2018
|
 | Pažitný, J; Bolvanský, M; Adamčíková, K Screening for resistance of progenies derived from Castanea sativa × C. crenata and C. crenata to Cryphonectria parasitica Journal Article Forest Pathology, 48 (5), pp. e12439, 2018, ISSN: 1439-0329. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Pažitný2018,
title = {Screening for resistance of progenies derived from Castanea sativa × C. crenata and C. crenata to Cryphonectria parasitica},
author = {J. Pažitný and M. Bolvanský and K. Adamčíková},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/efp.12439},
doi = {10.1111/efp.12439},
issn = {1439-0329},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-08-10},
journal = {Forest Pathology},
volume = {48},
number = {5},
pages = {e12439},
abstract = {The possibility of screening young seedlings of Castanea for chestnut blight resistance was examined to try to shorten time needed for a breeding programme. Two-year-old chestnut seedlings of eight progenies, derived from open and controlled pollination of three hybrids (Castanea sativa × C. crenata and a C. crenata tree by paternal tree of C. sativa) were screened for resistance to chestnut blight. One hybrid and a C. crenata were partially susceptible, and two hybrids were partially resistant to chestnut blight. A total of 179 seedlings were inoculated with two virulent and one hypovirulent strain of Cryphonectria parasitica at two dates (early June and early September). Stromata production was higher and canker size larger when seedlings were inoculated in early June. Differences in canker size among seedlings derived from different parental trees were observed only after September inoculation. However, differences in canker size among seedlings inoculated with the virulent strains were observed only after June inoculation. The only significant effect on seedling survival was based on fungal strains used for inoculation. Ratio of seedlings, which died after inoculation with the hypovirulent strain, was significantly lower (36.8%) than those that died after inoculation with virulent strains (88.4 and 95.1%). Survival of seedlings was affected only by fungal strains used in inoculation, and not influenced by parental trees. The risk of seedling dieback increased with increasing canker size and with decreasing stem diameter of seedlings. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The possibility of screening young seedlings of Castanea for chestnut blight resistance was examined to try to shorten time needed for a breeding programme. Two-year-old chestnut seedlings of eight progenies, derived from open and controlled pollination of three hybrids (Castanea sativa × C. crenata and a C. crenata tree by paternal tree of C. sativa) were screened for resistance to chestnut blight. One hybrid and a C. crenata were partially susceptible, and two hybrids were partially resistant to chestnut blight. A total of 179 seedlings were inoculated with two virulent and one hypovirulent strain of Cryphonectria parasitica at two dates (early June and early September). Stromata production was higher and canker size larger when seedlings were inoculated in early June. Differences in canker size among seedlings derived from different parental trees were observed only after September inoculation. However, differences in canker size among seedlings inoculated with the virulent strains were observed only after June inoculation. The only significant effect on seedling survival was based on fungal strains used for inoculation. Ratio of seedlings, which died after inoculation with the hypovirulent strain, was significantly lower (36.8%) than those that died after inoculation with virulent strains (88.4 and 95.1%). Survival of seedlings was affected only by fungal strains used in inoculation, and not influenced by parental trees. The risk of seedling dieback increased with increasing canker size and with decreasing stem diameter of seedlings. |
 | Crous, P W; Wingfield, M J; Burgess, T I; Hardy, G.E.St.J.; Gené, J; Guarro, J; García, Baseia I G D; Gusmão, L F P; Souza-Motta, C M; Thangavel, R; Adamčík, S; Barili, A; Barnes, C W; Bezerra, J D P; Bordallo, J J; Cano-Lira, J F; de Oliveira, R J V; Ercole, E; Hubka, V; Iturrieta-González, I; Kubátová, A; Martín, M P; Moreau, P -A; Morte, A; Ordoñez, M E; Rodríguez, A; Stchigel, A M; Vizzini, A; Abdollahzadeh, J; Abreu, V P; Adamčíková, K; Albuquerque, G M R; Alexandrova, A V; Álvarez_Duarte, E; Armstrong-Cho, C; Banniza, S; Barbosa, R N; Bellanger, J -M; Bezerra, J L; Cabral, T S; Caicedo, Caboňand M E; Cantillo, T; Carnegie, A J; Carmo, L T; Castañeda-Ruiz, R F; Clement, C R; Čmoková, A; Conceição, L B; Cruz, R H S F; Damm, U; da_Silva, B D B; da_Silva, G A; da_Silva, R M F; Santiago, A.L.C.M._de_A.; de_Oliveira, L F; de_Souza, C A F; Déniel, F; Dima, B; Dong, G; Edwards, J; Félix, C R; Fournier, J; Gibertoni, T B; Hosaka, K; Iturriaga, T; Jadan, M; Jany, J -L; Jurjević, Ž; Kolařík, M; Kušan, I; Landell, M F; Leite_Cordeiro, T R; Lima, X D; Loizides, M; Luo, S; Machado, A R; Madrid, H; Magalhães, O M C; Marinho, P; Matočec, N; Mešić, A; Miller, A N; Morozova, O V; Neves, R P; Nonaka, K; Nováková, A; Oberlies, N H; Oliveira-Filho, J R C; Oliveira, T G L; Papp, V; Pereira, O L; Perrone, G; Peterson, S W; Pham, T H G; Raja, H A; Raudabaugh, D B; Řehulka, J; RodrÃguez-Andrade, E; Saba, M; Schauflerova, A; Shivas, R G; Simonini, G; Siqueira, J P Z; Sousa, J O; Stajsic, V; Svetasheva, T; Tan, Y P; Tkalčec, Z; Ullah, S; Valente, P; Valenzuela-Lopez, N; Abrinbana, M; Viana_Marques, D A; Wong, P T W; Xavier_de_Lima, V; Groenewald, J Z Fungal Planet description sheets: 716-784 Journal Article Persoonia, 40 , pp. 240-393, 2018, ISSN: 1878-9080. Links | BibTeX @article{Crous2018,
title = {Fungal Planet description sheets: 716-784},
author = {P.W. Crous and M.J. Wingfield and T.I. Burgess and G.E.St.J. Hardy and J. Gené and J. Guarro and I.G. Baseia D. García and L.F.P. Gusmão and C.M. Souza-Motta and R. Thangavel and S. Adamčík and A. Barili and C.W. Barnes and J.D.P. Bezerra and J.J. Bordallo and J.F. Cano-Lira and R.J.V. de Oliveira and E. Ercole and V. Hubka and I. Iturrieta-González and A. Kubátová and M.P. Martín and P.-A. Moreau and A. Morte and M.E. Ordoñez and A. Rodríguez and A.M. Stchigel and A. Vizzini and J. Abdollahzadeh and V.P. Abreu and K. Adamčíková and G.M.R. Albuquerque and A.V. Alexandrova and E. Álvarez_Duarte and C. Armstrong-Cho and S. Banniza and R.N. Barbosa and J.-M. Bellanger and J.L. Bezerra and T.S. Cabral and M. Caboňand E. Caicedo and T. Cantillo and A.J. Carnegie and L.T. Carmo and R.F. Castañeda-Ruiz and C.R. Clement and A. Čmoková and L.B. Conceição and R.H.S.F Cruz and U. Damm and B.D.B. da_Silva and G.A. da_Silva and R.M.F. da_Silva and A.L.C.M._de_A. Santiago and L.F. de_Oliveira and C.A.F. de_Souza and F. Déniel and B. Dima and G. Dong and J. Edwards and C.R. Félix and J. Fournier and T.B. Gibertoni and K. Hosaka and T. Iturriaga and M. Jadan and J.-L. Jany and Ž. Jurjević and M. Kolařík and I. Kušan and M.F. Landell and T.R. Leite_Cordeiro and X.D. Lima and M. Loizides and S. Luo and A.R. Machado and H. Madrid and O.M.C. Magalhães and P. Marinho and N. Matočec and A. Mešić and A.N. Miller and O.V. Morozova and R.P. Neves and K. Nonaka and A. Nováková and N.H. Oberlies and J.R.C. Oliveira-Filho and T.G.L. Oliveira and V. Papp and O.L. Pereira and G. Perrone and S.W. Peterson and T.H.G. Pham and H.A. Raja and D.B. Raudabaugh and J. Řehulka and E. RodrÃguez-Andrade and M. Saba and A. Schauflerova and R.G. Shivas and G. Simonini and J.P.Z. Siqueira and J.O. Sousa and V. Stajsic and T. Svetasheva and Y.P. Tan and Z. Tkalčec and S. Ullah and P. Valente and N. Valenzuela-Lopez and M. Abrinbana and D.A. Viana_Marques and P.T.W. Wong and V. Xavier_de_Lima and J.Z. Groenewald},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.3767/persoonia.2018.40.10},
issn = {1878-9080},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-07-13},
journal = {Persoonia},
volume = {40},
pages = {240-393},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
 | Adamčík, S; Dima, B; Adamčíková, K; Læssøe, T; Moreau, P A; Vizzini, A; Jančovičová, S European Hodophilus (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) species with yellow stipe Journal Article Mycological Progress, 17 (9), pp. 1097-1111, 2018, ISSN: ISSN: 1861-8952 . Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Adamčík2018,
