Kádasi Horáková Miriam
Plant Pathology and Mycology RG
Researcher

Ing. Miriam Kádasi Horáková, PhD.
Slovak Academy of Sciences
Institute of Forest Ecology
Plant Pathology & Mycology Research Group
Akademická 2
949 01 Nitra
Phone: +421 37 6943 2419
Email: kadasi@ife.sk
Research Interests: molecular biology, population genetics, fungal diseases of woody plants, pathogen biology
Education:
- Ph.D in Institute of Plant Genetics and Biotechnology, Slovak Academy of Sciences (2009)
- Ing. (MSc.) in Applied Biology, Faculty of Agronomy of Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra (2001)
Academic employment:
- Researcher: Slovak Academy of Sciences, Institute of Forest Ecology, Branch for Woody Plants Biology (since 2011)
- Assistant lecturer: Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra, Faculty of Biotechnology and Food Sciences, Department of microbiology (2009-2011)
Projects:
- VEGA 2/0122/22 Diversity and pathogenicity of ophiostomatoid fungi in Scots pine stands infested by bark beetles (2022-2025, member of research team)
- APVV-19-0119 The potential for fungus Entomophaga maimaiga to regulate gypsy moth Lymantria dispar (L.) in Slovakia (2020-2022, member of research team).
- VEGA 2/0062/18 – Ash dieback: the causal agents and disease control strategy (2018-2021, project leader)
- VEGA 2/0077/18 – Identification, genetic variability a pathogenicity of economically important needle cast species on pines (2018-2021, member of research team)
- SK-FR-2017-0025 – Spatial analyses in population genetic studies of tree pathogens (2018-2019, member of research team)
- VEGA 2/0143/15 – Study of the effect of environmental variables on the incidence and spread of chestnut blight in European chestnut (Castanea sativa) in Slovakia and
possibilities to control on the disease (01/15-12/18) - VEGA 2/0071/14 – Species diversity and biological characteristics of parasitic fungi associated with damage and withering of woody plants (01/14-12/17)
- VEGA 2/0069/14 – Biology, spread and identification of harmful agent Dothistroma septosporum (Mycosphaerella pini), D. pini and other harmful agents of assimilatory organs of pines (01/14-12/17)
- COST FP1406 – PINESTRENGTH „Pine pitch canker“ – strategies for management of Gibberella circinata in greenhouses and forests
(05/15-05/19) - COST FP1103 Fraxinus dieback in Europe: elaborating guidelines and strategies for sustainable management (04/12-04/16)
- COST FP 1102 Determining invasiveness and risk of Dothistroma (Diarod) (07/11-12/15)
- HUSK/1101/2.2.1/0230 Our common natural resource: the European chestnut, Cross-border Co-operation Programme Hungary- Slovakia 2007-2013, European Regional Development Fund (10/12-07/14)
Internships:
- 2013, Short term research stay at The Silva Tarouca Research Institute for Landscape and Ornamental Gardening, Prague-Pruhonice, Czech Republic
List of my publications:
2025 |
|
 | Janás, M; Ailer, L; Ailer, Š; Selnekovič, A; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Barta, M Journal of microbiology, biotechnology and food sciences, 14 (5), pp. e12174, 2025. @article{Janás2025, title = {Evaluation of yield and wine qualitative parameters from grapevines expressing foliar symptoms of grapevine trunk diseases in Slovak climatic conditions}, author = {M. Janás and L. Ailer and Š. Ailer and A. Selnekovič and M. Kádasi-Horáková and M. Barta }, doi = {https://doi.org/10.55251/jmbfs.12174}, year = {2025}, date = {2025-04-01}, journal = {Journal of microbiology, biotechnology and food sciences}, volume = {14}, number = {5}, pages = {e12174}, abstract = {Grapevine trunk diseases represent a serious threat to viticulture, posing substantial challenges to the sustainability and productivity of vineyards. Fungal pathogens associated with the grapevine trunk diseases complex decompose the wood matter in grapevine trunks, leading to the disruption of vascular tissue integrity and the subsequent disruption of water and nutrient translocation within the plant. The aim of the work was to compare the yield and qualitative parameters of musts and wines from symptomatic and asymptomatic grapevines. The grape originated from the Nitra wine-growing district, from varieties Riesling Italico and Cabernet Sauvignon, aged 17 years, were used. Grapes from symptomatic and asymptomatic grapevines were processed into must and wines. The differences in yield quantity and physicochemical parameters of must and wine were analysed. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to analyse the physicochemical parameters. To test the statistical significance of the results, the Tukey’s test (p ≤ 0.05) was applied. Symptomatic grapevines of Cabernet Sauvignon exhibited significantly lower cluster weight and yield compared to asymptomatic grapevines, with a decrease of 504.71 g per bush. For Riesling Italico, no significant difference in yield was found. The must from symptomatic grapevines had significantly lower total sugar content, with Cabernet Sauvignon showing a decrease of 51.29 g/L and Riesling Italico a decrease of 23.72 g/L, along with higher acidity in Cabernet Sauvignon (+1.54 g/L). These findings confirm that grapevine trunk diseases exert a detrimental effect on both yield and must quality, with notable variability observed between grape varieties. }, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Grapevine trunk diseases represent a serious threat to viticulture, posing substantial challenges to the sustainability and productivity of vineyards. Fungal pathogens associated with the grapevine trunk diseases complex decompose the wood matter in grapevine trunks, leading to the disruption of vascular tissue integrity and the subsequent disruption of water and nutrient translocation within the plant. The aim of the work was to compare the yield and qualitative parameters of musts and wines from symptomatic and asymptomatic grapevines. The grape originated from the Nitra wine-growing district, from varieties Riesling Italico and Cabernet Sauvignon, aged 17 years, were used. Grapes from symptomatic and asymptomatic grapevines were processed into must and wines. The differences in yield quantity and physicochemical parameters of must and wine were analysed. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to analyse the physicochemical parameters. To test the statistical significance of the results, the Tukey’s test (p ≤ 0.05) was applied. Symptomatic grapevines of Cabernet Sauvignon exhibited significantly lower cluster weight and yield compared to asymptomatic grapevines, with a decrease of 504.71 g per bush. For Riesling Italico, no significant difference in yield was found. The must from symptomatic grapevines had significantly lower total sugar content, with Cabernet Sauvignon showing a decrease of 51.29 g/L and Riesling Italico a decrease of 23.72 g/L, along with higher acidity in Cabernet Sauvignon (+1.54 g/L). These findings confirm that grapevine trunk diseases exert a detrimental effect on both yield and must quality, with notable variability observed between grape varieties. |
2023 |
|
 | Adamčíková, K; Pastirčáková, K; Jánošíková, Z; Ostrovský, R; Pastirčák, M; Pažitný, J; Kobza, M; Adamčík, S; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Ondrušková, E New regional records of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens from Slovakia: distribution, hosts and pathogens characterization Journal Article Annals of Forest Research, 66 (1), pp. 99-111, 2023, ISSN: 1844-8135. @article{Adamčíková2023, title = {New regional records of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens from Slovakia: distribution, hosts and pathogens characterization}, author = {K. Adamčíková and K. Pastirčáková and Z. Jánošíková and R. Ostrovský and M. Pastirčák and J. Pažitný and M. Kobza and S. Adamčík and M. Kádasi-Horáková and E. Ondrušková}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.15287/afr.2023.2427}, issn = {1844-8135}, year = {2023}, date = {2023-07-25}, journal = {Annals of Forest Research}, volume = {66}, number = {1}, pages = {99-111}, abstract = {Dothistroma needle blight is one of the most severe needle diseases of pines caused by two closely related species, Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini. The further spread and distribution of this disease was investigated in Slovakia as well as new hosts and stand types were identified at regional level. Dothistroma septosporum was recorded in a natural stand at higher altitude on Pinus cembra in the High Tatras and the P. uncinata records are new host reports for Slovakia for this pathogen. Moreover, for D. pini, P. cembra as a new host at the country level was recorded and P. armandii was identified as new host species worldwide. Mating types for all collected samples and ITS haplotypes for D. pini isolates were determined. For D. pini, five localities with the presence of both mating types and three ITS haplotypes (Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2 and Dp_HAP.4) were reported. Samples where both mating types of the pathogens were identified, were selected for the microscopic examination of fruiting bodies aimed to detect sexual reproductive organs. In all inspected needle samples of D. pini, only conidiomata with typical hyaline cylindrical conidia were identified. The sexual state of D. septosporum was recorded in one sample of P. nigra needles.