planta conditions. The isolates artificially inoculated into the trunks of ash trees reduced the length of necroses formed by H. fraxineus co-inoculated in the same trunks. This effect depended on the isolate, and the inhibition was most prominent only on trunks inoculated with F. lateritium and D. aliena. Although the total length of necrotic lesions formed by the H. fraxineus infection was shorter in the ash trunks co-inoculated with the endophytes, the difference was not significant. |
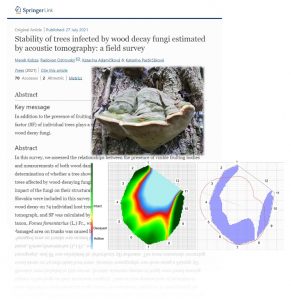 | Kobza, M; Ostrovský, R; Adamčíková, K; Pastirčáková, K Stability of trees infected by wood decay fungi estimated by acoustic tomography: a field survey Journal Article Trees Structure and Function, 36 (1), pp. 103-112, 2022, ISSN: 1432-2285. @article{Kobza2022, title = {Stability of trees infected by wood decay fungi estimated by acoustic tomography: a field survey}, author = {M. Kobza and R. Ostrovský and K. Adamčíková and K. Pastirčáková}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-021-02185-w}, doi = {10.1007/s00468-021-02185-w}, issn = {1432-2285}, year = {2022}, date = {2022-02-08}, journal = {Trees Structure and Function}, volume = {36}, number = {1}, pages = {103-112}, abstract = {In this survey, we assessed the relationships between the presence of visible fruiting bodies and measurements of both wood damage and tree safety factor (SF), the final aim being the determination of whether a tree showing wood decay signs should be felled or not. In general, trees affected by wood-decaying fungi cannot be considered risky prior to determining the impact of the fungi on their structural integrity. Trees of nine genera from 13 localities of Slovakia were included in this survey. In total, nineteen species of fungi were found causing wood decay on 74 individual host trees. Acoustic tomography was done using a Fakopp 3D tomograph, and SF was calculated by ArborSonic 3D software. The most commonly occurring taxon, Fomes fomentarius (L.) Fr., was found on six tree genera. The highest degree of damaged area on trunks was caused by fungi in the genera Fomes, Ganoderma, and Perenniporia (over 70%), while the lowest damage was caused by genera Spongipellis, Cerrena, and Auricularia (up to 30%). The lowest values of SF were measured on trees of the genus Acer infected by Fomes fomentarius; Prunus infected by Phellinus pomaceus (Pers.) Maire; and Fagus infected by Ganoderma pfeifferi Bres. Computation of the SF of individual trees plays a vital part in the stability evaluation of trees affected by wood decay fungi.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } In this survey, we assessed the relationships between the presence of visible fruiting bodies and measurements of both wood damage and tree safety factor (SF), the final aim being the determination of whether a tree showing wood decay signs should be felled or not. In general, trees affected by wood-decaying fungi cannot be considered risky prior to determining the impact of the fungi on their structural integrity. Trees of nine genera from 13 localities of Slovakia were included in this survey. In total, nineteen species of fungi were found causing wood decay on 74 individual host trees. Acoustic tomography was done using a Fakopp 3D tomograph, and SF was calculated by ArborSonic 3D software. The most commonly occurring taxon, Fomes fomentarius (L.) Fr., was found on six tree genera. The highest degree of damaged area on trunks was caused by fungi in the genera Fomes, Ganoderma, and Perenniporia (over 70%), while the lowest damage was caused by genera Spongipellis, Cerrena, and Auricularia (up to 30%). The lowest values of SF were measured on trees of the genus Acer infected by Fomes fomentarius; Prunus infected by Phellinus pomaceus (Pers.) Maire; and Fagus infected by Ganoderma pfeifferi Bres. Computation of the SF of individual trees plays a vital part in the stability evaluation of trees affected by wood decay fungi. |