title = {European Hodophilus (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) species with yellow stipe },
author = {S. Adamčík and B. Dima and K. Adamčíková and T. Læssøe and P.A. Moreau and A. Vizzini and S. Jančovičová},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-018-1418-1},
issn = {ISSN: 1861-8952 },
year = {2018},
date = {2018-06-29},
journal = {Mycological Progress},
volume = {17},
number = {9},
pages = {1097-1111},
abstract = {Phylogenetic reconstruction of Hodophilus species with a yellow colour on the stipe based on nrITS, nrLSU and rpb2 sequences revealed six European species. All these species correspond to the widely accepted European concept of a single species Hodophilus micaceus. Four of these species are described and illustrated. H. micaceus and H. phaeoxanthus are recognised as two separate species and H. albofloccipes as a synonym of the latter. Two species, H. anatinus and H. cambriensis, are described as new. Possible endemism of H. micaceus and H. cambriensis to the British Isles is discussed. All analysed North American samples represent different species to those found in Europe. The North American species Hygrophorus rugulosus is combined in the genus Hodophilus. The preliminary key uses position and development of the yellow colour during maturation as themost important distinguishing character.The presence of the yellow colour is discussed as a possible synapomorphic character.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Phylogenetic reconstruction of Hodophilus species with a yellow colour on the stipe based on nrITS, nrLSU and rpb2 sequences revealed six European species. All these species correspond to the widely accepted European concept of a single species Hodophilus micaceus. Four of these species are described and illustrated. H. micaceus and H. phaeoxanthus are recognised as two separate species and H. albofloccipes as a synonym of the latter. Two species, H. anatinus and H. cambriensis, are described as new. Possible endemism of H. micaceus and H. cambriensis to the British Isles is discussed. All analysed North American samples represent different species to those found in Europe. The North American species Hygrophorus rugulosus is combined in the genus Hodophilus. The preliminary key uses position and development of the yellow colour during maturation as themost important distinguishing character.The presence of the yellow colour is discussed as a possible synapomorphic character. |
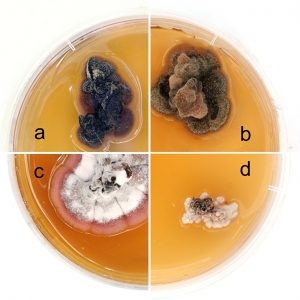 | Ondrušková, E; Jánošíková, Z; Adamčík, S; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Rákusová-Sládková, D; Adamčíková, K Needle blight caused by Dothistroma pini in Slovakia: distribution, host range and mating types Journal Article Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 33 (7), pp. 650-656, 2018, ISSN: 1651-1891. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Ondrušková2018,
title = {Needle blight caused by Dothistroma pini in Slovakia: distribution, host range and mating types},
author = {E. Ondrušková and Z. Jánošíková and S. Adamčík and M. Kádasi-Horáková and D. Rákusová-Sládková and K. Adamčíková},
doi = {10.1080/02827581.2018.1482954},
issn = {1651-1891},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-06-06},
journal = {Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research},
volume = {33},
number = {7},
pages = {650-656},
abstract = {Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) has been observed in Slovakia during the last two decades. Up until 2017, Dothistroma septosporum has only been detected and molecularly confirmed to cause DNB in
Slovakia. Here, we report the detection of Dothistroma pini at six localities around Slovakia, representing different plantation types. Four pine species (Pinus sylvestris, P. nigra, P. mugo and P. jeffreyi) were confirmed as hosts of D. pini in Slovakia, of which only P. mugo has been previously reported as host in Slovakia. Three gene regions (ITS, EF1 –α, and ß-tubulin) of each of the 13 isolates were sequenced and assigned as D. pini. Based on ITS sequences, the studied isolates represent the haplotypes Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2. Both mating types were detected but at different localities. Our results suggest that in addition to D. septosporum, D. pini may contribute to DNB also in Slovakia.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) has been observed in Slovakia during the last two decades. Up until 2017, Dothistroma septosporum has only been detected and molecularly confirmed to cause DNB in
Slovakia. Here, we report the detection of Dothistroma pini at six localities around Slovakia, representing different plantation types. Four pine species (Pinus sylvestris, P. nigra, P. mugo and P. jeffreyi) were confirmed as hosts of D. pini in Slovakia, of which only P. mugo has been previously reported as host in Slovakia. Three gene regions (ITS, EF1 –α, and ß-tubulin) of each of the 13 isolates were sequenced and assigned as D. pini. Based on ITS sequences, the studied isolates represent the haplotypes Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2. Both mating types were detected but at different localities. Our results suggest that in addition to D. septosporum, D. pini may contribute to DNB also in Slovakia. |
 | Jánošíková-Hečková, Z; Ondrušková, E; Barta, M; Ostrovský, R; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Pastirčáková, K; Kobza, M; Adamčíková, K The hosts and geographic range of Dothistroma needle blight in Slovakia Journal Article Forest Pathology, 48 (3), pp. e12421, 2018, ISSN: 1437-4781. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Jánošíková-Hečková2018,
title = {The hosts and geographic range of Dothistroma needle blight in Slovakia},
author = {Z. Jánošíková-Hečková and E. Ondrušková and M. Barta and R. Ostrovský and M. Kádasi-Horáková and K. Pastirčáková and M. Kobza and K. Adamčíková },
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/efp.12421},
doi = {10.1111/efp.12421},
issn = {1437-4781},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-02-15},
journal = {Forest Pathology},
volume = {48},
number = {3},
pages = {e12421},
abstract = {The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) were studied in 2014–2017 around Slovakia. A total of 84 localities, both native and planted, were investigated, and the presence of DNB was confirmed in 73 of them. In all positive locations, symptoms typical of DNB were observed and the Dothistroma species was confirmed using species-specific primers either from fungal cultures or directly from needles. Both Dothistroma species—D. septosporum and D. pini—were identified. Both species occurred together in 29 locations, only D. septosporum in 42 and only D. pini in two locations. The host range of D. septosporum included 10 pine species and two spruce species. The host range of D. pini comprised the same number of pine hosts but only one spruce species. Five pine hosts, P. aristata, P. coulteri, P. densiflora, P. jeffreyi, P. × schwerinii, and one spruce host P. abies are new hosts species of D. pini. P. densiflora and Picea pungens have earlier been reported to be susceptible for DNB. In this study, D. septosporum was found from both tree species.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) were studied in 2014–2017 around Slovakia. A total of 84 localities, both native and planted, were investigated, and the presence of DNB was confirmed in 73 of them. In all positive locations, symptoms typical of DNB were observed and the Dothistroma species was confirmed using species-specific primers either from fungal cultures or directly from needles. Both Dothistroma species—D. septosporum and D. pini—were identified. Both species occurred together in 29 locations, only D. septosporum in 42 and only D. pini in two locations. The host range of D. septosporum included 10 pine species and two spruce species. The host range of D. pini comprised the same number of pine hosts but only one spruce species. Five pine hosts, P. aristata, P. coulteri, P. densiflora, P. jeffreyi, P. × schwerinii, and one spruce host P. abies are new hosts species of D. pini. P. densiflora and Picea pungens have earlier been reported to be susceptible for DNB. In this study, D. septosporum was found from both tree species. |
2017
|
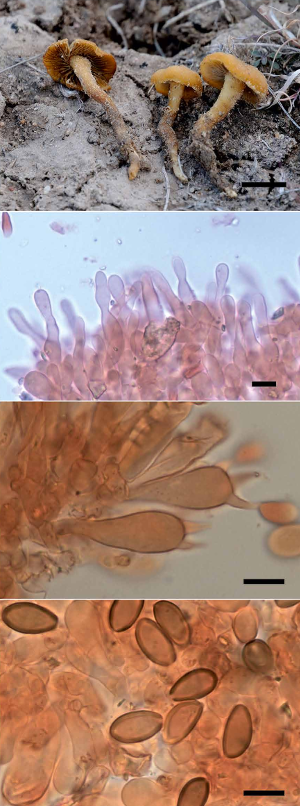