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Dothistroma needle blight is one of the most severe needle diseases of pines caused by two closely related species, Dothistroma septosporum and D. pini. The further spread and distribution of this disease was investigated in Slovakia as well as new hosts and stand types were identified at regional level. Dothistroma septosporum was recorded in a natural stand at higher altitude on Pinus cembra in the High Tatras and the P. uncinata records are new host reports for Slovakia for this pathogen. Moreover, for D. pini, P. cembra as a new host at the country level was recorded and P. armandii was identified as new host species worldwide. Mating types for all collected samples and ITS haplotypes for D. pini isolates were determined. For D. pini, five localities with the presence of both mating types and three ITS haplotypes (Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2 and Dp_HAP.4) were reported. Samples where both mating types of the pathogens were identified, were selected for the microscopic examination of fruiting bodies aimed to detect sexual reproductive organs. In all inspected needle samples of D. pini, only conidiomata with typical hyaline cylindrical conidia were identified. The sexual state of D. septosporum was recorded in one sample of P. nigra needles. |
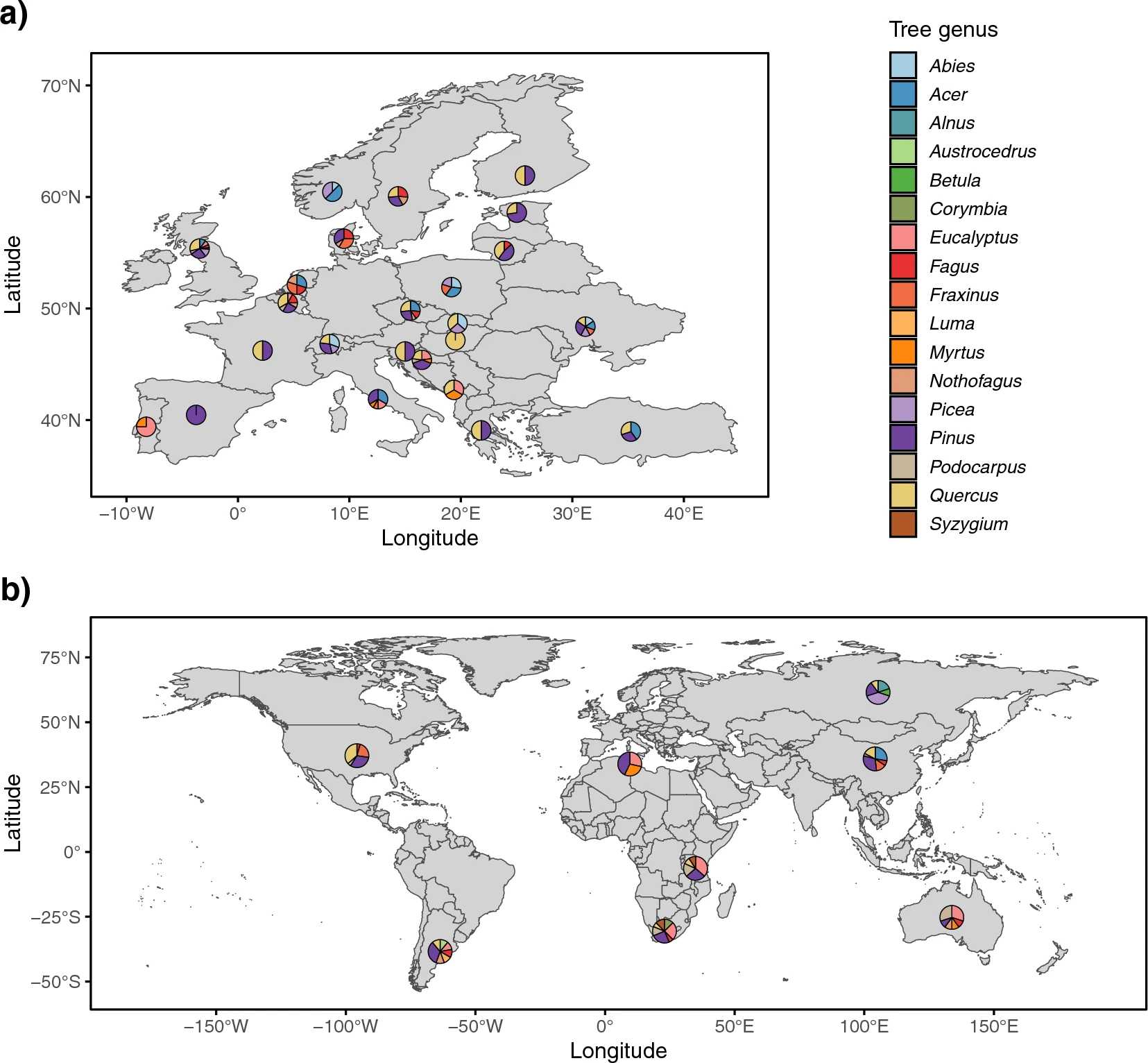 | Franić, Iva; Allan, Eric; Prospero, Simone; Adamson, Kalev; Attorre, Fabio; Auger-Rozenberg, Marie-Anne; Augustin, Sylvie; Avtzis, Dimitrios; Baert, Wim; Barta, Marek; Bauters, Kenneth; Bellahirech, Amani; Boroń, Piotr; Bragança, Helena; Brestovanská, Tereza; Brurberg, May Bente; Burgess, Treena; Burokienė, Daiva; Cleary, Michelle; Corley, Juan; Coyle, David R; Csóka, György; Černý, Karel; Davydenko, Kateryna; de Groot, Maarten; Diez, Julio Javier; Lehtijärvi, Tugba Doğmuş H; Drenkhan, Rein; Edwards, Jacqueline; Elsafy, Mohammed; Eötvös, Csaba Béla; Falko, Roman; Fan, Jianting; Feddern, Nina; Fürjes-Mikó, Ágnes; Gossner, Martin M; Grad, Bartłomiej; Hartmann, Martin; Havrdova, Ludmila; Horáková, Miriam Kádasi; Hrabětová, Markéta; Justesen, Mathias Just; Kacprzyk, Magdalena; Kenis, Marc; Kirichenko, Natalia; Kovač, Marta; Kramarets, Volodymyr; Lacković, Nikola; Lantschner, Maria Victoria; Lazarević, Jelena; Leskiv, Marianna; Li, Hongmei; Madsen, Corrie Lynne; Malumphy, Chris; Matošević, Dinka; Matsiakh, Iryna; May, Tom W; Meffert, Johan; Migliorini, Duccio; Nikolov, Christo; O’Hanlon, Richard; Oskay, Funda; Paap, Trudy; Parpan, Taras; Piškur, Barbara; Ravn, Hans Peter; Richard, John; Ronse, Anne; Roques, Alain; Ruffner, Beat; Santini, Alberto; Sivickis, Karolis; Soliani, Carolina; Talgø, Venche; Tomoshevich, Maria; Uimari, Anne; Ulyshen, Michael; Vettraino, Anna Maria; Villari, Caterina; Wang, Yongjun; Witzell, Johanna; Zlatković, Milica; Eschen, René Climate, host and geography shape insect and fungal communities of trees Journal Article Scientific Reports, 13 , pp. 11570 , 2023, ISSN: 2045-2322. @article{Franić2023, title = {Climate, host and geography shape insect and fungal communities of trees}, author = {Iva Franić and Eric Allan and Simone Prospero and Kalev Adamson and Fabio Attorre and Marie-Anne Auger-Rozenberg and Sylvie Augustin and Dimitrios Avtzis and Wim Baert and Marek Barta and Kenneth Bauters and Amani Bellahirech and Piotr Boroń and Helena Bragança and Tereza Brestovanská and May Bente Brurberg and Treena Burgess and Daiva Burokienė and Michelle Cleary and Juan Corley and David R. Coyle and György Csóka and Karel Černý and Kateryna Davydenko and Maarten de Groot and Julio Javier Diez and H. Tugba Doğmuş Lehtijärvi and Rein Drenkhan and Jacqueline Edwards and Mohammed Elsafy and Csaba Béla Eötvös and Roman Falko and Jianting Fan and Nina Feddern and Ágnes Fürjes-Mikó and Martin M. Gossner and Bartłomiej Grad and Martin Hartmann and Ludmila Havrdova and Miriam Kádasi Horáková and Markéta Hrabětová and Mathias Just Justesen and Magdalena Kacprzyk and Marc Kenis and Natalia Kirichenko and Marta Kovač and Volodymyr Kramarets and Nikola Lacković and Maria Victoria Lantschner and Jelena Lazarević and Marianna Leskiv and Hongmei Li and Corrie Lynne Madsen and Chris Malumphy and Dinka Matošević and Iryna Matsiakh and Tom W. May and Johan Meffert and Duccio Migliorini and Christo Nikolov and Richard O’Hanlon and Funda Oskay and Trudy Paap and Taras Parpan and Barbara Piškur and Hans Peter Ravn and John Richard and Anne Ronse and Alain Roques and Beat Ruffner and Alberto Santini and Karolis Sivickis and Carolina Soliani and Venche Talgø and Maria Tomoshevich and Anne Uimari and Michael Ulyshen and Anna Maria Vettraino and Caterina Villari and Yongjun Wang and Johanna Witzell and Milica Zlatković and René Eschen}, url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-36795-w}, doi = {10.1038/s41598-023-36795-w}, issn = {2045-2322}, year = {2023}, date = {2023-07-18}, journal = {Scientific Reports}, volume = {13}, pages = {11570 }, abstract = {Non-native pests, climate change, and their interactions are likely to alter relationships between trees and tree-associated organisms with consequences for forest health. To understand and predict such changes, factors structuring tree-associated communities need to be determined. Here, we analysed the data consisting of records of insects and fungi collected from dormant twigs from 155 tree species at 51 botanical gardens or arboreta in 32 countries. Generalized dissimilarity models revealed similar relative importance of studied climatic, host-related and geographic factors on differences in tree-associated communities. Mean annual temperature, phylogenetic distance between hosts and geographic distance between locations were the major drivers of dissimilarities. The increasing importance of high temperatures on differences in studied communities indicate that climate change could affect tree-associated organisms directly and indirectly through host range shifts. Insect and fungal communities were more similar between closely related vs. distant hosts suggesting that host range shifts may facilitate the emergence of new pests. Moreover, dissimilarities among tree-associated communities increased with geographic distance indicating that human-mediated transport may serve as a pathway of the introductions of new pests. The results of this study highlight the need to limit the establishment of tree pests and increase the resilience of forest ecosystems to changes in climate.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Non-native pests, climate change, and their interactions are likely to alter relationships between trees and tree-associated organisms with consequences for forest health. To understand and predict such changes, factors structuring tree-associated communities need to be determined. Here, we analysed the data consisting of records of insects and fungi collected from dormant twigs from 155 tree species at 51 botanical gardens or arboreta in 32 countries. Generalized dissimilarity models revealed similar relative importance of studied climatic, host-related and geographic factors on differences in tree-associated communities. Mean annual temperature, phylogenetic distance between hosts and geographic distance between locations were the major drivers of dissimilarities. The increasing importance of high temperatures on differences in studied communities indicate that climate change could affect tree-associated organisms directly and indirectly through host range shifts. Insect and fungal communities were more similar between closely related vs. distant hosts suggesting that host range shifts may facilitate the emergence of new pests. Moreover, dissimilarities among tree-associated communities increased with geographic distance indicating that human-mediated transport may serve as a pathway of the introductions of new pests. The results of this study highlight the need to limit the establishment of tree pests and increase the resilience of forest ecosystems to changes in climate. |