2021 |
|
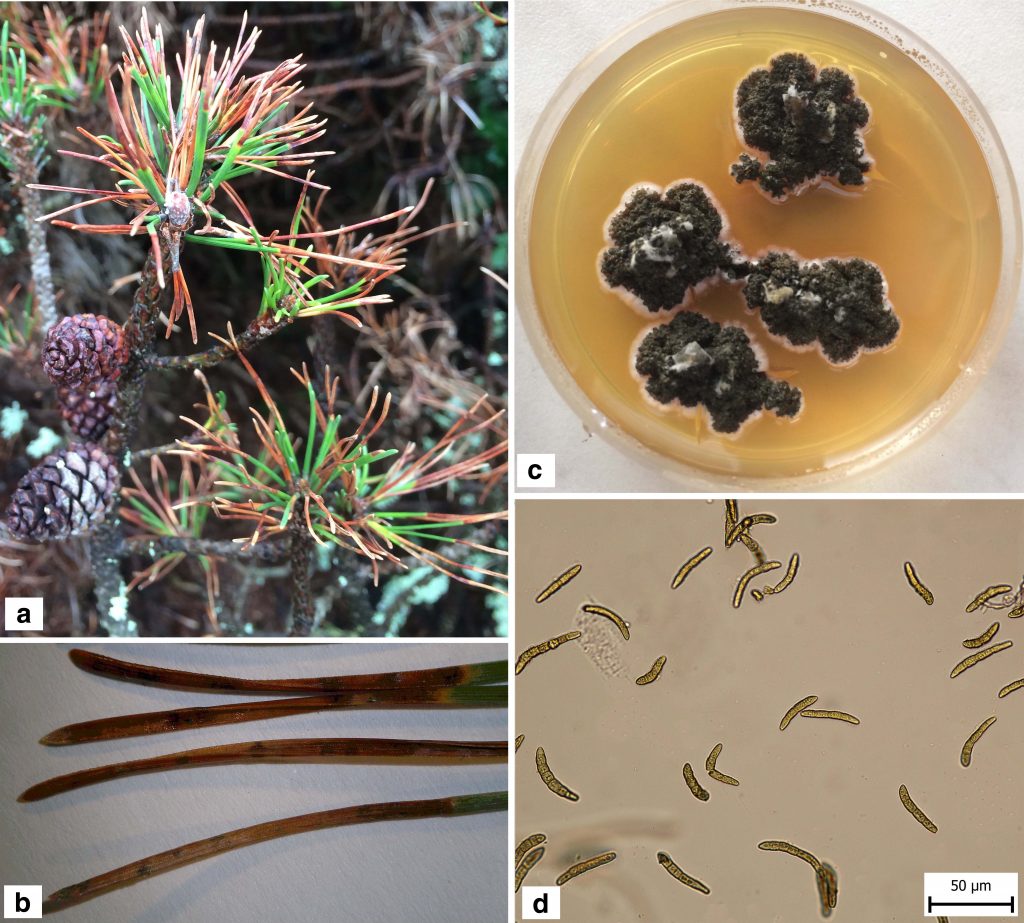 | Adamčíková, K; Jánošíková, Z; Adamčík, S; Ostrovský, R; Pastirčáková, K; Kobza, M; Ondrušková, E Host range, genetic variability, and mating types of Lecanosticta acicola in Slovakia Journal Article Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 36 (5), pp. 325-332, 2021, ISSN: 0282-7581. @article{Adamčíková2021b, title = {Host range, genetic variability, and mating types of \textit{Lecanosticta acicola} in Slovakia}, author = {K. Adamčíková and Z. Jánošíková and S. Adamčík and R. Ostrovský and K. Pastirčáková and M. Kobza and E. Ondrušková}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1080/02827581.2021.1941236}, doi = {10.1080/02827581.2021.1941236}, issn = {0282-7581}, year = {2021}, date = {2021-07-16}, journal = {Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research}, volume = {36}, number = {5}, pages = {325-332}, abstract = {In recent years, there has been an apparent Europe-wide emerging presence of brown spot needle blight, a disease of pine species caused by the fungus Lecanosticta acicola. In this study, we report the first well-documented occurrences of the pathogen in Slovakia, identified molecularly using species-specific primers and based on sequencing of the ITS region and TEF1 gene. Among the material collected from 84 locations within the country, L. acicola was present in 17 samples from 13 different locations, mainly distributed in urban environments. Four pine species were identified as hosts, among which, Pinus nigra and P. mugo were found to be the most frequently infected. Analysis of the mating type genes of 24 isolates obtained from two localities revealed the presence of a single mating type in Slovakia. All analyzed ITS sequences of the Slovak isolates were found to be uniform. However, although analysis of the TEF1 gene indicated that all Slovak isolates could be grouped into a single lineage, we detected nucleotide polymorphisms suggestive of a certain degree of genetic diversification within central European populations of the fungus.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } In recent years, there has been an apparent Europe-wide emerging presence of brown spot needle blight, a disease of pine species caused by the fungus Lecanosticta acicola. In this study, we report the first well-documented occurrences of the pathogen in Slovakia, identified molecularly using species-specific primers and based on sequencing of the ITS region and TEF1 gene. Among the material collected from 84 locations within the country, L. acicola was present in 17 samples from 13 different locations, mainly distributed in urban environments. Four pine species were identified as hosts, among which, Pinus nigra and P. mugo were found to be the most frequently infected. Analysis of the mating type genes of 24 isolates obtained from two localities revealed the presence of a single mating type in Slovakia. All analyzed ITS sequences of the Slovak isolates were found to be uniform. However, although analysis of the TEF1 gene indicated that all Slovak isolates could be grouped into a single lineage, we detected nucleotide polymorphisms suggestive of a certain degree of genetic diversification within central European populations of the fungus. |
2020 |
|
 | Ondrušková, Emília; Ostrovský, Radovan; Jánošíková, Zuzana; Adamčíková, Katarína; Kobza, Marek Selected climatic variables in Slovakia are favourable to the development of Dothistroma needle blight Journal Article Folia Oecologica, 47 (2), pp. 144-152, 2020. @article{Ondrušková2020b, title = {Selected climatic variables in Slovakia are favourable to the development of Dothistroma needle blight}, author = {Emília Ondrušková and Radovan Ostrovský and Zuzana Jánošíková and Katarína Adamčíková and Marek Kobza}, url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/foecol-2020-0008.pdf}, doi = {10.2478/foecol-2020-0017}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-11-24}, journal = {Folia Oecologica}, volume = {47}, number = {2}, pages = {144-152}, abstract = {Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) is a disease of pine needles. It causes significant defoliation of affected trees; intensive attacks lead to damages of the whole stand. The relationship of trends in disease severity and intensity with climatic variables were studied in three Austrian pine plantations (Jahodná, Kálnica, Litava) during 2014–2018. During the monitoring period, the greatest variability in disease severity was observed in the top third of the crowns, which showed the highest correlation with the variants of the most important climatic conditions (temperature and relative humidity) tested. For the spread of DNB, based on statistical assessment, a higher number of intervals of environmentally favourable climatic conditions is crucial. Both Dothistroma species (D. septosporum and D. pini), which are causal agents of the disease, were identified in Jahodná. In Kálnica and Litava, only D. septosporum was present.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) is a disease of pine needles. It causes significant defoliation of affected trees; intensive attacks lead to damages of the whole stand. The relationship of trends in disease severity and intensity with climatic variables were studied in three Austrian pine plantations (Jahodná, Kálnica, Litava) during 2014–2018. During the monitoring period, the greatest variability in disease severity was observed in the top third of the crowns, which showed the highest correlation with the variants of the most important climatic conditions (temperature and relative humidity) tested. For the spread of DNB, based on statistical assessment, a higher number of intervals of environmentally favourable climatic conditions is crucial. Both Dothistroma species (D. septosporum and D. pini), which are causal agents of the disease, were identified in Jahodná. In Kálnica and Litava, only D. septosporum was present. |
 | Brindza, J; Horčinová-Sedláčková, V; Grygorieva, O V; Klimenko, S; Kuklina, A; Svydenko, L; Vergun, O; Mňahončáková, E; Ostrovský, R; Ivanišová, E; Dítětová, P Názvy úžitkových druhov rastlín vo vybraných jazykoch Book Agrobiodiverzita pre lepšiu výživu, zdravie a kvalitu života, Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita v Nitre, 2020, ISBN: 978-80-552-2169-4. @book{Brindza2020, title = {Názvy úžitkových druhov rastlín vo vybraných jazykoch}, author = {J. Brindza and V. Horčinová-Sedláčková and O.V. Grygorieva and S. Klimenko and A. Kuklina and L. Svydenko and O. Vergun and E. Mňahončáková and R. Ostrovský and E. Ivanišová and P. Dítětová}, isbn = {978-80-552-2169-4}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-06-13}, publisher = {Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita v Nitre}, edition = {Agrobiodiverzita pre lepšiu výživu, zdravie a kvalitu života}, abstract = {Kolektív autorov prezentuje 202 úžitkových druhov rastlín s oficiálnymi latinskými názvami podľa botanickej databázy Kráľovskej Botanickej záhrady v Kew známej pod názvom The Plant List (TPL - http://www.theplantlist.org/ ). Pri každom druhu sú uvedené aj viaceré názvy rastlinného druhu v jazykoch 21 európskych krajín a synonymá druhu. Informácia o každom druhu je doplnená aj fotodokumentáciou pre lepšiu identifikáciu druhu. Pevne veríme, že takto spracovaná publikácia umožní záujemcom využiť hlavne názvy rastlín v rôznych jazykoch pri získavaní nových a hlavne tradičných poznatkov o ich pestovaní a využívaní. BAB Odborné monografie vydané v domácich vydavateľstvách.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {book} } Kolektív autorov prezentuje 202 úžitkových druhov rastlín s oficiálnymi latinskými názvami podľa botanickej databázy Kráľovskej Botanickej záhrady v Kew známej pod názvom The Plant List (TPL - http://www.theplantlist.org/ ). Pri každom druhu sú uvedené aj viaceré názvy rastlinného druhu v jazykoch 21 európskych krajín a synonymá druhu. Informácia o každom druhu je doplnená aj fotodokumentáciou pre lepšiu identifikáciu druhu. Pevne veríme, že takto spracovaná publikácia umožní záujemcom využiť hlavne názvy rastlín v rôznych jazykoch pri získavaní nových a hlavne tradičných poznatkov o ich pestovaní a využívaní. BAB Odborné monografie vydané v domácich vydavateľstvách. |