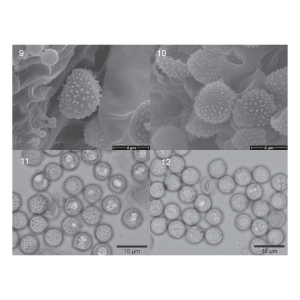 | Jančovičová, S; Adamčík, S; Looney, B P; Caboň, M; Čaplovičová, M; Kopáni, M; Pennycook, S R; Adamčíková, K Delimitation of European Crepidotus stenocystis as different from the North American species C. brunnescens (Crepidotaceae, Agariccales) Journal Article Phytotaxa, 328 (2), pp. 127-139, 2017, ISSN: 1179-3163. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Jančovičová2017,
title = {Delimitation of European Crepidotus stenocystis as different from the North American species C. brunnescens (Crepidotaceae, Agariccales)},
author = {S. Jančovičová and S. Adamčík and B.P. Looney and M. Caboň and M. Čaplovičová and M. Kopáni and S.R. Pennycook and K. Adamčíková},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.328.2.3},
issn = {1179-3163},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-11-17},
journal = {Phytotaxa},
volume = {328},
number = {2},
pages = {127-139},
abstract = {Crepidotus stenocystis and C. brunnescens are morphologically similar species defined by globose to subglobose spores,
the presence of clamp connections in all tissues and bottle-like or flask-like cheilocystidia. They are also similar in the
pileal aspect which is hygrophanous, glabrous or white-fibrillose, at first white but becoming brownish with age. Each
are described from separate continents and have only been reported from their respective continents, C. stenocystis from
Europe and C. brunnescens from North America. The phylogenetic analysis of IT S and LSU nrDNA regions from original
type material confirms the existence of two distinct species, C. brunnescens that is more closely related to C. malachioides,
and C. stenocystis that is more closely related to C. applanatus. Crepidotus stenocystis differs from C. brunnescens by its
more prominent spore ornamentation and longer cheilocystidia that are frequently narrowly utriform. Based on the studied
material and published data, it seems that C. stenocystis is distributed throughout all of Europe and does not occur in North
America, whereas C. brunnescens is only known from Michigan in the USA.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Crepidotus stenocystis and C. brunnescens are morphologically similar species defined by globose to subglobose spores,
the presence of clamp connections in all tissues and bottle-like or flask-like cheilocystidia. They are also similar in the
pileal aspect which is hygrophanous, glabrous or white-fibrillose, at first white but becoming brownish with age. Each
are described from separate continents and have only been reported from their respective continents, C. stenocystis from
Europe and C. brunnescens from North America. The phylogenetic analysis of IT S and LSU nrDNA regions from original
type material confirms the existence of two distinct species, C. brunnescens that is more closely related to C. malachioides,
and C. stenocystis that is more closely related to C. applanatus. Crepidotus stenocystis differs from C. brunnescens by its
more prominent spore ornamentation and longer cheilocystidia that are frequently narrowly utriform. Based on the studied
material and published data, it seems that C. stenocystis is distributed throughout all of Europe and does not occur in North
America, whereas C. brunnescens is only known from Michigan in the USA. |
 | Adamčík, S; Jančovičová, S; Looney, B P; Adamčíková, K; Griffith, G W; Læssøe, T; Moreau, P A; Vizzini, A; Matheny, P B Hodophilus (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) species with dark dots on the stipe: more than one species in Europe Journal Article Mycological Progress, 16 (8), pp. 811–821, 2017, ISSN: 1861-8952 . Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Adamčík2017b,
title = {Hodophilus (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) species with dark dots on the stipe: more than one species in Europe},
author = {S. Adamčík and S. Jančovičová and B.P. Looney and K. Adamčíková and G. W. Griffith and T. Læssøe and P.A. Moreau and A. Vizzini and P. B. Matheny },
doi = {DOI 10.1007/s11557-017-1318-9},
issn = {1861-8952 },
year = {2017},
date = {2017-07-01},
journal = {Mycological Progress},
volume = {16},
number = {8},
pages = {811–821},
abstract = {Hodophilus atropunctus is traditionally defined as the only species of this genus with dark brown or black dots on the stipe. Multi-locus phylogenetic reconstruction recognised two distinct clades morphologically corresponding to this species concept. The limited morphological description in the protologue of H. atropunctus and absence of a type specimen were limitations in an assignment of this name to one of the recognised phylogenetic species. The emended species concept and the selection of a neotype are based on careful analyses of the colour of the basidiomata and how this changes during maturation and drying. The name H. atropunctus is assigned to the paler of the two species which also shows colour change across the pileus and along the length of the stipe when dry. The second darker species is described here as new, H. variabilipes, but only seven out of 14 collections examined belonging to this taxon had distinct dark coloured dots on the stipe surface.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Hodophilus atropunctus is traditionally defined as the only species of this genus with dark brown or black dots on the stipe. Multi-locus phylogenetic reconstruction recognised two distinct clades morphologically corresponding to this species concept. The limited morphological description in the protologue of H. atropunctus and absence of a type specimen were limitations in an assignment of this name to one of the recognised phylogenetic species. The emended species concept and the selection of a neotype are based on careful analyses of the colour of the basidiomata and how this changes during maturation and drying. The name H. atropunctus is assigned to the paler of the two species which also shows colour change across the pileus and along the length of the stipe when dry. The second darker species is described here as new, H. variabilipes, but only seven out of 14 collections examined belonging to this taxon had distinct dark coloured dots on the stipe surface. |
 | Kádasi-Horáková, M; Adamčíková, K; Pastirčáková, K; Longauerová, V; Maľová, M Natural infection of Fraxinus angustifolia by Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Slovakia Journal Article Baltic Forestry, 23 (1), pp. 52-55, 2017, ISSN: 2029-9230. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{M.2017b,
title = {Natural infection of \textit{Fraxinus angustifolia} by \textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus} in Slovakia},
author = {M. Kádasi-Horáková and K. Adamčíková and K. Pastirčáková and V. Longauerová and M. Maľová},
url = {https://www.balticforestry.mi.lt/bf/PDF_Articles/2017-23%5B1%5D/Baltic%20Forestry%202017.1_052-055.pdf},
issn = {2029-9230},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-04-07},
journal = {Baltic Forestry},
volume = {23},
number = {1},
pages = {52-55},
abstract = {The fungus Hymenoscyphus fraxineus is responsible for dieback of common ash (Fraxinus excelsior) and in some parts of Europe also of narrow-leaved ash (F. angustifolia). The first symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded on F. excelsior in Slovakia since 2004. This study reports about the first natural occurrence of H. fraxineus on F. angustifolia in Slovakia. The field investigation was carried out in 2014. The segments of diseased shoots and last year’s petioles were collected in clonal seed orchard situated in southwest part of the country. The fungus was isolated from infected host tissue and identified using molecular techniques (DNA extraction from pure cultures and apothecia, conventional PCR).},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The fungus Hymenoscyphus fraxineus is responsible for dieback of common ash (Fraxinus excelsior) and in some parts of Europe also of narrow-leaved ash (F. angustifolia). The first symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded on F. excelsior in Slovakia since 2004. This study reports about the first natural occurrence of H. fraxineus on F. angustifolia in Slovakia. The field investigation was carried out in 2014. The segments of diseased shoots and last year’s petioles were collected in clonal seed orchard situated in southwest part of the country. The fungus was isolated from infected host tissue and identified using molecular techniques (DNA extraction from pure cultures and apothecia, conventional PCR). |