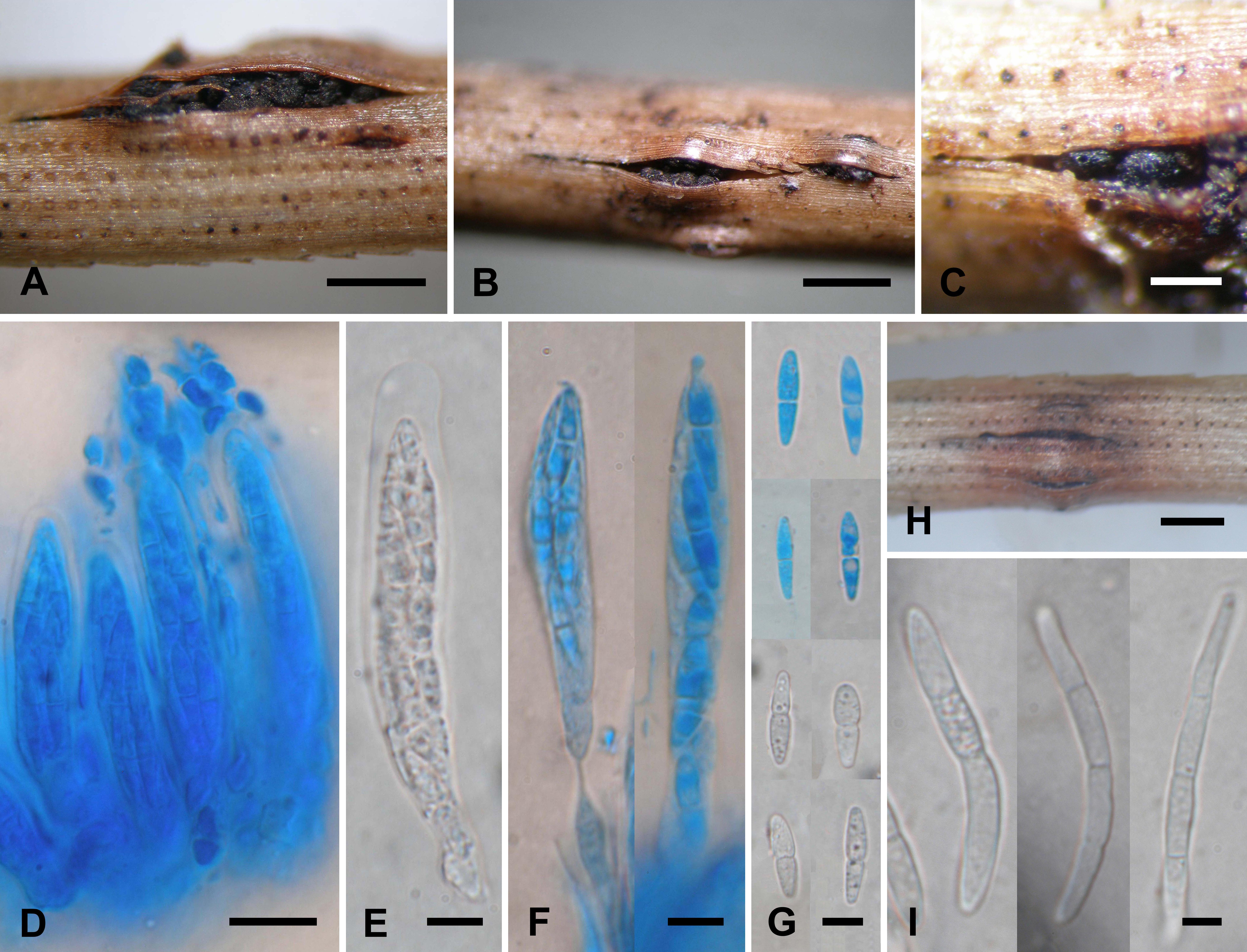
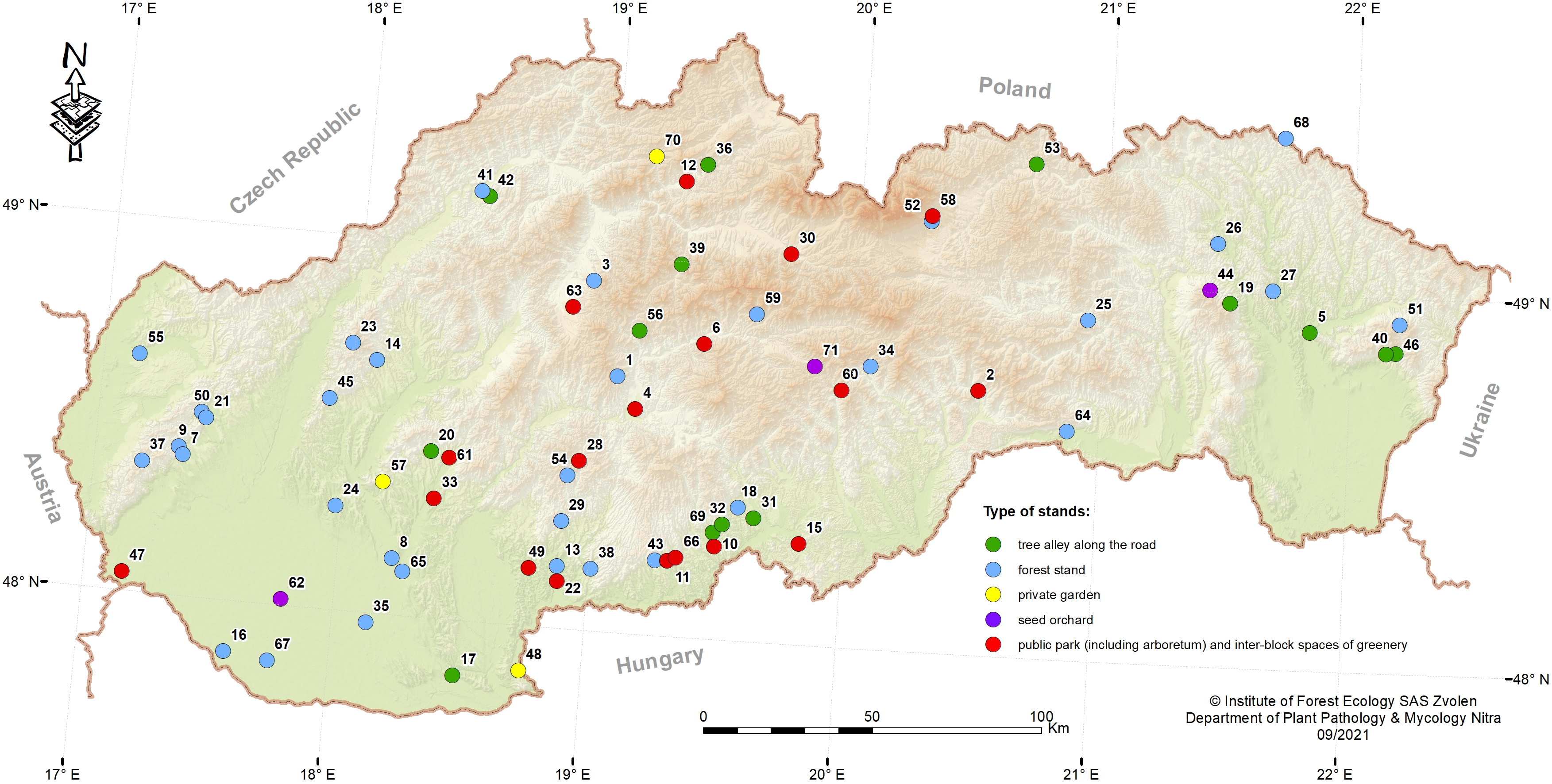 | Kádasi-Horáková, M; Barta, M; Adamčíková, K; Ostrovský, R; Pastirčáková, K Hymenoscyphus fraxineus on Fraxinus excelsior in Slovakia: distribution and mating types Journal Article Biologia, 78 (5), pp. 1219-1230, 2023, ISSN: 0006-3088. @article{Kádasi-Horáková2023, title = {\textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus} on \textit{Fraxinus excelsior} in Slovakia: distribution and mating types}, author = {M. Kádasi-Horáková and M. Barta and K. Adamčíková and R. Ostrovský and K. Pastirčáková}, doi = {10.1007/s11756-022-01023-9}, issn = {0006-3088}, year = {2023}, date = {2023-05-10}, journal = {Biologia}, volume = {78}, number = {5}, pages = {1219-1230}, abstract = {Hymenoscyphus fraxineus causes ash dieback in Europe and threatens the future existence of Fraxinus excelsior in large parts of its natural distribution range. In this study, we report the first documented distribution of the pathogen on the most common ash species F. excelsior in Slovakia, identified molecularly using species-specific primers and based on sequencing of the ITS region of rDNA. Analysis of the mating type genes of H. fraxineus isolates revealed the presence of both mating types in Slovakia. Hymenoscyphus fraxineus-positive trees were recorded in 70 localities with different types of management in different parts of the country, mainly in forest stands. The results indicate the widespread distribution of H. fraxineus across the entire country, wherever the host is present.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Hymenoscyphus fraxineus causes ash dieback in Europe and threatens the future existence of Fraxinus excelsior in large parts of its natural distribution range. In this study, we report the first documented distribution of the pathogen on the most common ash species F. excelsior in Slovakia, identified molecularly using species-specific primers and based on sequencing of the ITS region of rDNA. Analysis of the mating type genes of H. fraxineus isolates revealed the presence of both mating types in Slovakia. Hymenoscyphus fraxineus-positive trees were recorded in 70 localities with different types of management in different parts of the country, mainly in forest stands. The results indicate the widespread distribution of H. fraxineus across the entire country, wherever the host is present. |
2022 |
|
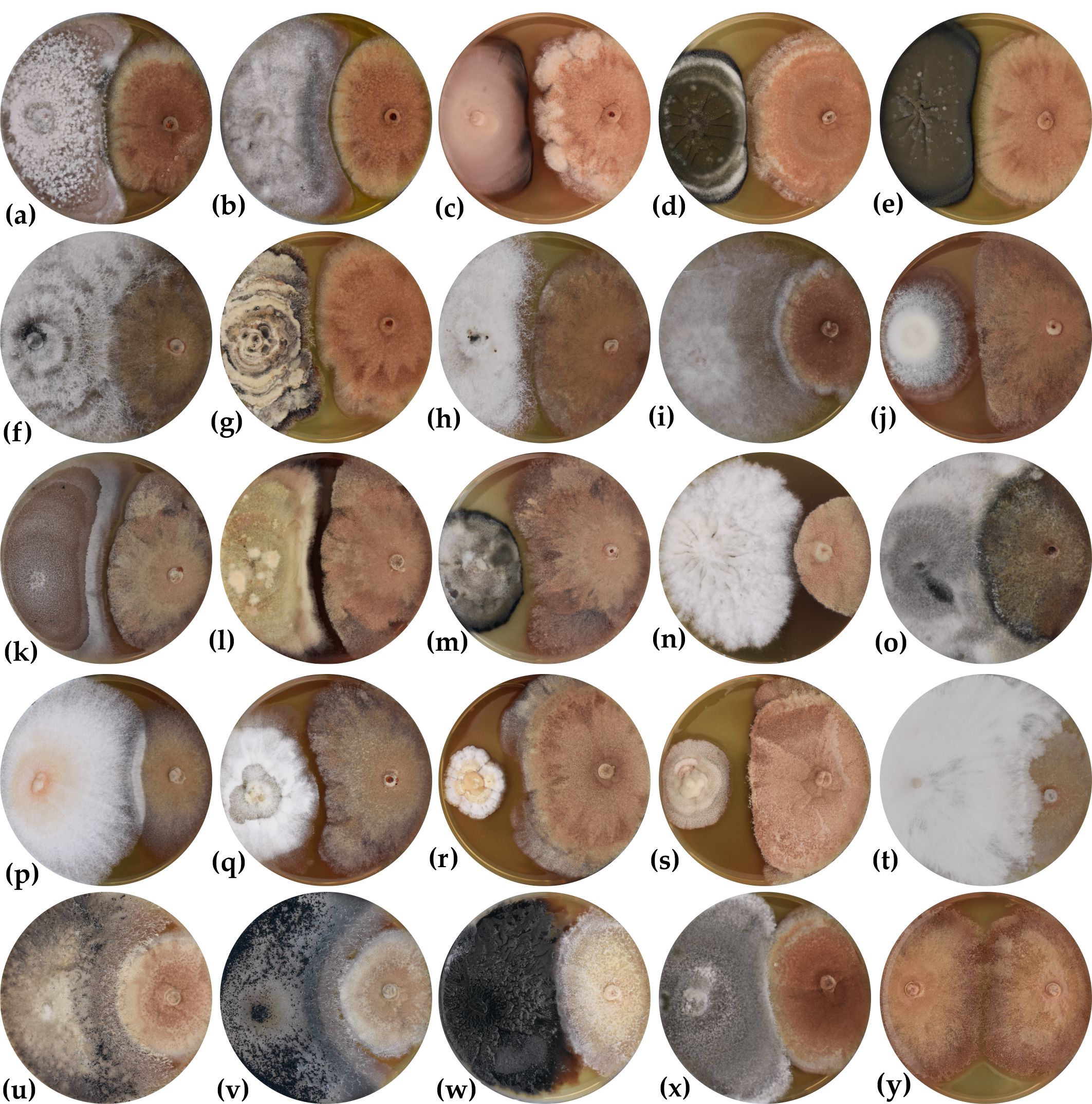 | Barta, M; Pastirčáková, K; Ostrovský, R; Kobza, M; Kádasi-Horáková, M Culturable endophytic fungi in Fraxinus excelsior and their interactions with Hymenoscyphus fraxineus Journal Article Forests, 13 (7), pp. 1-23, Article no. 1098, 2022, ISSN: 1999-4907. @article{Barta2022b, title = {Culturable endophytic fungi in \textit{Fraxinus excelsior} and their interactions with \textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus}}, author = {M. Barta and K. Pastirčáková and R. Ostrovský and M. Kobza and M. Kádasi-Horáková}, doi = {10.3390/f13071098}, issn = {1999-4907}, year = {2022}, date = {2022-07-13}, journal = {Forests}, volume = {13}, number = {7}, pages = {1-23, Article no. 1098}, abstract = {The species diversity of culturable endophytic fungi was studied in the leaves and twigs of symptomatic and asymptomatic Fraxinus excelsior trees. Endophytic mycobiota was dominated by Ascomycota species, with Pleosporales (44.17%) and Diaporthales (23.79%) endophytes being the most frequently observed in the tree samples. The number of endophytic isolates and species richness varied depending on the sampling date (May and October) and tissue location. Of the 54 species identified based on ITS sequences, 14 were classified as dominant. The most frequently isolated species were Diaporthe eres, followed by Alternaria alternata, Dothiorella gregaria, and Fraxinicola fraxini. The inhibitory effect of 41 species (75 isolates) of endophytes on the radial growth of a Hymenoscyphus fraxineus isolate was studied under in vitro conditions (dual cultures). The radial growth of H. fraxineus was the most inhibited by four endophytic fungi from twigs (Fusarium lateritium, Didymella aliena, Didymella macrostoma, and Dothiorella gregaria). The inhibitory effect of the four isolates was also studied under in planta conditions. The isolates artificially inoculated into the trunks of ash trees reduced the length of necroses formed by H. fraxineus co-inoculated in the same trunks. This effect depended on the isolate, and the inhibition was most prominent only on trunks inoculated with F. lateritium and D. aliena. Although the total length of necrotic lesions formed by the H. fraxineus infection was shorter in the ash trunks co-inoculated with the endophytes, the difference was not significant.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The species diversity of culturable endophytic fungi was studied in the leaves and twigs of symptomatic and asymptomatic Fraxinus excelsior trees. Endophytic mycobiota was dominated by Ascomycota species, with Pleosporales (44.17%) and Diaporthales (23.79%) endophytes being the most frequently observed in the tree samples. The number of endophytic isolates and species richness varied depending on the sampling date (May and October) and tissue location. Of the 54 species identified based on ITS sequences, 14 were classified as dominant. The most frequently isolated species were Diaporthe eres, followed by Alternaria alternata, Dothiorella gregaria, and Fraxinicola fraxini. The inhibitory effect of 41 species (75 isolates) of endophytes on the radial growth of a Hymenoscyphus fraxineus isolate was studied under in vitro conditions (dual cultures). The radial growth of H. fraxineus was the most inhibited by four endophytic fungi from twigs (Fusarium lateritium, Didymella aliena, Didymella macrostoma, and Dothiorella gregaria). The inhibitory effect of the four isolates was also studied under in planta conditions. The isolates artificially inoculated into the trunks of ash trees reduced the length of necroses formed by H. fraxineus co-inoculated in the same trunks. This effect depended on the isolate, and the inhibition was most prominent only on trunks inoculated with F. lateritium and D. aliena. Although the total length of necrotic lesions formed by the H. fraxineus infection was shorter in the ash trunks co-inoculated with the endophytes, the difference was not significant. |
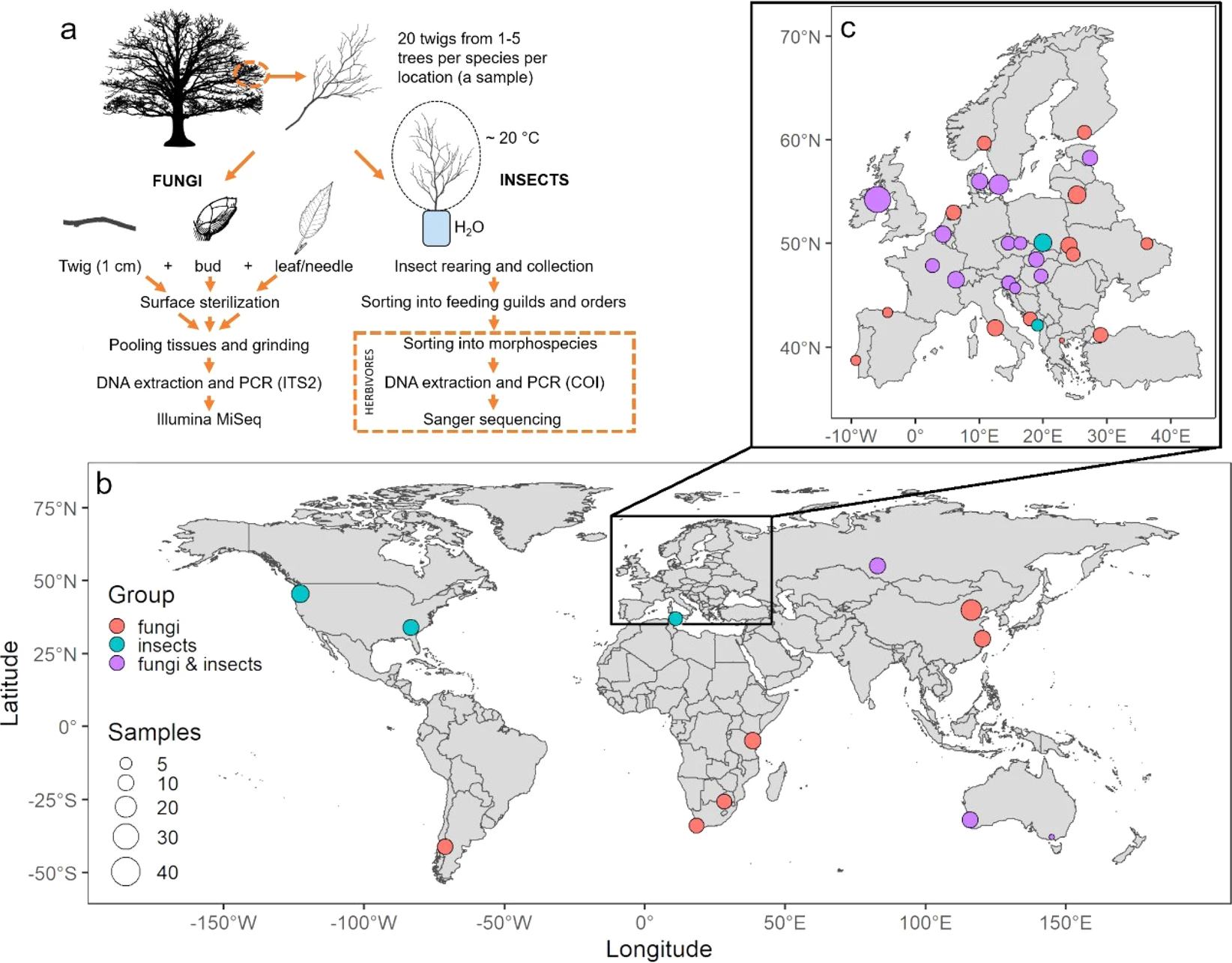 | Franić, Iva; Prospero, Simone; Adamson, Kalev; Allan, Eric; Attorre, Fabio; Auger-Rozenberg, Marie Anne; Augustin, Sylvie; Avtzis, Dimitrios; Baert, Wim; Barta, Marek; Bauters, Kenneth; Bellahirech, Amani; Boroń, Piotr; Bragança, Helena; Brestovanská, Tereza; Brurberg, May Bente; Burgess, Treena; Burokienė, Daiva; Cleary, Michelle; Corley, Juan; Coyle, David R; Csóka, György; Černý, Karel; Davydenko, Kateryna; de Groot, Maarten; Diez, Julio Javier; Lehtijärvi, Tuğba Doğmuş H; Drenkhan, Rein; Edwards, Jacqueline; Elsafy, Mohammed; Eötvös, Csaba Béla; Falko, Roman; Fan, Jianting; Feddern, Nina; Fürjes-Mikó, Ágnes; Gossner, Martin M; Grad, Bartłomiej; Hartmann, Martin; Havrdova, Ludmila; Horáková, Miriam Kádasi; Hrabětová, Markéta; Justesen, Mathias Just; Kacprzyk, Magdalena; Kenis, Marc; Kirichenko, Natalia; Kovač, Marta; Kramarets, Volodymyr; Lacković, Nikola; Lantschner, Maria Victoria; Lazarević, Jelena; Leskiv, Marianna; Li, Hongmei; Madsen, Corrie Lynne; Malumphy, Chris; Matošević, Dinka; Matsiakh, Iryna; May, Tom W; Meffert, Johan; Migliorini, Duccio; Nikolov, Christo; O’Hanlon, Richard; Oskay, Funda; Paap, Trudy; Parpan, Taras; Piškur, Barbara; Ravn, Hans Peter; Richard, John; Ronse, Anne; Roques, Alain; Ruffner, Beat; Sivickis, Karolis; Soliani, Carolina; Talgø, Venche; Tomoshevich, Maria; Uimari, Anne; Ulyshen, Michael; Vettraino, Anna