2018 |
|
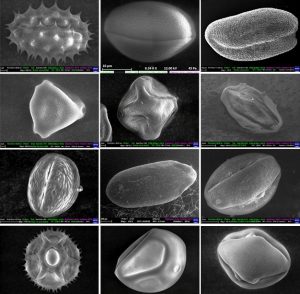 | Brindza, J; Motyleva, S; Ostrovský, R; Grygorieva, O V; Adamchuk, L; Horčinová-Sedláčková, V; Juríková, T; Fatrcová-Šramková, K; Schwarzová, M; Brovarskyi, V; Velichko, S; Tkachenko, O Peľ a včelie peľové obnôžky z niektorých druhov rastlín Book Chapter Brindza, J; Motyleva, S (Ed.): Chapter 4, pp. 147, Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita v Nitre, Tr. A. Hlinku 2, 949 01 Nitra, FarmersEduca, 2018, ISBN: 978-80-552-1862-5. @inbook{Brindza2018, title = {Peľ a včelie peľové obnôžky z niektorých druhov rastlín}, author = {J. Brindza and S. Motyleva and R. Ostrovský and O.V. Grygorieva and L. Adamchuk and V. Horčinová-Sedláčková and T. Juríková and K. Fatrcová-Šramková and M. Schwarzová and V. Brovarskyi and S. Velichko and O. Tkachenko}, editor = {J. Brindza and S. Motyleva}, isbn = {978-80-552-1862-5}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-12-17}, pages = {147}, publisher = {Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita v Nitre}, address = {Tr. A. Hlinku 2, 949 01 Nitra}, edition = {FarmersEduca}, chapter = {4}, abstract = {Odborná publikácia, v ktorej autori prezentujú niektoré rastlinné druhy, z ktorých včely zbierajú peľové zrná a využívajú ich na formovanie obnôžok. Publikácia poskytuje základné informácie o peli a včelích peľových obnôžkach s prezentáciou na skupine charakterizovaných druhov. Je určená pre malých, mladých a rodinných farmárov, včelárov, pestovateľov rastlín, množiteľov a spravovateľov. Uvedená kapitola predstavuje dominantnú časť publikácie. V kapitole je prezentovaná morfometrická charakteristika peľových zŕn a včelích peľových obnôžok vybranej skupiny 26 rastlinných druhov.}, type = {inbook}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inbook} } Odborná publikácia, v ktorej autori prezentujú niektoré rastlinné druhy, z ktorých včely zbierajú peľové zrná a využívajú ich na formovanie obnôžok. Publikácia poskytuje základné informácie o peli a včelích peľových obnôžkach s prezentáciou na skupine charakterizovaných druhov. Je určená pre malých, mladých a rodinných farmárov, včelárov, pestovateľov rastlín, množiteľov a spravovateľov. Uvedená kapitola predstavuje dominantnú časť publikácie. V kapitole je prezentovaná morfometrická charakteristika peľových zŕn a včelích peľových obnôžok vybranej skupiny 26 rastlinných druhov. |
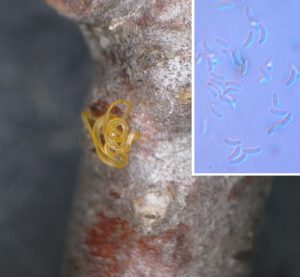 | Pastirčáková, K; Ostrovský, R; Pastirčák, M Mycobiota in dead and damaged branches of silver birch in Slovakia Journal Article Baltic Forestry, 24 (1), pp. 17-23, 2018, ISSN: 1392-1355. @article{Pastirčáková2018b, title = {Mycobiota in dead and damaged branches of silver birch in Slovakia}, author = {K. Pastirčáková and R. Ostrovský and M. Pastirčák}, url = {https://www.balticforestry.mi.lt/bf/PDF_Articles/2018-24%5B1%5D/Baltic%20Forestry%202018.1_017-023.pdf}, issn = {1392-1355}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-08-23}, journal = {Baltic Forestry}, volume = {24}, number = {1}, pages = {17-23}, abstract = {The species composition of the mycobiota in dead and damaged branches of silver birch (Betula pendula) was studied. The study material collected at 44 localities in Slovakia during the period of 2009 to 2015 was examined. In total, 27 fungal taxa (11 Ascomycetes and 16 Deuteromycetes) were identified on the basis of fruiting body morphology. Sixteen of them have never been recorded on birch trees in the country. Prosthemium betulinum, Trimmatostroma betulinum, Cytospora betulicola, Cryptosporella betulae, Coryneum lanciforme, Myxocyclus polycystis, Pleomassaria siparia, and Disculina betulina were the dominant colonisers of dead branches. The spectrum of fungi colonising dead and dying branches of B. pendula was compared in the following different types of stands: public parks and inter-block spaces of greenery, private gardens, forests, and tree alleys alongside roads. The average number of fungal taxa on birch trees growing in different habitats was not significantly different.