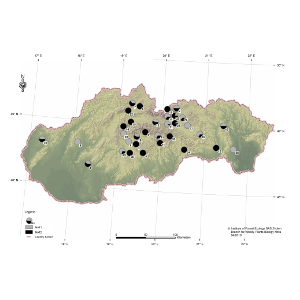 | Ondrušková, E; Hečková, Z; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Koltay, A; Ostrovský, R; Pažitný, J; Adamčíková, K Distribution and characterization of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens on Pinus mugo in Slovakia Journal Article European Journal of Plant Pathology, 148 (2), pp. 283-294, 2017, ISSN: 0929-1873. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Ondrušková2017,
title = {Distribution and characterization of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens on Pinus mugo in Slovakia},
author = {E. Ondrušková and Z. Hečková and M. Kádasi-Horáková and A. Koltay and R. Ostrovský and J. Pažitný and K. Adamčíková},
url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10658-016-1088-2},
doi = {10.1007/s10658-016-1088-2},
issn = {0929-1873},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {European Journal of Plant Pathology},
volume = {148},
number = {2},
pages = {283-294},
abstract = {The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) on Pinus mugo was studied in 2014–2015 around the Slovakia. In total, 42 localities were investigated both native and planted ones. Symptoms of DNB were observed on 35 localities only on planted shrubs. All these 35 localities are new P. mugo DNB stands. No DNB symptoms were observed in natural and naturally regenerated plantations. DNAwas extracted from a total of 236 isolates and eight needle samples. Based on the ITS-rDNA comparisons and using species specific primers, both pathogenic Dothistroma species were detected: D. septosporum and D. pini. Isolates of D. septosporum had ITS sequences identical to D. septosporum from Europe and both mating types were identified with slight predominance of MAT2. The ratio of D. septosporum mating types varies significantly between sites, ranging from an equal proportion of each mating type to single mating type populations. D. pini ITS sequence grouped with D. pini from Ukraine, Russia and Switzerland and only MAT2 was found.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) on Pinus mugo was studied in 2014–2015 around the Slovakia. In total, 42 localities were investigated both native and planted ones. Symptoms of DNB were observed on 35 localities only on planted shrubs. All these 35 localities are new P. mugo DNB stands. No DNB symptoms were observed in natural and naturally regenerated plantations. DNAwas extracted from a total of 236 isolates and eight needle samples. Based on the ITS-rDNA comparisons and using species specific primers, both pathogenic Dothistroma species were detected: D. septosporum and D. pini. Isolates of D. septosporum had ITS sequences identical to D. septosporum from Europe and both mating types were identified with slight predominance of MAT2. The ratio of D. septosporum mating types varies significantly between sites, ranging from an equal proportion of each mating type to single mating type populations. D. pini ITS sequence grouped with D. pini from Ukraine, Russia and Switzerland and only MAT2 was found. |
2016
|
 | Adamčík, S; Jančovičová, S; Looney, B P; Adamčíková, K; Birkebak, J M; Moreau, P A; Vizziny, A; Matheny, P B Circumscription of species in the Hodophilus foetens complex (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) in Europe Journal Article Mycological Progress, 16 (1), pp. 47–62, 2016, ISSN: 1617-416X. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Adamčík2017,
title = {Circumscription of species in the Hodophilus foetens complex (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) in Europe},
author = {S. Adamčík and S. Jančovičová and B.P. Looney and K. Adamčíková and J.M. Birkebak and P.A. Moreau and A. Vizziny and P.B. Matheny},
doi = {DOI 10.1007/s11557-016-1249-x},
issn = {1617-416X},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-12-12},
journal = {Mycological Progress},
volume = {16},
number = {1},
pages = {47–62},
abstract = {Four European Hodophilus species with an odour similar to naphthalene, a strong unpleasant odour similar to that of mothballs, are recognized based on sequence and/or morphological data. The traditional concept defines Ho. foetens as the only Hodophilus species with a naphthalene odour in Europe. This name is now assigned to one of the studied species based on morphological examination of the holotype specimen. A recently collected specimen is proposed as the epitype. The other three species with a naphthalene odour are described here as new: Ho. pallidus, Ho. subfoetens and Ho. tenuicystidiatus. They are distinguishable in the field based on a combination of lamellae number and colour of basidiomata. All four species are grouped in the Ho. foetens superclade, one of two superclades, together with the Ho. micaceus superclade, in the genus Hodophilus. All are different species from North American taxa with a naphthalene-like odour recognised in a previous study. The Ho. foetens superclade also includes one species identified as Ho. atropunctus that does not have a distinctive odour. The type collection of Ho. albofloccipes, a recently described European species with a naphthalene odour, is placed together with some collections without a distinctive odour in the Ho. micaceus superclade.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Four European Hodophilus species with an odour similar to naphthalene, a strong unpleasant odour similar to that of mothballs, are recognized based on sequence and/or morphological data. The traditional concept defines Ho. foetens as the only Hodophilus species with a naphthalene odour in Europe. This name is now assigned to one of the studied species based on morphological examination of the holotype specimen. A recently collected specimen is proposed as the epitype. The other three species with a naphthalene odour are described here as new: Ho. pallidus, Ho. subfoetens and Ho. tenuicystidiatus. They are distinguishable in the field based on a combination of lamellae number and colour of basidiomata. All four species are grouped in the Ho. foetens superclade, one of two superclades, together with the Ho. micaceus superclade, in the genus Hodophilus. All are different species from North American taxa with a naphthalene-like odour recognised in a previous study. The Ho. foetens superclade also includes one species identified as Ho. atropunctus that does not have a distinctive odour. The type collection of Ho. albofloccipes, a recently described European species with a naphthalene odour, is placed together with some collections without a distinctive odour in the Ho. micaceus superclade. |
 | Bulman, L S; Bradshaw, R E; Fraser, S; Martín‐García, J; Barnes, I; Musolin, D L; Porta, La N; Woods, A J; Diez, J J; Koltay, A; Drenkhan, R; Ahumada, R; Poljakovic‐Pajnik, L; Queloz, V; Piškur, B; Doğmuş‐Lehtijärvi, H T; Chira, D; Tomešová‐Haataja, V; Georgieva, M; Jankovský, L; Anselmi, N; Markovskaja, S; Papazova‐Anakieva, I; Sotirovski, K; Lazarević, J; Adamčíková, K; Boroń, P; Bragança, H; Vettraino, A M; Selikhovkin, A V; Bulgakov, T S; Tubby, K A worldwide perspective on the management and control of Dothistroma needle blight Journal Article Forest Pathology : Journal de pathologie forestiere, 46 (5), pp. 472-488, 2016, ISSN: 1437-4781. Links | BibTeX @article{Bulman2016,
title = {A worldwide perspective on the management and control of Dothistroma needle blight},
author = {L. S. Bulman and R. E. Bradshaw and S. Fraser and J. Martín‐García and I. Barnes and D. L. Musolin and N. La Porta and A. J. Woods and J. J. Diez and A. Koltay and R. Drenkhan and R. Ahumada and L. Poljakovic‐Pajnik and V. Queloz and B. Piškur and H. T. Doğmuş‐Lehtijärvi and D. Chira and V. Tomešová‐Haataja and M. Georgieva and L. Jankovský and N. Anselmi and S. Markovskaja and I. Papazova‐Anakieva and K. Sotirovski and J. Lazarević and K. Adamčíková and P. Boroń and H. Bragança and A. M. Vettraino and A. V. Selikhovkin and T. S. Bulgakov and K. Tubby },
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1111/efp.12305},
issn = {1437-4781},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-09-22},
journal = {Forest Pathology : Journal de pathologie forestiere},
volume = {46},
number = {5},
pages = {472-488},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
 | Adamčík, S; Looney, B P; Birkebak, J M; Jančovičová, S; Adamčíková, K; Marhold, K; Matheny, P B Circumscription of species of Hodophilus (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) in North America with naphthalene odours Journal Article Botany, 94 (10), pp. 941-956, 2016, ISSN: 1916-2804. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{ADAMČÍK2016,