Maria; Villari, Caterina; Wang, Yongjun; Witzell, Johanna; Zlatković, Milica; Eschen, René Worldwide diversity of endophytic fungi and insects associated with dormant tree twigs Journal Article Scientific Data, 9 (62 (2022)), pp. 1-9, 2022, ISSN: 2052-4463. @article{Franić2022, title = {Worldwide diversity of endophytic fungi and insects associated with dormant tree twigs}, author = {Iva Franić and Simone Prospero and Kalev Adamson and Eric Allan and Fabio Attorre and Marie Anne Auger-Rozenberg and Sylvie Augustin and Dimitrios Avtzis and Wim Baert and Marek Barta and Kenneth Bauters and Amani Bellahirech and Piotr Boroń and Helena Bragança and Tereza Brestovanská and May Bente Brurberg and Treena Burgess and Daiva Burokienė and Michelle Cleary and Juan Corley and David R. Coyle and György Csóka and Karel Černý and Kateryna Davydenko and Maarten de Groot and Julio Javier Diez and H. Tuğba Doğmuş Lehtijärvi and Rein Drenkhan and Jacqueline Edwards and Mohammed Elsafy and Csaba Béla Eötvös and Roman Falko and Jianting Fan and Nina Feddern and Ágnes Fürjes-Mikó and Martin M. Gossner and Bartłomiej Grad and Martin Hartmann and Ludmila Havrdova and Miriam Kádasi Horáková and Markéta Hrabětová and Mathias Just Justesen and Magdalena Kacprzyk and Marc Kenis and Natalia Kirichenko and Marta Kovač and Volodymyr Kramarets and Nikola Lacković and Maria Victoria Lantschner and Jelena Lazarević and Marianna Leskiv and Hongmei Li and Corrie Lynne Madsen and Chris Malumphy and Dinka Matošević and Iryna Matsiakh and Tom W. May and Johan Meffert and Duccio Migliorini and Christo Nikolov and Richard O’Hanlon and Funda Oskay and Trudy Paap and Taras Parpan and Barbara Piškur and Hans Peter Ravn and John Richard and Anne Ronse and Alain Roques and Beat Ruffner and Karolis Sivickis and Carolina Soliani and Venche Talgø and Maria Tomoshevich and Anne Uimari and Michael Ulyshen and Anna Maria Vettraino and Caterina Villari and Yongjun Wang and Johanna Witzell and Milica Zlatković and René Eschen}, doi = {10.1038/s41597-022-01162-3}, issn = {2052-4463}, year = {2022}, date = {2022-03-01}, journal = {Scientific Data}, volume = {9}, number = {62 (2022)}, pages = {1-9}, abstract = {International trade in plants and climate change are two of the main factors causing damaging tree pests (i.e. fungi and insects) to spread into new areas. To mitigate these risks, a large-scale assessment of tree-associated fungi and insects is needed. We present records of endophytic fungi and insects in twigs of 17 angiosperm and gymnosperm genera, from 51 locations in 32 countries worldwide. Endophytic fungi were characterized by high-throughput sequencing of 352 samples from 145 tree species in 28 countries. Insects were reared from 227 samples of 109 tree species in 18 countries and sorted into taxonomic orders and feeding guilds. Herbivorous insects were grouped into morphospecies and were identified using molecular and morphological approaches. This dataset reveals the diversity of tree-associated taxa, as it contains 12,721 fungal Amplicon Sequence Variants and 208 herbivorous insect morphospecies, sampled across broad geographic and climatic gradients and for many tree species. This dataset will facilitate applied and fundamental studies on the distribution of fungal endophytes and insects in trees.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } International trade in plants and climate change are two of the main factors causing damaging tree pests (i.e. fungi and insects) to spread into new areas. To mitigate these risks, a large-scale assessment of tree-associated fungi and insects is needed. We present records of endophytic fungi and insects in twigs of 17 angiosperm and gymnosperm genera, from 51 locations in 32 countries worldwide. Endophytic fungi were characterized by high-throughput sequencing of 352 samples from 145 tree species in 28 countries. Insects were reared from 227 samples of 109 tree species in 18 countries and sorted into taxonomic orders and feeding guilds. Herbivorous insects were grouped into morphospecies and were identified using molecular and morphological approaches. This dataset reveals the diversity of tree-associated taxa, as it contains 12,721 fungal Amplicon Sequence Variants and 208 herbivorous insect morphospecies, sampled across broad geographic and climatic gradients and for many tree species. This dataset will facilitate applied and fundamental studies on the distribution of fungal endophytes and insects in trees. |
2021 |
|
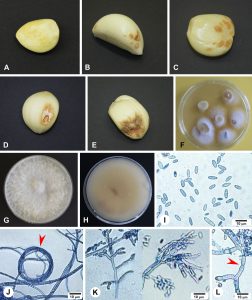 | Horáková, Miriam Kádasi; Tancik, Jan; Barta, Marek Fusarium proliferatum causing dry rot of stored garlic in Slovakia Journal Article Journal of Plant Pathology, 2021, ISSN: 2239-7264. @article{Horáková2021, title = {Fusarium proliferatum causing dry rot of stored garlic in Slovakia}, author = {Miriam Kádasi Horáková and Jan Tancik and Marek Barta}, doi = {10.1007/s42161-021-00883-5}, issn = {2239-7264}, year = {2021}, date = {2021-06-10}, journal = {Journal of Plant Pathology}, abstract = {Symptoms of dry clove rot of Allium sativum produced in Slovakia were noticed during storage in 2019. In 2020, garlic bulbs of eight cultivars were analysed and fungal isolates were obtained. Morphological and molecular identification confirmed the isolation of Fusarium proliferatum from all cultivars. The mean proportion of symptomatic cloves in evaluated samples reached 78.68%, and the mean area of clove surface damaged by the disease ranged from 5.97% to 14.83% 5 weeks after the harvest. The pathogenicity of the selected F. proliferatum isolate was verified by inoculation of garlic cloves in laboratory bioassays. This is the first report of F. proliferatum causing dry rot of garlic bulbs in Slovakia.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Symptoms of dry clove rot of Allium sativum produced in Slovakia were noticed during storage in 2019. In 2020, garlic bulbs of eight cultivars were analysed and fungal isolates were obtained. Morphological and molecular identification confirmed the isolation of Fusarium proliferatum from all cultivars. The mean proportion of symptomatic cloves in evaluated samples reached 78.68%, and the mean area of clove surface damaged by the disease ranged from 5.97% to 14.83% 5 weeks after the harvest. The pathogenicity of the selected F. proliferatum isolate was verified by inoculation of garlic cloves in laboratory bioassays. This is the first report of F. proliferatum causing dry rot of garlic bulbs in Slovakia. |
2020 |
|
 | Barta, Marek; Takov, Danail; Pilarska, Daniela; Doychev, Danail; Horáková, Miriam Kádasi Journal of Forest Science, 66 (10), pp. 420-435, 2020, ISSN: 1212-4834. @article{Barta2020b, title = {Entomopathogenic fungi of the genus Beauveria and their pathogenicity to Ips typographus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in the Vitosha National Park, Bulgaria}, author = {Marek Barta and Danail Takov and Daniela Pilarska and Danail Doychev and Miriam Kádasi Horáková}, url = {https://www.agriculturejournals.cz/web/jfs.htm?type=article&id=123_2020-JFS}, doi = {10.17221/123/2020-JFS}, issn = {1212-4834}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-10-01}, journal = {Journal of Forest Science}, volume = {66}, number = {10}, pages = {420-435}, abstract = {Ips typographus is a serious pest for forestry in Eurasia. Effective control is difficult due to its cryptic habits and insect pathogenic microorganisms, including entomopathogenic fungi that are believed to be a promising alternative to the traditional control measures of this pest. In 2018, diversity of entomopathogenic fungi of the genus Beauveria was studied in populations of I. typographus in the Vitosha National Park, Bulgaria. Two species, B. bassiana and B. caledonica, were identified and 33 in vitro strains were obtained. Phylogenetic positions of the strains were evaluated according to phylogenetic inferences based on ITS and TEF-1α. Pathogenicity of the strains against bark beetles was tested in laboratory. All strains were pathogenic, although there was some variability in the efficacy of B. bassiana strains. Virulence of the five most pathogenic strains (four B. bassiana strains and one B. caledonica strain) was compared with the commercial mycoinsecticide Boverol® and highly-virulent B. bassiana strain ARSEF 12957 isolated from I. typographus in Slovakia. The strain from Boverol® was least virulent and the Slovak strain ARSEF 12957 was more efficient than the Bulgarian strains, but the difference was not significant. The laboratory experiments suggest that the Bulgarian strains have a potential for the control of bark beetle adults.