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The species composition of the mycobiota in dead and damaged branches of silver birch (Betula pendula) was studied. The study material collected at 44 localities in Slovakia during the period of 2009 to 2015 was examined. In total, 27 fungal taxa (11 Ascomycetes and 16 Deuteromycetes) were identified on the basis of fruiting body morphology. Sixteen of them have never been recorded on birch trees in the country. Prosthemium betulinum, Trimmatostroma betulinum, Cytospora betulicola, Cryptosporella betulae, Coryneum lanciforme, Myxocyclus polycystis, Pleomassaria siparia, and Disculina betulina were the dominant colonisers of dead branches. The spectrum of fungi colonising dead and dying branches of B. pendula was compared in the following different types of stands: public parks and inter-block spaces of greenery, private gardens, forests, and tree alleys alongside roads. The average number of fungal taxa on birch trees growing in different habitats was not significantly different. |
 | Jánošíková-Hečková, Z; Ondrušková, E; Barta, M; Ostrovský, R; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Pastirčáková, K; Kobza, M; Adamčíková, K The hosts and geographic range of Dothistroma needle blight in Slovakia Journal Article Forest Pathology, 48 (3), pp. e12421, 2018, ISSN: 1437-4781. @article{Jánošíková-Hečková2018, title = {The hosts and geographic range of Dothistroma needle blight in Slovakia}, author = {Z. Jánošíková-Hečková and E. Ondrušková and M. Barta and R. Ostrovský and M. Kádasi-Horáková and K. Pastirčáková and M. Kobza and K. Adamčíková }, url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/efp.12421}, doi = {10.1111/efp.12421}, issn = {1437-4781}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-02-15}, journal = {Forest Pathology}, volume = {48}, number = {3}, pages = {e12421}, abstract = {The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) were studied in 2014–2017 around Slovakia. A total of 84 localities, both native and planted, were investigated, and the presence of DNB was confirmed in 73 of them. In all positive locations, symptoms typical of DNB were observed and the Dothistroma species was confirmed using species-specific primers either from fungal cultures or directly from needles. Both Dothistroma species—D. septosporum and D. pini—were identified. Both species occurred together in 29 locations, only D. septosporum in 42 and only D. pini in two locations. The host range of D. septosporum included 10 pine species and two spruce species. The host range of D. pini comprised the same number of pine hosts but only one spruce species. Five pine hosts, P. aristata, P. coulteri, P. densiflora, P. jeffreyi, P. × schwerinii, and one spruce host P. abies are new hosts species of D. pini. P. densiflora and Picea pungens have earlier been reported to be susceptible for DNB. In this study, D. septosporum was found from both tree species.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) were studied in 2014–2017 around Slovakia. A total of 84 localities, both native and planted, were investigated, and the presence of DNB was confirmed in 73 of them. In all positive locations, symptoms typical of DNB were observed and the Dothistroma species was confirmed using species-specific primers either from fungal cultures or directly from needles. Both Dothistroma species—D. septosporum and D. pini—were identified. Both species occurred together in 29 locations, only D. septosporum in 42 and only D. pini in two locations. The host range of D. septosporum included 10 pine species and two spruce species. The host range of D. pini comprised the same number of pine hosts but only one spruce species. Five pine hosts, P. aristata, P. coulteri, P. densiflora, P. jeffreyi, P. × schwerinii, and one spruce host P. abies are new hosts species of D. pini. P. densiflora and Picea pungens have earlier been reported to be susceptible for DNB. In this study, D. septosporum was found from both tree species. |