title = {Circumscription of species of Hodophilus (Clavariaceae, Agaricales) in North America with naphthalene odours},
author = {S. Adamčík and B.P. Looney and J.M. Birkebak and S. Jančovičová and K. Adamčíková and K. Marhold and P.B. Matheny},
doi = {dx.doi.org/10.1139/cjb-2016-0091},
issn = {1916-2804},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-06-14},
journal = {Botany},
volume = {94},
number = {10},
pages = {941-956},
abstract = {Five North American Hodophilus species with naphthalene-like odours are now recognized based on
sequence and (or) morphological data and molecular annotation of type collections. Two well-supported eastern
North American species do not match any of the studied types and are described here as new: Hodophilus hesleri
and Hodophilus smithii. The previously described Hodophilus paupertinus is found to represent an autonomous
species and appears restricted to western North America. Hodophilus subfuscescens is found to be an independent
lineage in eastern North America. A morphological type study of Hodophilus peckianus shows that it is a distinct
species and not represented among recent collections. Multilocus phylogenetic analyses of European and North
American material of species with naphthalene odours reveal no species with transatlantic distributions. Overall,
Hodophilus comprises two superclades (the Hodophilus foetens superclade and the Hodophilus micaceus superclade) and
16 terminal clades that correspond to phylogenetic species. This study introduces a new approach for morphological
delimitation of agaricoid Clavariaceae combining shape and dimensions of particular elements in the pileipellis
and caulocystidia. All previously described taxa included in this study, which were previously treated in the
genera Hygrophorus, Camarophyllopsis, or Hygrotrama, are formally transferred to Hodophilus.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Five North American Hodophilus species with naphthalene-like odours are now recognized based on
sequence and (or) morphological data and molecular annotation of type collections. Two well-supported eastern
North American species do not match any of the studied types and are described here as new: Hodophilus hesleri
and Hodophilus smithii. The previously described Hodophilus paupertinus is found to represent an autonomous
species and appears restricted to western North America. Hodophilus subfuscescens is found to be an independent
lineage in eastern North America. A morphological type study of Hodophilus peckianus shows that it is a distinct
species and not represented among recent collections. Multilocus phylogenetic analyses of European and North
American material of species with naphthalene odours reveal no species with transatlantic distributions. Overall,
Hodophilus comprises two superclades (the Hodophilus foetens superclade and the Hodophilus micaceus superclade) and
16 terminal clades that correspond to phylogenetic species. This study introduces a new approach for morphological
delimitation of agaricoid Clavariaceae combining shape and dimensions of particular elements in the pileipellis
and caulocystidia. All previously described taxa included in this study, which were previously treated in the
genera Hygrophorus, Camarophyllopsis, or Hygrotrama, are formally transferred to Hodophilus. |
2015
|
 | Adamčíková, K; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Jankovský, L; Havrdová, L Identification of Hymenoscyphus fraxineus, the causal agent of ash dieback in Slovakia Journal Article Biologia, 70 (5), pp. 559–564, 2015. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{K.2015,
title = {Identification of \textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus}, the causal agent of ash dieback in Slovakia},
author = {K. Adamčíková and M. Kádasi-Horáková and L. Jankovský and L. Havrdová},
url = {http://www.degruyter.com/view/j/biolog.2015.70.issue-5/biolog-2015-0075/biolog-2015-0075.xml},
doi = {10.1515/biolog-2015-0075},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-06-23},
journal = {Biologia},
volume = {70},
number = {5},
pages = {559–564},
abstract = {Symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded in Slovakia since 2004. The field sampling was carried out in 2013, included 59 segments of shoots and 10 and more petioles per locality from four localities. The causal agent of ash dieback, the hyphomycete Chalara fraxinea T. Kowalski, was isolated from Fraxinus excelsior L. from seven localities in Slovakia. The morphology of C. fraxinea isolates and the teleomorph Hymenoscyphus fraxineus (T. Kowalski) Baral, Queloz, Hosoya are described and ITS sequences are provided.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded in Slovakia since 2004. The field sampling was carried out in 2013, included 59 segments of shoots and 10 and more petioles per locality from four localities. The causal agent of ash dieback, the hyphomycete Chalara fraxinea T. Kowalski, was isolated from Fraxinus excelsior L. from seven localities in Slovakia. The morphology of C. fraxinea isolates and the teleomorph Hymenoscyphus fraxineus (T. Kowalski) Baral, Queloz, Hosoya are described and ITS sequences are provided. |
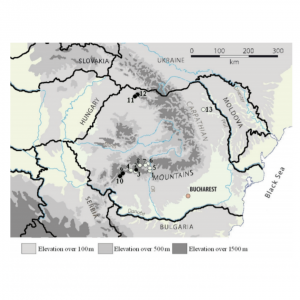 | Adamčíková, K; Ondrušková, E; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Botu, M; Kobza, M; Achim, G Distribution and population structure of the chestnut blight fungus in Romania Journal Article Plant Protection Science, 51 (3), pp. 141-149, 2015. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Adamčíková2015,
title = {Distribution and population structure of the chestnut blight fungus in Romania},
author = {K. Adamčíková and E. Ondrušková and M. Kádasi-Horáková and M. Botu and M. Kobza and G. Achim},
url = {http://www.agriculturejournals.cz/publicFiles/157004.pdf},
doi = {10.17221/52/2014-PPS},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
journal = {Plant Protection Science},
volume = {51},
number = {3},
pages = {141-149},
abstract = {The occurrence of chestnut blight (Cryphonectria parasitica) was studied in 2011-2012 at 13 locations in the main chestnut growing areas of Romania. Infections were detected at four localities. The symptoms and the fungus were detected on European chestnut (four localities) and also on oak trees (two localities). A total of 89 isolates of C. parasitica were isolated and characterised. Based on canker and isolate morphology (culture morphology and the Bavendamm test), both virulent and hypovirulent samples were isolated; hypovirulent isolates were found at only one locality. Two vegetative compatibility types corresponding to EU-12 and EU-2 were identified among isolates. Both mating types were found, with a dominance of MAT-1 in southern Romania and MAT-2 in northern Romania.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The occurrence of chestnut blight (Cryphonectria parasitica) was studied in 2011-2012 at 13 locations in the main chestnut growing areas of Romania. Infections were detected at four localities. The symptoms and the fungus were detected on European chestnut (four localities) and also on oak trees (two localities). A total of 89 isolates of C. parasitica were isolated and characterised. Based on canker and isolate morphology (culture morphology and the Bavendamm test), both virulent and hypovirulent samples were isolated; hypovirulent isolates were found at only one locality. Two vegetative compatibility types corresponding to EU-12 and EU-2 were identified among isolates. Both mating types were found, with a dominance of MAT-1 in southern Romania and MAT-2 in northern Romania. |
2014
|
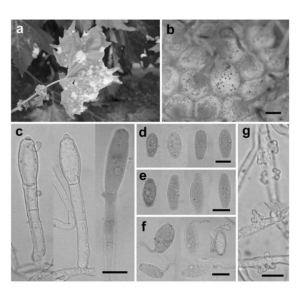 | Pastirčáková, K; Pastirčák, M; Adamčiková, K; Bouznad, Z; Kedad, A; El_Guilli, M; Diminić, D; Hofte, M Global distribution of Erysiphe platani: new records, teleomorph formation and re-examination of herbarium collections Journal Article Cryptogamie, Mycologie, 35 (2), pp. 163-176, 2014, ISSN: 0181-1584. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{K.2014,
title = {Global distribution of \textit{Erysiphe platani}: new records, teleomorph formation and re-examination of herbarium collections},
author = {K. Pastirčáková and M. Pastirčák and K. Adamčiková and Z. Bouznad and A. Kedad and M. El_Guilli and D. Diminić and M. Hofte},