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Ips typographus is a serious pest for forestry in Eurasia. Effective control is difficult due to its cryptic habits and insect pathogenic microorganisms, including entomopathogenic fungi that are believed to be a promising alternative to the traditional control measures of this pest. In 2018, diversity of entomopathogenic fungi of the genus Beauveria was studied in populations of I. typographus in the Vitosha National Park, Bulgaria. Two species, B. bassiana and B. caledonica, were identified and 33 in vitro strains were obtained. Phylogenetic positions of the strains were evaluated according to phylogenetic inferences based on ITS and TEF-1α. Pathogenicity of the strains against bark beetles was tested in laboratory. All strains were pathogenic, although there was some variability in the efficacy of B. bassiana strains. Virulence of the five most pathogenic strains (four B. bassiana strains and one B. caledonica strain) was compared with the commercial mycoinsecticide Boverol® and highly-virulent B. bassiana strain ARSEF 12957 isolated from I. typographus in Slovakia. The strain from Boverol® was least virulent and the Slovak strain ARSEF 12957 was more efficient than the Bulgarian strains, but the difference was not significant. The laboratory experiments suggest that the Bulgarian strains have a potential for the control of bark beetle adults. |
 | Barta, Marek; Horáková, Miriam Kádasi; Georgieva, Margarita; Mirchev, Plamen; Zaemdzhikova, Gergana; Pilarska, Daniela; Takov, Danail; Todorov, Milcho; Hubenov, Zdravko; Pilarski, Plamen; Georgiev, Georgi Acta Zoologica Bulgarica, Supplementum 15 , pp. 89-96, 2020, ISSN: 0324-0770. @article{Barta2020, title = {Entomopathogenic Fungi (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) as Natural Antagonists of the Pine Processionary Moth Thaumetopoea pityocampa (Denis & Schiffermüller, 1775) (Lepidoptera: Notodontidae) in Bulgaria}, author = {Marek Barta and Miriam Kádasi Horáková and Margarita Georgieva and Plamen Mirchev and Gergana Zaemdzhikova and Daniela Pilarska and Danail Takov and Milcho Todorov and Zdravko Hubenov and Plamen Pilarski and Georgi Georgiev}, url = {http://www.acta-zoologica-bulgarica.eu/Suppl_15_19.pdf}, issn = {0324-0770}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-08-01}, journal = {Acta Zoologica Bulgarica}, volume = {Supplementum 15}, pages = {89-96}, abstract = {Thaumetopoea pityocampa, a moth naturally distributed in pine ecosystems of Mediterranean region, is considered the most dangerous defoliator in Bulgarian pine forests. Caterpillars of this species also represent a health hazard because their hairs, which contain an urticating protein – thaumetopoein, are responsible for painful skin irritations, rashes and allergic reactions in some people. Therefore, T. pityocampa is not only a serious forest pest, but also a public health problem. Populations of the moth are regulated by a complex of natural enemies. There is only limited information about a parasitic activity of entomopathogenic fungi. These fungi are natural antagonists of insects helping to control of host population and prevention of outbreaks formation. A goal of the present study was to identify species of entomopathogenic fungi in natural populations of T. pityocampa in Bulgaria. During the study, 908 larvae and pupae were collected from two sites (Fotinovo and Kandilka villages) in the south-eastern Rhodopes. In laboratory conditions, 147 larvae or pupae showing characteristic symptoms of mycoses were observed and on 27 of them in vitro isolates were obtained. The cultures were microscopically identified and subsequently analysed by a sequencing study of the internal transcribed region of rDNA and a partial sequence of TEF1-α gene. Altogether, two Beauveria species (B. pseudobassiana – 7 isolates and B. varroae – 6 isolates) and Purpureocillium lilacinum (14 isolates) were identified. The three entomopathogens are reported from T. pityocampa for the first time.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Thaumetopoea pityocampa, a moth naturally distributed in pine ecosystems of Mediterranean region, is considered the most dangerous defoliator in Bulgarian pine forests. Caterpillars of this species also represent a health hazard because their hairs, which contain an urticating protein – thaumetopoein, are responsible for painful skin irritations, rashes and allergic reactions in some people. Therefore, T. pityocampa is not only a serious forest pest, but also a public health problem. Populations of the moth are regulated by a complex of natural enemies. There is only limited information about a parasitic activity of entomopathogenic fungi. These fungi are natural antagonists of insects helping to control of host population and prevention of outbreaks formation. A goal of the present study was to identify species of entomopathogenic fungi in natural populations of T. pityocampa in Bulgaria. During the study, 908 larvae and pupae were collected from two sites (Fotinovo and Kandilka villages) in the south-eastern Rhodopes. In laboratory conditions, 147 larvae or pupae showing characteristic symptoms of mycoses were observed and on 27 of them in vitro isolates were obtained. The cultures were microscopically identified and subsequently analysed by a sequencing study of the internal transcribed region of rDNA and a partial sequence of TEF1-α gene. Altogether, two Beauveria species (B. pseudobassiana – 7 isolates and B. varroae – 6 isolates) and Purpureocillium lilacinum (14 isolates) were identified. The three entomopathogens are reported from T. pityocampa for the first time. |
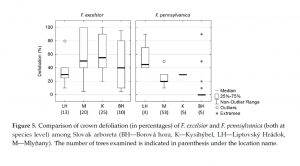 | Pastirčáková, K; Adamčíková, K; Barta, M; Pažitný, J; Hoťka, P; Sarvašová, I; Kádasi-Horáková, M Host range of Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Slovak arboreta Journal Article Forests, 11 (5), pp. 1-18, Article Number: 596, 2020, ISSN: 1999-4907. @article{Pastirčáková25.0, title = {Host range of \textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus} in Slovak arboreta}, author = {K. Pastirčáková and K. Adamčíková and M. Barta and J. Pažitný and P. Hoťka and I. Sarvašová and M. Kádasi-Horáková}, doi = {10.3390/f11050596}, issn = {1999-4907}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-05-25}, journal = {Forests}, volume = {11}, number = {5}, pages = {1-18, Article Number: 596}, abstract = {The health of 34 different Fraxinus taxa in association with the pathogenic fungus Hymenoscyphus fraxineus was assessed in four Slovak arboreta. Averaged across all arboreta, nearly one-quarter (24.9%) of all evaluated trees showed ash dieback symptoms. The damage was most serious on the common ash F. excelsior, a native species. The percentage of dead trees did not exceed 2% for all evaluated trees. Generally, ash trees of all ages were affected, though the intensity of the damage varied among the sites. The identity of H. fraxineus was confirmed by conventional PCR targeting the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences of the nuclear ribosomal DNA, as well as the 18S gene/ITS-2 region of the rDNA operon. In Slovakia, the pathogen has expanded its host range from native species not only to their ornamental cultivars, but also to introduced North American (F. cinerea, F. latifolia, F. pennsylvanica, F. quadrangulata) and Asian (F. bungeana, F. chinensis ssp. rhynchophylla, F. mandshurica) ash species. H. fraxineus was also observed on the previous year’s leaf petioles of the native European species F. ornus, considered a weakly susceptible host. In Slovak arboreta, H. fraxineus was found on 23 Fraxinus taxa; 21 of them represent first records for the country. F. bungeana is recorded as a new host species of H. fraxineus.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The health of 34 different Fraxinus taxa in association with the pathogenic fungus Hymenoscyphus fraxineus was assessed in four Slovak arboreta. Averaged across all arboreta, nearly one-quarter (24.9%) of all evaluated trees showed ash dieback symptoms. The damage was most serious on the common ash F. excelsior, a native species. The percentage of dead trees did not exceed 2% for all evaluated trees. Generally, ash trees of all ages were affected, though the intensity of the damage varied among the sites. The identity of H. fraxineus was confirmed by conventional PCR targeting the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences of the nuclear ribosomal DNA, as well as the 18S gene/ITS-2 region of the rDNA operon. In Slovakia, the pathogen has expanded its host range from native species not only to their ornamental cultivars, but also to introduced North American (F. cinerea, F. latifolia, F. pennsylvanica, F. quadrangulata) and Asian (F. bungeana, F. chinensis ssp. rhynchophylla, F. mandshurica) ash species. H. fraxineus was also observed on the previous year’s leaf petioles of the native European species F. ornus, considered a weakly susceptible host. In Slovak arboreta, H. fraxineus was found on 23 Fraxinus taxa; 21 of them represent first records for the country. F. bungeana is recorded as a new host species of H. fraxineus. |