2017 |
|
 | Ostrovský, R; Kobza, M; Gažo, J Extensively damaged trees tested with acoustic tomography considering tree stability in urban greenery Journal Article Trees Structure and Function, 31 (3), pp. 1015-1023, 2017, ISSN: 1432-2285. @article{Ostrovský2017, title = {Extensively damaged trees tested with acoustic tomography considering tree stability in urban greenery}, author = {R. Ostrovský and M. Kobza and J. Gažo}, url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00468-017-1526-6}, doi = {10.1007/s00468-017-1526-6}, issn = {1432-2285}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-02-07}, journal = {Trees Structure and Function}, volume = {31}, number = {3}, pages = {1015-1023}, abstract = {Objectives of study were to assess the accuracy and reliability of the acoustic tomography technique for detecting internal structural defects compared to visual assessment on extensively damaged trees of five species in urban greenery. Tomography was realized by Fakopp 3D acoustic tomograph tool. Several types of structural defects were determined, such as heartwood and sapwood decay, internal and lateral cracks, ring shake and hollow. Acoustic tomography inspection revealed correct detection of damage in all disc samples involved in study. Accuracy of damaged area determination reached 90%. Total accuracy determination for both area and location of damage was 83%. Overestimation of damaged area was observed in eight samples, contrary to seven underestimated samples. Difference in estimated false-positive area in comparison to false-negative area was minimal. Irregularity of cross section shape does not affect the final accuracy of tomograph. Accuracy is not influenced by diameter of tree trunk. We determined strong positive correlation between real area of damage and results of tomography (r = 0.75; p = 0.001). Acoustic tomography provides satisfactory accuracy in damage area determination inside tree trunk and for overall tree stability assessment on even extensively damaged trees in urban greenery.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Objectives of study were to assess the accuracy and reliability of the acoustic tomography technique for detecting internal structural defects compared to visual assessment on extensively damaged trees of five species in urban greenery. Tomography was realized by Fakopp 3D acoustic tomograph tool. Several types of structural defects were determined, such as heartwood and sapwood decay, internal and lateral cracks, ring shake and hollow. Acoustic tomography inspection revealed correct detection of damage in all disc samples involved in study. Accuracy of damaged area determination reached 90%. Total accuracy determination for both area and location of damage was 83%. Overestimation of damaged area was observed in eight samples, contrary to seven underestimated samples. Difference in estimated false-positive area in comparison to false-negative area was minimal. Irregularity of cross section shape does not affect the final accuracy of tomograph. Accuracy is not influenced by diameter of tree trunk. We determined strong positive correlation between real area of damage and results of tomography (r = 0.75; p = 0.001). Acoustic tomography provides satisfactory accuracy in damage area determination inside tree trunk and for overall tree stability assessment on even extensively damaged trees in urban greenery. |