url = {http://www.bioone.org/doi/abs/10.7872/crym.v35.iss2.2014.163?journalCode=crym},
doi = {10.7872/crym.v35.iss2.2014.163},
issn = {0181-1584},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-06-01},
journal = {Cryptogamie, Mycologie},
volume = {35},
number = {2},
pages = {163-176},
abstract = {A global survey of the spread of the Platanus powdery mildew, Erysiphe platani, has been carried out. E. platani teleomorph formation was recorded in countries where the fungus anamorph has been present for several years. The first findings of chasmothecia were recorded in Austria, Czech Republic, France, Italy and Slovakia. New records of E. platani (including the teleomorph) were found in Belgium, Croatia and Denmark. The occurrence of this fungus in Sweden and in two countries of North Africa (Algeria and Morocco) was confirmed. Descriptions of morphological features, illustrations, and worldwide distribution of E. platani are provided. Herbarium collections of powdery mildews on Platanus spp. were re-examined and revised. The occurrence of Phyllactinia guttata on Platanus is discussed and questioned.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
A global survey of the spread of the Platanus powdery mildew, Erysiphe platani, has been carried out. E. platani teleomorph formation was recorded in countries where the fungus anamorph has been present for several years. The first findings of chasmothecia were recorded in Austria, Czech Republic, France, Italy and Slovakia. New records of E. platani (including the teleomorph) were found in Belgium, Croatia and Denmark. The occurrence of this fungus in Sweden and in two countries of North Africa (Algeria and Morocco) was confirmed. Descriptions of morphological features, illustrations, and worldwide distribution of E. platani are provided. Herbarium collections of powdery mildews on Platanus spp. were re-examined and revised. The occurrence of Phyllactinia guttata on Platanus is discussed and questioned. |
![Príčiny hromadného hynutia gaštana jedlého [Causal agent of European chestnut blight]](https://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/IFE_adamcikova_katarina_article_08.jpg) | Juhásová, G; Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M; Ostrovský, R Príčiny hromadného hynutia gaštana jedlého [Causal agent of European chestnut blight] Journal Article Zahradnictví : časopis profesionálních zahradníků, 13 (7), pp. 48-51, 2014, ISSN: 1213-7596. BibTeX @article{Juhásová2014,
title = {Príčiny hromadného hynutia gaštana jedlého [Causal agent of European chestnut blight]},
author = {G. Juhásová and K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza and R. Ostrovský},
issn = {1213-7596},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {Zahradnictví : časopis profesionálních zahradníků},
volume = {13},
number = {7},
pages = {48-51},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
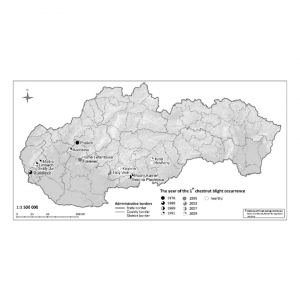 | Bolvanský, M; Ostrovský, R; Kobza, M; Adamčíková, K; Pažitný, J; Juhásová, G; Kajaba, P Spread of chestnut blight in Slovakia in relation to the site topography and climatic characteristics Inproceedings Acta Horticulturae: Proceedings of the second European congress on chestnut : Debrecen, Hungary, Baia Mare, Romania, Modry Kamen, Slovakia, October 9-12, 2013. , pp. 35-42, ISHS, 2014, ISBN: 978 94 6261 032 3. BibTeX @inproceedings{Bolvanský2014,
title = {Spread of chestnut blight in Slovakia in relation to the site topography and climatic characteristics},
author = {M. Bolvanský and R. Ostrovský and M. Kobza and K. Adamčíková and J. Pažitný and G. Juhásová and P. Kajaba},
isbn = {978 94 6261 032 3},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
booktitle = {Acta Horticulturae: Proceedings of the second European congress on chestnut : Debrecen, Hungary, Baia Mare, Romania, Modry Kamen, Slovakia, October 9-12, 2013. },
number = {1043},
pages = {35-42},
publisher = {ISHS},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
|
![Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku a v Európe : pestovanie, ochrana, variabilita a využitie [European chestnut in Slovakia : growing, protection, use and genetic variability]](http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/IFE_adamcikova_katarina_article_08.jpg) | Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M; Juhásová, G; Ondrušková, E; Bolvanský, M; Kádasi-Horáková, M Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku a v Európe : pestovanie, ochrana, variabilita a využitie [European chestnut in Slovakia : growing, protection, use and genetic variability] Book Garamond, Nitra, 2014, ISBN: 978-80-89408-18-4. BibTeX @book{Adamčíková2014,
title = {Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku a v Európe : pestovanie, ochrana, variabilita a využitie [European chestnut in Slovakia : growing, protection, use and genetic variability]},
author = {K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza and G. Juhásová and E. Ondrušková and M. Bolvanský and M. Kádasi-Horáková},
isbn = {978-80-89408-18-4},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
volume = {1},
pages = {155},
publisher = {Garamond},
address = {Nitra},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
|
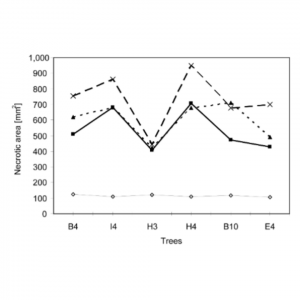 | Bolvanský, M; Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M Screening resistance to chestnut blight in young chestnut trees derived from Castanea sativa × C. crenata hybrids Journal Article Folia Oecologica, 41 (1), pp. 1-7, 2014, ISSN: 1336-5266. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Bolvanský2014c,
title = {Screening resistance to chestnut blight in young chestnut trees derived from \textit{Castanea sativa} × \textit{C. crenata} hybrids},
author = {M. Bolvanský and K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza},
url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/FO_v41_iss1_1to7.pdf},
issn = {1336-5266},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {Folia Oecologica},
volume = {41},
number = {1},
pages = {1-7},
abstract = {In 2010, 2011 and 2012 four trials were carried out to prove a reliability of the new screening method for resistance to chestnut blight caused by Cryphonectria parasitica. In the selected trees of hybrid origin (C. sativa × C. crenata)) 10 cm long cut-branch sections were inoculated with mycelia of three virulent isolates and one hypovirulent isolate (in two last trials) and cultivated for 7 days in the dark at 25 °C with 95% humidity. Then the bark of branch segments was peeled off and the size of necrotic lesions formed on the wood tissue around the inoculation place was measured. The size of necrotic areas varied by sampling date, type of fungus strains and tested trees. In all three summer trials necrotic lesions were larger than lesions in a spring trial of 2011, in which still dormant stem sections were used. Unlike the summer trials in the spring trial higher differences in the size of necrotic lesions among tested trees and among used virulent strains were observed. In the spring trial interactions between tested trees and fungal isolates were not so frequent like in summer trials where more trees exhibited different response to the same virulent strain. Majority of trees showed different susceptibility in particular trials. Observed high variation of reactions of tested trees to both virulent and hypovirulent isolates has pointed at the need to prove other screening methods, and to find such one, that would be highly effective to reveal an inherited resistance and/or a lower degree of susceptibility to chestnut blight.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
In 2010, 2011 and 2012 four trials were carried out to prove a reliability of the new screening method for resistance to chestnut blight caused by Cryphonectria parasitica. In the selected trees of hybrid origin (C. sativa × C. crenata)) 10 cm long cut-branch sections were inoculated with mycelia of three virulent isolates and one hypovirulent isolate (in two last trials) and cultivated for 7 days in the dark at 25 °C with 95% humidity. Then the bark of branch segments was peeled off and the size of necrotic lesions formed on the wood tissue around the inoculation place was measured. The size of necrotic areas varied by sampling date, type of fungus strains and tested trees. In all three summer trials necrotic lesions were larger than lesions in a spring trial of 2011, in which still dormant stem sections were used. Unlike the summer trials in the spring trial higher differences in the size of necrotic lesions among tested trees and among used virulent strains were observed. In the spring trial interactions between tested trees and fungal isolates were not so frequent like in summer trials where more trees exhibited different response to the same virulent strain. Majority of trees showed different susceptibility in particular trials. Observed high variation of reactions of tested trees to both virulent and hypovirulent isolates has pointed at the need to prove other screening methods, and to find such one, that would be highly effective to reveal an inherited resistance and/or a lower degree of susceptibility to chestnut blight. |
2013
|
![Diversity of microfungi on branches of Castanea sativa in Slovakia [Diverzita mikroskopických húb na konároch Castanea sativa na Slovensku]](http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/g4646.png) | Adamčíková, K; Juhásová, G; Kobza, M; Ondrušková, E Diversity of microfungi on branches of Castanea sativa in Slovakia [Diverzita mikroskopických húb na konároch Castanea sativa na Slovensku] Journal Article Polish Botanical Journal, 58 (2), pp. 741-746, 2013, ISSN: 1641-8180. Abstract | BibTeX @article{Adamčíková2013,
title = {Diversity of microfungi on branches of Castanea sativa in Slovakia [Diverzita mikroskopických húb na konároch Castanea sativa na Slovensku]},
author = {K. Adamčíková and G. Juhásová and M. Kobza and E. Ondrušková},
issn = {1641-8180},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
journal = {Polish Botanical Journal},
volume = {58},
number = {2},
pages = {741-746},
abstract = {Localities in Castanea sativa Mill. plantations were visited in a study aimed at identifying the mycoflora of C. sativa in Slovakia [excluding Cryphonectria parasitica (Murr.), Barr for which much data is available]. Samples from chestnut tree branches and stems were examined visually and microscopically. Seven species of microfungi were recorded, three with their anamorphs. Coryneum modonium (Sacc.) Griffon & Maubl. and Phomopsis castaneae Woron. were the most common. Libertella quercina Tul. & C. Tul. was identified in both states (anamorph and teleomorph) at two new localities. The records of Gloniopsis praelonga (Schwein.) Underw. & Earle and Dothidotthia celtidis (Ellis & Everh.) M. E. Barr are the first for Slovakia. These species were rare, found only in one locality. Two microscopic fungi were detected: Valsa ambiens (Pers.) Fr. [Cytospora leucosperma (Pers.) Fr.] and Diplodina castaneae Prill. & Delacr.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Localities in Castanea sativa Mill. plantations were visited in a study aimed at identifying the mycoflora of C. sativa in Slovakia [excluding Cryphonectria parasitica (Murr.), Barr for which much data is available]. Samples from chestnut tree branches and stems were examined visually and microscopically. Seven species of microfungi were recorded, three with their anamorphs. Coryneum modonium (Sacc.) Griffon & Maubl. and Phomopsis castaneae Woron. were the most common. Libertella quercina Tul. & C. Tul. was identified in both states (anamorph and teleomorph) at two new localities. The records of Gloniopsis praelonga (Schwein.) Underw. & Earle and Dothidotthia celtidis (Ellis & Everh.) M. E. Barr are the first for Slovakia. These species were rare, found only in one locality. Two microscopic fungi were detected: Valsa ambiens (Pers.) Fr. [Cytospora leucosperma (Pers.) Fr.] and Diplodina castaneae Prill. & Delacr. |
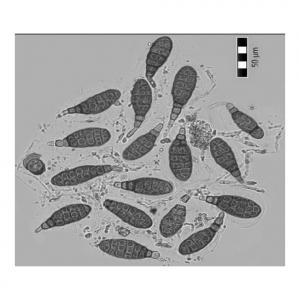 | Hečková, Z; Adamčíková, K; Strelková, M; Rózová, Z Ascomycetes and their anamorphs associated with shoots of silver birch (Betula pendula) growing in the urban greenery of Nitra in Slovak Republic Journal Article Folia Oecologica, 40 (1), pp. 137-140, 2013, ISSN: 1336-5266. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Hečková2013,
title = {Ascomycetes and their anamorphs associated with shoots of silver birch (Betula pendula) growing in the urban greenery of Nitra in Slovak Republic},
author = {Z. Hečková and K. Adamčíková and M. Strelková and Z. Rózová},
url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Hečkova.pdf},
issn = {1336-5266},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
journal = {Folia Oecologica},
volume = {40},
number = {1},
pages = {137-140},
abstract = {Microfungi of silver birch (Betula pendula) were studied in urban greenery of Nitra. Samples
were collected in November 2011 and April 2012. In this investigation were used incubations
of fresh material in moist chambers and the conventional photomicroscopy for morphological
descriptions. During the study of the mycoflora of birch shoots seven anamorph species of
Ascomycetes were recorded on the collected samples. Fungus found on shoots was Disculina
betulina. Discula betulae, Alternaria alternata and Fusarium sp. were the other fungi recorded on
leaves. Prosthemium betulinum, Myxocyclus polycystis and Phoma sp. were found on wood and
bark. Disease symptoms and some distinctive morphological features are described in this work.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Microfungi of silver birch (Betula pendula) were studied in urban greenery of Nitra. Samples
were collected in November 2011 and April 2012. In this investigation were used incubations
of fresh material in moist chambers and the conventional photomicroscopy for morphological
descriptions. During the study of the mycoflora of birch shoots seven anamorph species of
Ascomycetes were recorded on the collected samples. Fungus found on shoots was Disculina
betulina. Discula betulae, Alternaria alternata and Fusarium sp. were the other fungi recorded on
leaves. Prosthemium betulinum, Myxocyclus polycystis and Phoma sp. were found on wood and
bark. Disease symptoms and some distinctive morphological features are described in this work. |
 | Juhásová, G; Meleg, J; Juhás, D; Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M; Ondrušková, E; Kadási-Horáková, M Phytopathological evaluation of woody plants in the Arboretum Včelárska paseka in Kráľová pri Senci, Slovak Republic Journal Article Folia Oecologica, 40 (1), pp. 41-49, 2013, ISSN: 1336-5266. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Juhásová2013b,
title = {Phytopathological evaluation of woody plants in the Arboretum Včelárska paseka in Kráľová pri Senci, Slovak Republic},
author = {G. Juhásová and J. Meleg and D. Juhás and K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza and E. Ondrušková and M. Kadási-Horáková},
url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Juhasova.pdf},
issn = {1336-5266},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
journal = {Folia Oecologica},
volume = {40},
number = {1},
pages = {41-49},
abstract = {We presented the results of an evaluation of woody plants health condition in the Arboretum
Včelárska paseka in Kráľová pri Senci. The park has an area at about 7 ha with 954 woody
plant species (1120 stems) belonging into 73 genera. The damage degree of the woody plants
was classified according to a 6-point scale, from degree (0) representing healthy trees to 4 and 5
indicating the necessity of immediate sanitation. The classification was specified by appending
of numerical evaluation ranging from 1 to 94 and the proposal of a sanitary measure selected
from a 47-point list. Woody plants damaged in degrees 1 and 2 (533) were recommended as
perspective, woody plants exhibiting damage degree 3 were recommended for further cultivation
after an appropriate treatment (117). Not perspective species with damage degrees 4 and 5 were
recommended to remove (91). We have found that severe damage of woody plants were caused
by fungi of genera Phellinus, Polyporus, Laetiporus, Schizophyllum, Vuilleminia, Trametes,
Daedella, Armillaria.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
We presented the results of an evaluation of woody plants health condition in the Arboretum
Včelárska paseka in Kráľová pri Senci. The park has an area at about 7 ha with 954 woody
plant species (1120 stems) belonging into 73 genera. The damage degree of the woody plants
was classified according to a 6-point scale, from degree (0) representing healthy trees to 4 and 5
indicating the necessity of immediate sanitation. The classification was specified by appending
of numerical evaluation ranging from 1 to 94 and the proposal of a sanitary measure selected
from a 47-point list. Woody plants damaged in degrees 1 and 2 (533) were recommended as
perspective, woody plants exhibiting damage degree 3 were recommended for further cultivation
after an appropriate treatment (117). Not perspective species with damage degrees 4 and 5 were
recommended to remove (91). We have found that severe damage of woody plants were caused
by fungi of genera Phellinus, Polyporus, Laetiporus, Schizophyllum, Vuilleminia, Trametes,
Daedella, Armillaria. |
2012
|
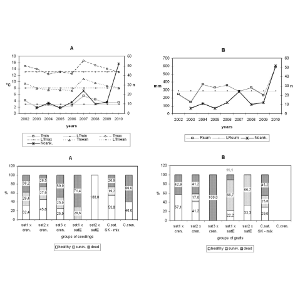 | Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M; Bolvanský, M; Ondrušková, E Spread and population structure of Cryphonectria parasitica in a young chestnut orchard in Slovakia Journal Article Central European Journal of Biology, 7 (2), pp. 267–274, 2012. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{K.2012,
title = {Spread and population structure of \textit{Cryphonectria parasitica} in a young chestnut orchard in Slovakia},
author = {K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza and M. Bolvanský and E. Ondrušková},
url = {http://link.springer.com/article/10.2478/s11535-012-0009-4},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-02-10},
journal = {Central European Journal of Biology},
volume = {7},
number = {2},
pages = {267–274},
abstract = {The chestnut blight pathogen Cryphonectria parasitica was studied in a chestnut collection composed of both seedlings and grafts derived from selected Castanea sativa and C. sativa x C. crenata trees located in south-east Slovakia, near village Príbelce on an area of approximately 3.5 ha. The study was conducted during eight years (2003-2010). During this period 133 trees were infected, which represents 59.82% of chestnut trees of all chestnut accessions. Based on the phenotype of the fungus culture and the type of cankers in the field, all isolates were determined to be virulent. No hypovirulent strains were found. No vegetative compatibility (vc) type diversity was observed. More than 130 isolates were analyzed for vc and all were in single vc type, which was identical with EU 12. All isolates assayed for mating type were MAT-1. No perithecia were observed. No significant differences were found between the proportion of cankered and dead cankered trees in seedlings and grafts of hybrid origin (C. sativa x C. crenata) and of C. sativa origin. However, particular seedlings and grafts of hybrid origin seemed to exhibit certain resistance to chestnut blight.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The chestnut blight pathogen Cryphonectria parasitica was studied in a chestnut collection composed of both seedlings and grafts derived from selected Castanea sativa and C. sativa x C. crenata trees located in south-east Slovakia, near village Príbelce on an area of approximately 3.5 ha. The study was conducted during eight years (2003-2010). During this period 133 trees were infected, which represents 59.82% of chestnut trees of all chestnut accessions. Based on the phenotype of the fungus culture and the type of cankers in the field, all isolates were determined to be virulent. No hypovirulent strains were found. No vegetative compatibility (vc) type diversity was observed. More than 130 isolates were analyzed for vc and all were in single vc type, which was identical with EU 12. All isolates assayed for mating type were MAT-1. No perithecia were observed. No significant differences were found between the proportion of cankered and dead cankered trees in seedlings and grafts of hybrid origin (C. sativa x C. crenata) and of C. sativa origin. However, particular seedlings and grafts of hybrid origin seemed to exhibit certain resistance to chestnut blight. |
 | Juhásová, G; Adamčíková, K; Bolvanský, M; Ivanová, H; Tokár, F; Hrubík, P; Konôpková, J; Kobza, M; Ondrušková, M; Kollár, J; Kunová, A Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku. Perspektívy jeho ochrany a pestovania. Book Garmond, Nitra, 2012, ISBN: 978-80-89408-14-6 1. BibTeX @book{Juhásová2012,
title = {Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku. Perspektívy jeho ochrany a pestovania.},
author = {G. Juhásová and K. Adamčíková and M. Bolvanský and H. Ivanová and F. Tokár and P. Hrubík and J. Konôpková and M. Kobza and M. Ondrušková and J. Kollár and A. Kunová},
isbn = {978-80-89408-14-6 1},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
pages = {156},
publisher = {Garmond},
address = {Nitra},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
|
2009
|
 | Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M; Juhasová, G The development of population structure of Cryphonectria parasitica on European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) in the Experimental Castanetarium Horne Lefantovce, observed over a 12-year study period Journal Article Horticultural Science , 36 (2), pp. 55-60, 2009. Abstract | Links | BibTeX @article{Adamcikova2009,
title = { The development of population structure of Cryphonectria parasitica on European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) in the Experimental Castanetarium Horne Lefantovce, observed over a 12-year study period},
author = {K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza and G. Juhasová},
url = {http://www.agriculturejournals.cz/publishedArticles/HORTSCI/2009-36-2-55.pdf},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-01-01},
journal = {Horticultural Science },
volume = {36},
number = {2},
pages = {55-60},
abstract = {We studied occurrence of chestnut blight disease in the Experimental Castanetarium Horne Lefantovce, SW Slovakia. The study ran in years 2006-2007 on a set consisting of 889 chestnut trees growing in the clonal orchard on Biological Plot 105. From this number, 857 trees were found healthy without disease symptoms. The chestnut blight disease was identified on 32 of them. The infected trees were examined for presence of pycnidia and perithecia of the causal agent. In all positive cases, the observed morphological characters indicated virulency of the obtained isolates. No hypovirulent isolate was detected on the evaluated experimental plot. In total, six vegetative compatibility (vc) types were specified in the sample consisting of 31 isolates. Our vc types corresponded to the European vc types EU 2, EU 12, EU 13, EU 14, EU 17, EU 19. Two vc types - EU 2 and EU 19 - were dominant. Vc type EU 19 accounted 35.5% and EU 2 32.2% of isolates. The vc type EU 19, which was the most frequent one in the evaluated site, was detected in Slovakia for the first time.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
We studied occurrence of chestnut blight disease in the Experimental Castanetarium Horne Lefantovce, SW Slovakia. The study ran in years 2006-2007 on a set consisting of 889 chestnut trees growing in the clonal orchard on Biological Plot 105. From this number, 857 trees were found healthy without disease symptoms. The chestnut blight disease was identified on 32 of them. The infected trees were examined for presence of pycnidia and perithecia of the causal agent. In all positive cases, the observed morphological characters indicated virulency of the obtained isolates. No hypovirulent isolate was detected on the evaluated experimental plot. In total, six vegetative compatibility (vc) types were specified in the sample consisting of 31 isolates. Our vc types corresponded to the European vc types EU 2, EU 12, EU 13, EU 14, EU 17, EU 19. Two vc types - EU 2 and EU 19 - were dominant. Vc type EU 19 accounted 35.5% and EU 2 32.2% of isolates. The vc type EU 19, which was the most frequent one in the evaluated site, was detected in Slovakia for the first time. |
















![Príčiny hromadného hynutia gaštana jedlého [Causal agent of European chestnut blight]](https://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/IFE_adamcikova_katarina_article_08.jpg)

![Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku a v Európe : pestovanie, ochrana, variabilita a využitie [European chestnut in Slovakia : growing, protection, use and genetic variability]](http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/IFE_adamcikova_katarina_article_08.jpg)

![Diversity of microfungi on branches of Castanea sativa in Slovakia [Diverzita mikroskopických húb na konároch Castanea sativa na Slovensku]](http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/g4646.png)