2019 |
|
 | Barta, Marek; Lalík, Michal; Rell, Slavomír; Kunca, Andrej; Horáková, Miriam Kádasi; Mudrončeková, Silvia; Galko, Juraj Forests, 10 (634), pp. 1-18, 2019, ISSN: 1999-4907. @article{Barta2019, title = {Hypocrealean fungi associated with Hylobius abietis in Slovakia, their virulence against weevil adults and effect on feeding damage in laboratory}, author = {Marek Barta and Michal Lalík and Slavomír Rell and Andrej Kunca and Miriam Kádasi Horáková and Silvia Mudrončeková and Juraj Galko}, doi = {10.3390/f10080634}, issn = {1999-4907}, year = {2019}, date = {2019-07-29}, journal = {Forests}, volume = {10}, number = {634}, pages = {1-18}, abstract = {In temperate regions of Europe, the large pine weevil, Hylobius abietis, is a major pest of coniferous forests mostly at sites where clear-felling is followed by planting of saplings. Control measures against this pest are based on silvicultural techniques, an application of physical barriers on stems of saplings and insecticide treatments. To avoid the use of insecticides, alternative measures such as biological control have been investigated. The goal of the present study was to obtain local strains of entomopathogenic fungi (Ascomycota, Hypocreales) from natural populations of H. abietis, and to investigate their efficacy against the weevil. A survey on entomopathogenic fungi was undertaken at clear-felled areas of spruce forests in northern Slovakia. Two Beauveria species, B. bassiana and B. pseudobassiana, were identified, and 22 in vitro strains were obtained. Mean prevalence of infected adults was low (2.10%) and the mycosis was mostly recorded during May and June. Virulence of Beauveria strains against the weevil was tested in laboratory. B. bassiana strain AMEP20 was significantly most virulent (LC50 of 0.65 x 108 conidia/ml). Treatment with conidia of AMEP20 strain affected feeding damage by the weevil on bark of Scots pine twigs. Daily bark consumption by B. bassiana-treated weevils was lower than by untreated individuals and decreased with increasing conidia concentration used for the treatment. In the outdoor experiment, AMEP20 strain killed weevils that fed on spruce saplings treated with conidia suspensions. Mortality due to mycosis on weevils exposed to the conidia-treated saplings reached 30.0%–76.5% and 55.0%–88.2% after 32 and 46 days, respectively.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } In temperate regions of Europe, the large pine weevil, Hylobius abietis, is a major pest of coniferous forests mostly at sites where clear-felling is followed by planting of saplings. Control measures against this pest are based on silvicultural techniques, an application of physical barriers on stems of saplings and insecticide treatments. To avoid the use of insecticides, alternative measures such as biological control have been investigated. The goal of the present study was to obtain local strains of entomopathogenic fungi (Ascomycota, Hypocreales) from natural populations of H. abietis, and to investigate their efficacy against the weevil. A survey on entomopathogenic fungi was undertaken at clear-felled areas of spruce forests in northern Slovakia. Two Beauveria species, B. bassiana and B. pseudobassiana, were identified, and 22 in vitro strains were obtained. Mean prevalence of infected adults was low (2.10%) and the mycosis was mostly recorded during May and June. Virulence of Beauveria strains against the weevil was tested in laboratory. B. bassiana strain AMEP20 was significantly most virulent (LC50 of 0.65 x 108 conidia/ml). Treatment with conidia of AMEP20 strain affected feeding damage by the weevil on bark of Scots pine twigs. Daily bark consumption by B. bassiana-treated weevils was lower than by untreated individuals and decreased with increasing conidia concentration used for the treatment. In the outdoor experiment, AMEP20 strain killed weevils that fed on spruce saplings treated with conidia suspensions. Mortality due to mycosis on weevils exposed to the conidia-treated saplings reached 30.0%–76.5% and 55.0%–88.2% after 32 and 46 days, respectively. |
2018 |
|
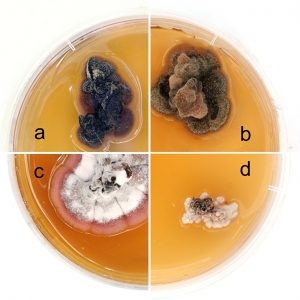 | Ondrušková, E; Jánošíková, Z; Adamčík, S; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Rákusová-Sládková, D; Adamčíková, K Needle blight caused by Dothistroma pini in Slovakia: distribution, host range and mating types Journal Article Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 33 (7), pp. 650-656, 2018, ISSN: 1651-1891. @article{Ondrušková2018, title = {Needle blight caused by Dothistroma pini in Slovakia: distribution, host range and mating types}, author = {E. Ondrušková and Z. Jánošíková and S. Adamčík and M. Kádasi-Horáková and D. Rákusová-Sládková and K. Adamčíková}, doi = {10.1080/02827581.2018.1482954}, issn = {1651-1891}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-06-06}, journal = {Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research}, volume = {33}, number = {7}, pages = {650-656}, abstract = {Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) has been observed in Slovakia during the last two decades. Up until 2017, Dothistroma septosporum has only been detected and molecularly confirmed to cause DNB in Slovakia. Here, we report the detection of Dothistroma pini at six localities around Slovakia, representing different plantation types. Four pine species (Pinus sylvestris, P. nigra, P. mugo and P. jeffreyi) were confirmed as hosts of D. pini in Slovakia, of which only P. mugo has been previously reported as host in Slovakia. Three gene regions (ITS, EF1 –α, and ß-tubulin) of each of the 13 isolates were sequenced and assigned as D. pini. Based on ITS sequences, the studied isolates represent the haplotypes Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2. Both mating types were detected but at different localities. Our results suggest that in addition to D. septosporum, D. pini may contribute to DNB also in Slovakia.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) has been observed in Slovakia during the last two decades. Up until 2017, Dothistroma septosporum has only been detected and molecularly confirmed to cause DNB in Slovakia. Here, we report the detection of Dothistroma pini at six localities around Slovakia, representing different plantation types. Four pine species (Pinus sylvestris, P. nigra, P. mugo and P. jeffreyi) were confirmed as hosts of D. pini in Slovakia, of which only P. mugo has been previously reported as host in Slovakia. Three gene regions (ITS, EF1 –α, and ß-tubulin) of each of the 13 isolates were sequenced and assigned as D. pini. Based on ITS sequences, the studied isolates represent the haplotypes Dp_HAP.1, Dp_HAP.2. Both mating types were detected but at different localities. Our results suggest that in addition to D. septosporum, D. pini may contribute to DNB also in Slovakia. |
Kunová, S; Kántor, A; Terentjeva, M; Felsöciová, S; Ivanišová, E; Kluz, M; Hanus, P; Puchalski, C; Horáková, Kádasi M; Kačániová, M Microscopic fungi isolated from different Slovak grape varieties Journal Article Potravinarstvo Slovak Journal of Food Sciences, 12 (1), pp. 438-443, 2018, ISSN: 1337-0960. @article{Kunová2018, title = {Microscopic fungi isolated from different Slovak grape varieties}, author = {S. Kunová and A. Kántor and M. Terentjeva and S. Felsöciová and E. Ivanišová and M. Kluz and P. Hanus and C. Puchalski and M. Kádasi Horáková and M. Kačániová}, editor = {S. Kunová and A. Kántor and M. Terentjeva and S. Felsöciová and E. Ivanišová and M. Kluz and P. Hanus and C. Puchalski and M. Kádasi Horáková and M. Kačániová}, url = {http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/893-5354-2-PB-1-4-pdf-212x300.jpg}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.5219/893}, issn = {1337-0960}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-04-24}, journal = {Potravinarstvo Slovak Journal of Food Sciences}, volume = {12}, number = {1}, pages = {438-443}, abstract = { The aim of this study was to isolate and identify microscopic fungi in different grape samples. We collected 13 grapes varienties samples (9 white and 4 red) from local Slovak winemakers in the end of the September 2017. Used 13 grape samples in this study: Alibernet, Irsai Oliver, Dornfelder, Blue Frankish, Feteasca regala, Green Veltliner, Pálava, Mūller Thurgau, Rhinriesling, Cabernet Savignon, Pinot Blanc, Savignon Blanc and Welschriesling. Microscopic fungi in grape samples were detected on Malt extract agar by spread plate method. The number of microscopic fungi ranged from 2.85 log cfu.g-1 in Cabernet Savignon to 4.83 log cfu.g-1 in Feteasca regala. A total of 627 isolates of microscopic fungi were obtained in this study. The most abundant fungi belonged to genera Alternaria and Penicillium (100% frequency). The high frequency was also detected for Aspergillus (76.92%) and Cladosporium (76.92%) but with lesser relative density. Alternaria sp., Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus sp., Botrytis cinerea, Cladosporium sp., Penicillium expansum, Phoma sp., Rhizopus sp. and Trichoderma sp. species were isolated from grape berries. }, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The aim of this study was to isolate and identify microscopic fungi in different grape samples. We collected 13 grapes varienties samples (9 white and 4 red) from local Slovak winemakers in the end of the September 2017. Used 13 grape samples in this study: Alibernet, Irsai Oliver, Dornfelder, Blue Frankish, Feteasca regala, Green Veltliner, Pálava, Mūller Thurgau, Rhinriesling, Cabernet Savignon, Pinot Blanc, Savignon Blanc and Welschriesling. Microscopic fungi in grape samples were detected on Malt extract agar by spread plate method. The number of microscopic fungi ranged from 2.85 log cfu.g-1 in Cabernet Savignon to 4.83 log cfu.g-1 in Feteasca regala. A total of 627 isolates of microscopic fungi were obtained in this study. The most abundant fungi belonged to genera Alternaria and Penicillium (100% frequency). The high frequency was also detected for Aspergillus (76.92%) and Cladosporium (76.92%) but with lesser relative density. Alternaria sp., Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus sp., Botrytis cinerea, Cladosporium sp., Penicillium expansum, Phoma sp., Rhizopus sp. and Trichoderma sp. species were isolated from grape berries. | |
 | Jánošíková-Hečková, Z; Ondrušková, E; Barta, M; Ostrovský, R; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Pastirčáková, K; Kobza, M; Adamčíková, K The hosts and geographic range of Dothistroma needle blight in Slovakia Journal Article Forest Pathology, 48 (3), pp. e12421, 2018, ISSN: 1437-4781. @article{Jánošíková-Hečková2018, title = {The hosts and geographic range of Dothistroma needle blight in Slovakia}, author = {Z. Jánošíková-Hečková and E. Ondrušková and M. Barta and R. Ostrovský and M. Kádasi-Horáková and K. Pastirčáková and M. Kobza and K. Adamčíková }, url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/efp.12421}, doi = {10.1111/efp.12421}, issn = {1437-4781}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-02-15}, journal = {Forest Pathology}, volume = {48}, number = {3}, pages = {e12421}, abstract = {The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) were studied in 2014–2017 around Slovakia. A total of 84 localities, both native and planted, were investigated, and the presence of DNB was confirmed in 73 of them. In all positive locations, symptoms typical of DNB were observed and the Dothistroma species was confirmed using species-specific primers either from fungal cultures or directly from needles. Both Dothistroma species—D. septosporum and D. pini—were identified. Both species occurred together in 29 locations, only D. septosporum in 42 and only D. pini in two locations. The host range of D. septosporum included 10 pine species and two spruce species. The host range of D. pini comprised the same number of pine hosts but only one spruce species. Five pine hosts, P. aristata, P. coulteri, P. densiflora, P. jeffreyi, P. × schwerinii, and one spruce host P. abies are new hosts species of D. pini. P. densiflora and Picea pungens have earlier been reported to be susceptible for DNB. In this study, D. septosporum was found from both tree species.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) were studied in 2014–2017 around Slovakia. A total of 84 localities, both native and planted, were investigated, and the presence of DNB was confirmed in 73 of them. In all positive locations, symptoms typical of DNB were observed and the Dothistroma species was confirmed using species-specific primers either from fungal cultures or directly from needles. Both Dothistroma species—D. septosporum and D. pini—were identified. Both species occurred together in 29 locations, only D. septosporum in 42 and only D. pini in two locations. The host range of D. septosporum included 10 pine species and two spruce species. The host range of D. pini comprised the same number of pine hosts but only one spruce species. Five pine hosts, P. aristata, P. coulteri, P. densiflora, P. jeffreyi, P. × schwerinii, and one spruce host P. abies are new hosts species of D. pini. P. densiflora and Picea pungens have earlier been reported to be susceptible for DNB. In this study, D. septosporum was found from both tree species. |
2017 |
|
 | Kádasi-Horáková, M; Adamčíková, K; Pastirčáková, K; Longauerová, V; Maľová, M Natural infection of Fraxinus angustifolia by Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Slovakia Journal Article Baltic Forestry, 23 (1), pp. 52-55, 2017, ISSN: 2029-9230. @article{M.2017b, title = {Natural infection of \textit{Fraxinus angustifolia} by \textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus} in Slovakia}, author = {M. Kádasi-Horáková and K. Adamčíková and K. Pastirčáková and V. Longauerová and M. Maľová}, url = {https://www.balticforestry.mi.lt/bf/PDF_Articles/2017-23%5B1%5D/Baltic%20Forestry%202017.1_052-055.pdf}, issn = {2029-9230}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-04-07}, journal = {Baltic Forestry}, volume = {23}, number = {1}, pages = {52-55}, abstract = {The fungus Hymenoscyphus fraxineus is responsible for dieback of common ash (Fraxinus excelsior) and in some parts of Europe also of narrow-leaved ash (F. angustifolia). The first symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded on F. excelsior in Slovakia since 2004. This study reports about the first natural occurrence of H. fraxineus on F. angustifolia in Slovakia. The field investigation was carried out in 2014. The segments of diseased shoots and last year’s petioles were collected in clonal seed orchard situated in southwest part of the country. The fungus was isolated from infected host tissue and identified using molecular techniques (DNA extraction from pure cultures and apothecia, conventional PCR).}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The fungus Hymenoscyphus fraxineus is responsible for dieback of common ash (Fraxinus excelsior) and in some parts of Europe also of narrow-leaved ash (F. angustifolia). The first symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded on F. excelsior in Slovakia since 2004. This study reports about the first natural occurrence of H. fraxineus on F. angustifolia in Slovakia. The field investigation was carried out in 2014. The segments of diseased shoots and last year’s petioles were collected in clonal seed orchard situated in southwest part of the country. The fungus was isolated from infected host tissue and identified using molecular techniques (DNA extraction from pure cultures and apothecia, conventional PCR). |