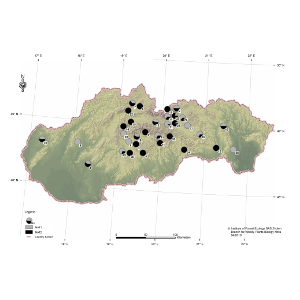 | Ondrušková, E; Hečková, Z; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Koltay, A; Ostrovský, R; Pažitný, J; Adamčíková, K Distribution and characterization of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens on Pinus mugo in Slovakia Journal Article European Journal of Plant Pathology, 148 (2), pp. 283-294, 2017, ISSN: 0929-1873. @article{Ondrušková2017, title = {Distribution and characterization of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens on Pinus mugo in Slovakia}, author = {E. Ondrušková and Z. Hečková and M. Kádasi-Horáková and A. Koltay and R. Ostrovský and J. Pažitný and K. Adamčíková}, url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10658-016-1088-2}, doi = {10.1007/s10658-016-1088-2}, issn = {0929-1873}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, journal = {European Journal of Plant Pathology}, volume = {148}, number = {2}, pages = {283-294}, abstract = {The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) on Pinus mugo was studied in 2014–2015 around the Slovakia. In total, 42 localities were investigated both native and planted ones. Symptoms of DNB were observed on 35 localities only on planted shrubs. All these 35 localities are new P. mugo DNB stands. No DNB symptoms were observed in natural and naturally regenerated plantations. DNAwas extracted from a total of 236 isolates and eight needle samples. Based on the ITS-rDNA comparisons and using species specific primers, both pathogenic Dothistroma species were detected: D. septosporum and D. pini. Isolates of D. septosporum had ITS sequences identical to D. septosporum from Europe and both mating types were identified with slight predominance of MAT2. The ratio of D. septosporum mating types varies significantly between sites, ranging from an equal proportion of each mating type to single mating type populations. D. pini ITS sequence grouped with D. pini from Ukraine, Russia and Switzerland and only MAT2 was found.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) on Pinus mugo was studied in 2014–2015 around the Slovakia. In total, 42 localities were investigated both native and planted ones. Symptoms of DNB were observed on 35 localities only on planted shrubs. All these 35 localities are new P. mugo DNB stands. No DNB symptoms were observed in natural and naturally regenerated plantations. DNAwas extracted from a total of 236 isolates and eight needle samples. Based on the ITS-rDNA comparisons and using species specific primers, both pathogenic Dothistroma species were detected: D. septosporum and D. pini. Isolates of D. septosporum had ITS sequences identical to D. septosporum from Europe and both mating types were identified with slight predominance of MAT2. The ratio of D. septosporum mating types varies significantly between sites, ranging from an equal proportion of each mating type to single mating type populations. D. pini ITS sequence grouped with D. pini from Ukraine, Russia and Switzerland and only MAT2 was found. |
2015 |
|
![Škodcovia gaštana jedlého [Pests of European chestnut]](http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Img-1-206x300.jpg) | Kobza, M; Ostrovský, R Škodcovia gaštana jedlého [Pests of European chestnut] Book Chapter Cagáň, Ľ (Ed.): Choroby a škodcovia záhradníckych rastlín, pp. 301-307, SPU v Nitre, Nitra, 1, 2015, ISBN: 978-80-552-1448-1. @inbook{Kobza2015, title = {Škodcovia gaštana jedlého [Pests of European chestnut]}, author = {M. Kobza and R. Ostrovský}, editor = {Ľ. Cagáň}, isbn = {978-80-552-1448-1}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, booktitle = {Choroby a škodcovia záhradníckych rastlín}, pages = {301-307}, publisher = {SPU v Nitre}, address = {Nitra}, edition = {1}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inbook} } |
Kobza, M; Ostrovský, R Škodcovia orecha kráľovského [Pest of walnut] Book Chapter Cagáň, Ľ (Ed.): Choroby a škodcovia záhradníckych rastlín, pp. 293-299, SPU v Nitre, Nitra, 1, 2015, ISBN: 978-80-552-1448-1. @inbook{Kobza2015b, title = {Škodcovia orecha kráľovského [Pest of walnut]}, author = {M. Kobza and R. Ostrovský}, editor = {Ľ. Cagáň}, isbn = {978-80-552-1448-1}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, booktitle = {Choroby a škodcovia záhradníckych rastlín}, pages = {293-299}, publisher = {SPU v Nitre}, address = {Nitra}, edition = {1}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inbook} } | |
Kobza, M; Ostrovský, R Škodcovia moruší [Pests of mulberries] Book Chapter Cagáň, Ľ (Ed.): Choroby a škodcovia záhradníckych rastlín, pp. 437-445, SPU v Nitre, Nitra, 1, 2015, ISBN: 978-80-552-1448-1. @inbook{Kobza2015b, title = {Škodcovia moruší [Pests of mulberries]}, author = {M. Kobza and R. Ostrovský}, editor = {Ľ. Cagáň}, isbn = {978-80-552-1448-1}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, booktitle = {Choroby a škodcovia záhradníckych rastlín}, pages = {437-445}, publisher = {SPU v Nitre}, address = {Nitra}, edition = {1}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inbook} } | |
 | Ostrovský, R; Kobza, M Význam starostlivosti o dreviny vo verejnej zeleni Proceeding Ústav ekológie lesa SAV Zvolen, Pobočka biológie drevín Nitra, Nitra, 2015, ISBN: 978-80-89408-19-1. @proceedings{Ostrovský2015, title = {Význam starostlivosti o dreviny vo verejnej zeleni}, author = {R. Ostrovský and M. Kobza}, editor = {P. Hrubík and H. Ivanová}, isbn = {978-80-89408-19-1}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, booktitle = {Zborník príspevkov z konferencie s medzinárodnou účasťou, 28. - 29. 4 2015, Nitra [Importance of care of trees in urban area: conference proceedings]}, pages = {159}, publisher = {Ústav ekológie lesa SAV Zvolen, Pobočka biológie drevín Nitra}, address = {Nitra}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {proceedings} } |
2014 |
|
![Príčiny hromadného hynutia gaštana jedlého [Causal agent of European chestnut blight]](https://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/IFE_adamcikova_katarina_article_08.jpg) | Juhásová, G; Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M; Ostrovský, R Príčiny hromadného hynutia gaštana jedlého [Causal agent of European chestnut blight] Journal Article Zahradnictví : časopis profesionálních zahradníků, 13 (7), pp. 48-51, 2014, ISSN: 1213-7596. @article{Juhásová2014, title = {Príčiny hromadného hynutia gaštana jedlého [Causal agent of European chestnut blight]}, author = {G. Juhásová and K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza and R. Ostrovský}, issn = {1213-7596}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Zahradnictví : časopis profesionálních zahradníků}, volume = {13}, number = {7}, pages = {48-51}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
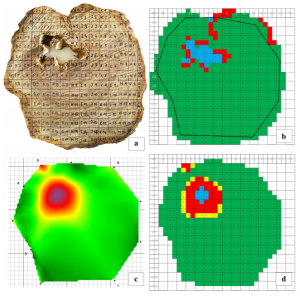
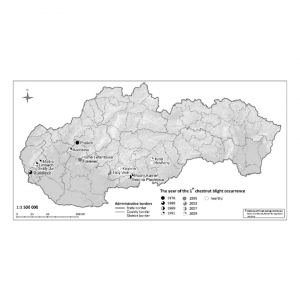 | Bolvanský, M; Ostrovský, R; Kobza, M; Adamčíková, K; Pažitný, J; Juhásová, G; Kajaba, P Spread of chestnut blight in Slovakia in relation to the site topography and climatic characteristics Inproceedings Acta Horticulturae: Proceedings of the second European congress on chestnut : Debrecen, Hungary, Baia Mare, Romania, Modry Kamen, Slovakia, October 9-12, 2013. , pp. 35-42, ISHS, 2014, ISBN: 978 94 6261 032 3. @inproceedings{Bolvanský2014, title = {Spread of chestnut blight in Slovakia in relation to the site topography and climatic characteristics}, author = {M. Bolvanský and R. Ostrovský and M. Kobza and K. Adamčíková and J. Pažitný and G. Juhásová and P. Kajaba}, isbn = {978 94 6261 032 3}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, booktitle = {Acta Horticulturae: Proceedings of the second European congress on chestnut : Debrecen, Hungary, Baia Mare, Romania, Modry Kamen, Slovakia, October 9-12, 2013. }, number = {1043}, pages = {35-42}, publisher = {ISHS}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |