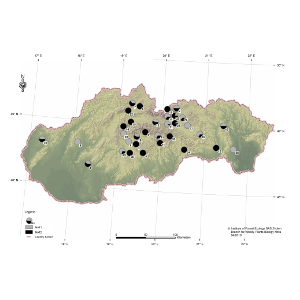 | Ondrušková, E; Hečková, Z; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Koltay, A; Ostrovský, R; Pažitný, J; Adamčíková, K Distribution and characterization of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens on Pinus mugo in Slovakia Journal Article European Journal of Plant Pathology, 148 (2), pp. 283-294, 2017, ISSN: 0929-1873. @article{Ondrušková2017, title = {Distribution and characterization of Dothistroma needle blight pathogens on Pinus mugo in Slovakia}, author = {E. Ondrušková and Z. Hečková and M. Kádasi-Horáková and A. Koltay and R. Ostrovský and J. Pažitný and K. Adamčíková}, url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10658-016-1088-2}, doi = {10.1007/s10658-016-1088-2}, issn = {0929-1873}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, journal = {European Journal of Plant Pathology}, volume = {148}, number = {2}, pages = {283-294}, abstract = {The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) on Pinus mugo was studied in 2014–2015 around the Slovakia. In total, 42 localities were investigated both native and planted ones. Symptoms of DNB were observed on 35 localities only on planted shrubs. All these 35 localities are new P. mugo DNB stands. No DNB symptoms were observed in natural and naturally regenerated plantations. DNAwas extracted from a total of 236 isolates and eight needle samples. Based on the ITS-rDNA comparisons and using species specific primers, both pathogenic Dothistroma species were detected: D. septosporum and D. pini. Isolates of D. septosporum had ITS sequences identical to D. septosporum from Europe and both mating types were identified with slight predominance of MAT2. The ratio of D. septosporum mating types varies significantly between sites, ranging from an equal proportion of each mating type to single mating type populations. D. pini ITS sequence grouped with D. pini from Ukraine, Russia and Switzerland and only MAT2 was found.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The occurrence and distribution of Dothistroma needle blight (DNB) on Pinus mugo was studied in 2014–2015 around the Slovakia. In total, 42 localities were investigated both native and planted ones. Symptoms of DNB were observed on 35 localities only on planted shrubs. All these 35 localities are new P. mugo DNB stands. No DNB symptoms were observed in natural and naturally regenerated plantations. DNAwas extracted from a total of 236 isolates and eight needle samples. Based on the ITS-rDNA comparisons and using species specific primers, both pathogenic Dothistroma species were detected: D. septosporum and D. pini. Isolates of D. septosporum had ITS sequences identical to D. septosporum from Europe and both mating types were identified with slight predominance of MAT2. The ratio of D. septosporum mating types varies significantly between sites, ranging from an equal proportion of each mating type to single mating type populations. D. pini ITS sequence grouped with D. pini from Ukraine, Russia and Switzerland and only MAT2 was found. |
2015 |
|
 | Adamčíková, K; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Jankovský, L; Havrdová, L Identification of Hymenoscyphus fraxineus, the causal agent of ash dieback in Slovakia Journal Article Biologia, 70 (5), pp. 559–564, 2015. @article{K.2015, title = {Identification of \textit{Hymenoscyphus fraxineus}, the causal agent of ash dieback in Slovakia}, author = {K. Adamčíková and M. Kádasi-Horáková and L. Jankovský and L. Havrdová}, url = {http://www.degruyter.com/view/j/biolog.2015.70.issue-5/biolog-2015-0075/biolog-2015-0075.xml}, doi = {10.1515/biolog-2015-0075}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-06-23}, journal = {Biologia}, volume = {70}, number = {5}, pages = {559–564}, abstract = {Symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded in Slovakia since 2004. The field sampling was carried out in 2013, included 59 segments of shoots and 10 and more petioles per locality from four localities. The causal agent of ash dieback, the hyphomycete Chalara fraxinea T. Kowalski, was isolated from Fraxinus excelsior L. from seven localities in Slovakia. The morphology of C. fraxinea isolates and the teleomorph Hymenoscyphus fraxineus (T. Kowalski) Baral, Queloz, Hosoya are described and ITS sequences are provided.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Symptoms of ash dieback have been recorded in Slovakia since 2004. The field sampling was carried out in 2013, included 59 segments of shoots and 10 and more petioles per locality from four localities. The causal agent of ash dieback, the hyphomycete Chalara fraxinea T. Kowalski, was isolated from Fraxinus excelsior L. from seven localities in Slovakia. The morphology of C. fraxinea isolates and the teleomorph Hymenoscyphus fraxineus (T. Kowalski) Baral, Queloz, Hosoya are described and ITS sequences are provided. |
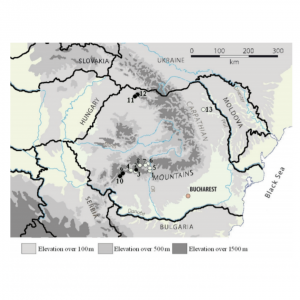 | Adamčíková, K; Ondrušková, E; Kádasi-Horáková, M; Botu, M; Kobza, M; Achim, G Distribution and population structure of the chestnut blight fungus in Romania Journal Article Plant Protection Science, 51 (3), pp. 141-149, 2015. @article{Adamčíková2015, title = {Distribution and population structure of the chestnut blight fungus in Romania}, author = {K. Adamčíková and E. Ondrušková and M. Kádasi-Horáková and M. Botu and M. Kobza and G. Achim}, url = {http://www.agriculturejournals.cz/publicFiles/157004.pdf}, doi = {10.17221/52/2014-PPS}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, journal = {Plant Protection Science}, volume = {51}, number = {3}, pages = {141-149}, abstract = {The occurrence of chestnut blight (Cryphonectria parasitica) was studied in 2011-2012 at 13 locations in the main chestnut growing areas of Romania. Infections were detected at four localities. The symptoms and the fungus were detected on European chestnut (four localities) and also on oak trees (two localities). A total of 89 isolates of C. parasitica were isolated and characterised. Based on canker and isolate morphology (culture morphology and the Bavendamm test), both virulent and hypovirulent samples were isolated; hypovirulent isolates were found at only one locality. Two vegetative compatibility types corresponding to EU-12 and EU-2 were identified among isolates. Both mating types were found, with a dominance of MAT-1 in southern Romania and MAT-2 in northern Romania.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The occurrence of chestnut blight (Cryphonectria parasitica) was studied in 2011-2012 at 13 locations in the main chestnut growing areas of Romania. Infections were detected at four localities. The symptoms and the fungus were detected on European chestnut (four localities) and also on oak trees (two localities). A total of 89 isolates of C. parasitica were isolated and characterised. Based on canker and isolate morphology (culture morphology and the Bavendamm test), both virulent and hypovirulent samples were isolated; hypovirulent isolates were found at only one locality. Two vegetative compatibility types corresponding to EU-12 and EU-2 were identified among isolates. Both mating types were found, with a dominance of MAT-1 in southern Romania and MAT-2 in northern Romania. |
2014 |
|
![Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku a v Európe : pestovanie, ochrana, variabilita a využitie [European chestnut in Slovakia : growing, protection, use and genetic variability]](http://ife.sk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/IFE_adamcikova_katarina_article_08.jpg) | Adamčíková, K; Kobza, M; Juhásová, G; Ondrušková, E; Bolvanský, M; Kádasi-Horáková, M Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku a v Európe : pestovanie, ochrana, variabilita a využitie [European chestnut in Slovakia : growing, protection, use and genetic variability] Book Garamond, Nitra, 2014, ISBN: 978-80-89408-18-4. @book{Adamčíková2014, title = {Gaštan jedlý na Slovensku a v Európe : pestovanie, ochrana, variabilita a využitie [European chestnut in Slovakia : growing, protection, use and genetic variability]}, author = {K. Adamčíková and M. Kobza and G. Juhásová and E. Ondrušková and M. Bolvanský and M. Kádasi-Horáková}, isbn = {978-80-89408-18-4}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, volume = {1}, pages = {155}, publisher = {Garamond}, address = {Nitra}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {book} } |
